![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
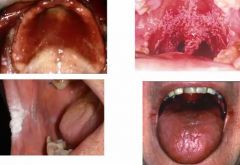
what are these? |
candidal infections |
|
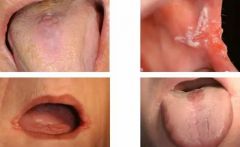
what are these? |
candidal infections |
|
|
what kind of candida is albicans? |
imperfect (perfect are rarely associated with disease) |
|
|
what are the morphologies of candida albicans? |
trimorphic blastospore, chlamydospore |
|
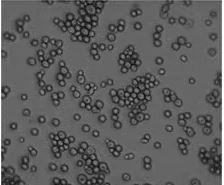
what form of candida albicans is this? |
blastospore vegetative yeast cells that undergo cell division |
|
|
what is the chlamydospore form of candida? |
very thick walled and probably associated with increased cell survival
|
|
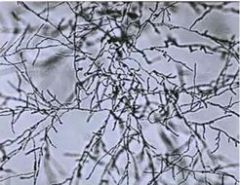
what form of candida albicans is this? |
mycelial form aka differentiated form associated with disease- invades tissues associated with virulence factors associated with candida little or no cell division |
|
|
what are the symptoms of a candidal infection? |
usually asymptomatic burning sensation occasionally acute erythematous can be painful |
|
|
what are the local predisposing factors for candida? |
salivary gland hypofunction broad spec AB topical and systemic eg tetracyclines steroid inhalers poor denture hygiene or trauma smoking irradiation |
|
|
what are the systemic predisposing factors for candida? |
extremes of age drugs (immunosuppressants, chemo) malnutrition anaemia immune defects (HIV, caner, diabetes, down syn, nphil or t cell defects) endocrine disorders malignancy |
|
|
what are the acute/chronic/associated primary oral candidoses |
acute: erythematous, pseudomembranous chronic: erythematous, pseudomembranous, hyperplastic associated lesions: angular chelitis, median rhomboid glossitis, denture induced stomatitis |
|
|
what is the secondary oral candidoses? how do they present IO/EO? |
systemic mucocutaneous candidoses aka systemic candidal infection if they have oral lesions will be chronic pseudomembranous or chronic hyperplastic plus EO- skin lesions, nail lesions, endocrinopathy, haematological disorders |
|
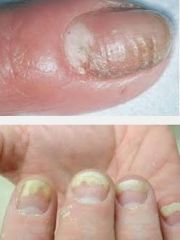
whats this? |
candidal nail lesion |
|
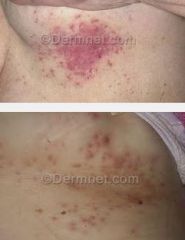
whats this? |
candidal skin lesion |
|
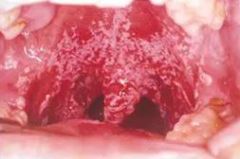
whats this? what happens if you scrape it? |
pseudomembranous candidosis can be scraped off to give erythematous bleeding base |
|
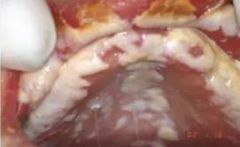
whats this? what happens if you scrape it? |
pseudomembranous candidosis can be scraped off to give erythematous bleeding base |
|
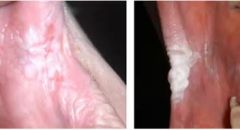
whats this? can you scrape it off? whats it associated with? |
CHC no smokers |
|
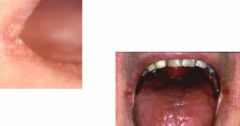
whats this? generally whats the cause? |
angular chelitis skin crusted sore and erythematous usually primary infections with candida but can be secondarily infected with staph aureus |
|
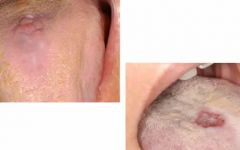
whats this? what are the types? |
median rhomboid glossitis tongue, midline, anterior to circumvallate papilla area of depapillation but can be hyperplastic also |
|
|
how are candidal infections diagnosed? whats the SI? |
clinical appearance, C&S (swab and rinse) biopsy for CHC (exclude dysplasia and candidal hypae can be seen in upper epithelial layers) consider blood tests- FBC, ESR, glucose, haematinics, LFT (azole antifungals work on the liver) particularly for CHC |
|
|
whats the management for candida? |
treat predisposing antifungal med long term r/v for CHC- premalignant- smoking and alcohol cessation |
|
|
how is MRG diagnosed? whats the SI? whats the treatment? |
appearance blood +- swab remove predisposing, topical antifungals but if persists may need systemic |
|
|
whats the differential diagnosis for angular chelitis? how is it diagnosed? whats the SI? whats the treatment? |
facial eczema or secondary to oral crohns/OFG clinical appearance and swab +- bloods eliminate predisposing |
|
|
what are the topical antifungals? |
CHX amphotericin lozenges (polyene) nystatin suspension (polyene) miconazole gel (tri-azole) |
|
|
whats the systemic antifungals? |
fluconazole (tri-azoles) |
|
|
what do you prescribe for candida IO/EO? |
IO- miconazole gel/nystatin suspension/amphotericin lozenges EO- miconazole gel or cream/nystatin cream |
|
|
what do you prescribe for staph IO/EO? |
IO- N/A EO- fusidic acid cream |
|
|
what do you prescribe for a mixed candida/staph infection or unknown prior to swab results? |
IO- miconazole gel EO- miconazole gel/cream |
|
|
what does miconazole and fluconazole interact with? |
warfarin statins |
|
|
what is CHX? what is it active against? how does it work? |
chemical antiseptic active against bacteria (cial and static) and candida membrane disruption |
|
|
what is nystatin a product of? what drug class? how does it work? |
product of streptomyces noursei polyene binds to ergosterol in the fungi cell membrane sufficient quantities form pores and cell death |
|
|
what is amphotericin B a product of? what drug class? how does it work? |
product of streptomyces nodosus polyene binds to ergosterol in fungal cell membrane produces an aggregate with ergosteral that forms a transmembrane channel cell constituents leak out |
|
|
how is miconazole made? what drug class? how does it work? |
chemically synthesised imidazole class blocks the synthesis of ergosterol |
|
|
what drug class is fluconazole? how does it work? whats the downside? |
triazole class inhibits both human and fungal cytochrome P450 but doing so interferes with ergosterol synthesis in fungi
|

