![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is linkage, syntenty and recombination fraction?
|
Linkage- Alleles at two different gene loci on the same chromosome are often inherited together than chance alone
Syntenty- Two genes on the same chromosome appear not to be linked because they are so far apart from each other Recombination Fraction- Tells you the distance between two loci. The fraction of offspring of a parent heterozygous at two loci who have inherited a chromosome carrying a recombination between two loci. The closer two genes are together the more likely they will stay together so LESS recombination |
|
|
What is the difference between physical and genetic mapping?
|
Physical mapping- location of a gene is known by FISH analysis, somatic cell hybrid analysis,
Genetic mapping is when the location of the gene is determined using family studies |
|
|
What are the requirements for an adequate mapping study?
|
1) Sufficiently large families
2) Double heterozygotes (Need to be heterozygous at the marker and the gene loci of interest) 3) Homogenous group (Need to have the same phenotype caused by the same mutation at the same gene loci) 4) Phase known vs phase unknown (a phase is the alignment of the alleles at two or more different gene loci) - You have to know the phase |
|
|
What is a recombinant and how does it apply to linkage studies?
|
A recombinant is an individual with different genetic material than the parents
|
|
|
What are LOD scores and how are they used in a linkage study?
|
LOD scores are a more precise way to measure theta--> the recombination fraction.
An LOD score greater than 3 proves linkage and a linkage score less than -2 rules against linkage. |
|
|
What is the impact of phase-unknown individuals in a linkage study?
|
You don't know which one of the offsprings are recombinant and which are non-recombinant.
This reduces overall linkage and results in the highest LOD score for a phase-unknown study. |
|
|
What is the impact of locus heterogeneity on linkage studies?
|
When there is locus heterogeneity, the LOD data of the families will be split into two groups:
Those with positive LOD scores, which indicates a cause of the disease that is linked to the marker being used Those with negative LOD scores, which indicates a different cause for the disease that is not linked to the marker When this is identified, it is important to split these families into two groups and recalculate the total LOD scores so that only the scores for the same locus are being added together. |
|
|
How do you calculate the risk of being affected for pre-symptomatic and prenatal situations?
|
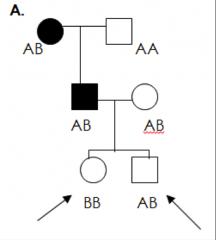
In both cases, you start by determining the phase of the disease with the gene it is linked with (used as a marker). You then follow this marker through the pedigree and use the recombination frequency of the marker and the disease gene to determine probability. Example:
This disease is present in individual II-1. who inherited it from individual I-1. A and B represent markers that are seen to be linked to the disease. This marker is within 15% recombination of the disease locus (meaning that there is an 85% chance they will remain linked). II-1 can only get the disease and the B gene from I-1, so those must be in the same phase. III-1 has received this B from II-1, so he has an 85% chance of having the disease. III-2, on the other hand, received only one B, and it is impossible to tell which parent he received it from (the marker is uninformative). Therefore, he has his original 50% chance of being affected. |

