![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
[ respiration ] fish must be much more efficient in their... |
uptake of oxygen (water is oxygen-poor) |
|
|
[ respiration ] what are gill arches? |
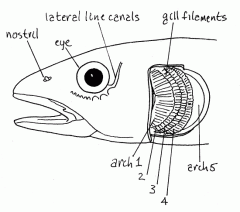
bony or cartilaginous arches in the throat of fish to which the filaments and rakers of the gills are attached
|
|
|
[ respiration ] function of gill arches |
provide support for gill filaments |
|
|
[ respiration ] what are gill filaments? |
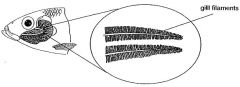
a.k.a. primary lamellae
|
|
|
[ respiration ] function of gill filaments |
takes up oxygen into blood from water passing through the gills..cartilaginous gas exchange |
|
|
[ respiration ] secondary lemellae |
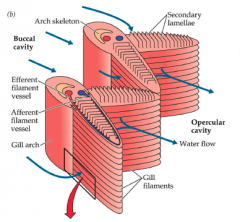
projections on the surface of each primary lamella
|
|
|
[ respiration ] function of secondary lemellae |
increase surface area to gain efficiency...raised ridges |
|
|
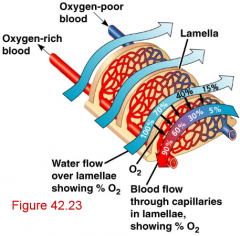
diffusion of gases across the gill membrane is further enhanced by __________________, thereby maximizing the __________________ |
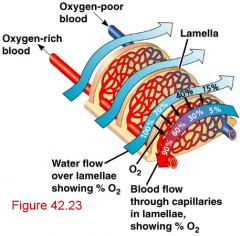
diffusion of gases across the gill membrane is further enhanced by blood in the secondary lamellae flowing in the opposite direction to the water passing over the gills,thereby maximizing the diffusion gradient across the entire lamellar surface |
|
|
[ respiration ] countercurrent flow |
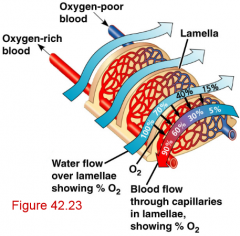
water flow and blood flow occurs in opposite directions creating concentration gradient from high to low pressure |
|
|
[ respiration ] advantage of countercurrent flow |
ensures that asthe blood picks up oxygen from the water it moves along the exchange surface to an area where the adjacent water has an even higher oxygen concentration...basically oxygenated water is contacting poorly oxygenated blood, thus giving it more oxygen |
|
|
[ respiration ] what are the 2 basic ways fish move water across gill membranes? |
|
|
|
[ respiration ] gill pumping |
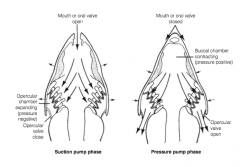
synchronized pressure changes in the buccal and opercular chambers |
|
|
how does gill pumping work? |
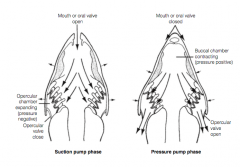
the expansion and contraction of the buccal and opercular chambers is timed so that the pressure in the buccal chamber is greater than the pressure in the opercular chamber, thereby ensuring that the water flows in the anterior to posterior direction throughout the breathing cycle
|
|
|
[ respiration ] ram ventilation |
|
|
|
[ respiration ] aerial respiration |
|
|
|
[ respiration ] facultative vs. obligate aerial respiration |
|

