![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does PV and FV mean?
|
Present value of future cash flows (discounted at the appropriate discount rate)
Future value of cash flows after one or more periods. |
|
|
What is another term for discount rate?
|
Interest rate - the exchange rate between earlier and later money.
|
|
|
What is the formula for future value of money.
|
FV = PV(1+r) t
r = period interest rate, expressed as decimal t = number of periods t should be small (to the power of). |
|
|
What is simple interest?
|
Interest earned only on the original principal (amount).
|
|
|
What is compound interest?
|
Interest earned on principal and on the interest received.
|
|
|
What is the FV formula for simple interest?
|
FV = PV + (PV x r%)
Therefore FV with compound is: FV = PV(1+r%) t (in order words... PV(1+r)(1+r)(1+r) etc) |
|
|
"What is the interest on interest" means...
|
Compound interest total - simple interest total
How much interest did you get, from gaining further interest on the interest. |
|
|
What are the 2 important relationships of future value?
|
Longer time period = greater FV
Higher interest rate = greater FV |
|
|
What is present value?
|
The current value of an amount to be received in the future.
The current value of future cashflows discounted at the appropriate discount rate. |
|
|
Why is present value less than future face value?
|
- Opportunity cost
- Risk and uncertainty |
|
|
What is discounting?
|
Finding the present value of one or more future amounts.
|
|
|
What is the formula for present value?
|
PV = FV / ( 1 + r%) t
Basically divide instead for PV, Example FV = 10 * (1.05)t PV = 10 / (1.05)t t only occurs after the / or * to the 1.% figure, not the whole sum! |
|
|
What are the important relationships of present value?
|
Longer time period = smaller present value
Higher interest rate = smaller present value OPPOSITE relationships for future value |
|
|
How do you find out the implied discount rate?
|
r = (FV / PV) 1/r[as a power] THEN MINUS 1
You are looking at an investment that will pay £1200 in 5 years if you invest £1000 today. r = (1200/1000) POWERED /0.2 MINUS 1 = 0.037 = 3.7% |
|
|
How do you find out the implied number of periods?
|
t = In(FV/PV) / In(1+r)
|
|
|
Describe the rule of 72 method.
|
A quick way of checking how long it will take to double your money given an interest rate and compound interest.
Example: double £1000 at 8% = 72/8% = 9 years |
|
|
Summary:
What are the calculations for PV, FV, r and t. |
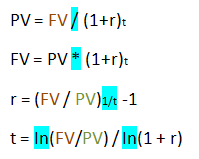
|
|
|
How do you calculate simple interest?
|
Principle x r x t
|

