![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3-19C1
What happens to the conductivity of photoconductive material when light shines on it? |
It increases
|
|
|
3-19C2
What is the photoconductive effect? |
The increased conductivity of an illuminated semiconductor junction
|
|
|
3-19C3
What does the photoconductive effect in crystalline solids produce a noticeable change in? |
The resistance of the solid
|
|
|
3-19C4
What is the description of an optoisolator? |
An LED and a photosensitive device
|
|
|
3-19C5
What happens to the conductivity of a photosensitive semiconductor junction when it is illuminated? |
The junction resistance decreases
|
|
|
3-19C6
What is the description of an optocoupler? |
An LED and a photosensitive device
|
|
|
3-20C1
What factors determine the capacitance of a capacitor? |
Distance between the plates and the dielectric constant of the material between the plates
|
|
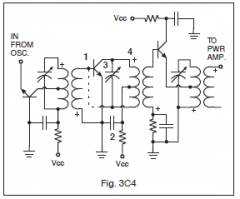
3-20C2
In Figure 3C4, if a small variable capacitor were installed in place of the dashed line, it would? |
Decrease parasitic oscillations
|
|
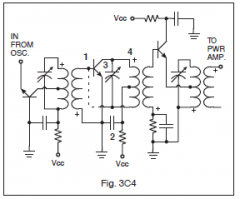
3-20C3
In Figure 3C4, which component (labeled 1 through 4) is used to provide a signal ground? |
2
|
|
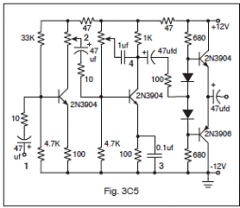
3-20C4
In Figure 3C5, which capacitor (labeled 1 through 4) is being used as a bypass capacitor? |
3
|
|
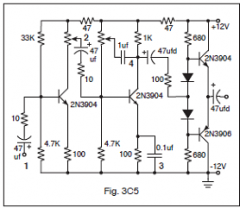
3-20C5
In Figure 3C5, the 1 μF capacitor is connected to a potentiometer that is used to: |
Adjust tone
|
|
|
3-20C6
What is the purpose of a coupling capacitor? |
It blocks direct current and passes alternating current
|
|
|
3-21C1
A capacitor is sometimes placed in series with the primary of a power transformer to: |
Improve the power factor
|
|
|
3-21C2
A transformer used to step up its input voltage must have: |
More turns of wire on its secondary than on its primary
|
|
|
3-21C3
A transformer primary of 2250 turns connected to 120 VAC will develop what voltage across a 500-turn secondary? |
26.7 volts
|
|
|
3-21C4
What is the ratio of the output frequency to the input frequency of a single-phase full-wave rectifier? |
2:1
|
|
|
3-21C5
A power transformer has a single primary winding and three secondary windings producing 5.0 volts, 12.6 volts, and 150 volts. Assuming similar wire sizes, which of the three secondary windings will have the highest measured DC resistance? |
The 150 volt winding
|
|
|
3-21C6
A power transformer has a primary winding of 200 turns of #24 wire and a secondary winding consisting of 500 turns of the same size wire. When 20 volts are applied to the primary winding, the expected secondary voltage will be: |
50 volts
|
|
|
3-22C1
In a linear electronic voltage regulator: |
The conduction of a control element is varied in direct proportion to the line voltage or load current
|
|
|
3-22C2
A switching electronic voltage regulator: |
Switches the control device on or off, with the duty cycle proportional to the line or load conditions
|
|
|
3-22C3
What device is usually used as a stable reference voltage in a linear voltage regulator? |
Zener diode
|
|
|
3-22C4
In a regulated power supply, what type of component will most likely be used to establish a reference voltage? |
Zener Diode
|
|
|
3-22C5
A three-terminal regulator: |
Contains a voltage reference, error amplifier, sensing resistors and transistors, and a pass element
|
|
|
3-22C6
What is the range of voltage ratings available in Zener diodes? |
2.4 volts to 200 volts and above
|
|
|
3-23C1
How might two similar SCRs be connected to safely distribute the power load of a circuit? |
In parallel, reverse polarity
|
|
|
3-23C2
What are the three terminals of an SCR? |
Anode, cathode, and gate
|
|
|
3-23C3
Which of the following devices acts as two SCRs connected back to back, but facing in opposite directions and sharing a common gate? |
TRIAC
|
|
|
3-23C4
What is the transistor called that is fabricated as two complementary SCRs in parallel with a common gate terminal? |
TRIAC
|
|
|
3-23C5
What are the three terminals of a TRIAC? |
Gate, anode 1, and anode 2
|
|
|
3-23C6
What circuit might contain a SCR? |
A light-dimming circuit
|
|
|
3-24C1
What is one common use for PIN diodes? |
RF switch
|
|
|
3-24C2
What is a common use of a hot-carrier diode? |
VHF and UHF mixers and detectors
|
|
|
3-24C3
Structurally, what are the two main categories of semiconductor diodes? |
Junction and point contact
|
|
|
3-24C4
What special type of diode is capable of both amplification and oscillation? |
Tunnel diodes
|
|
|
3-24C5
What type of semiconductor diode varies its internal capacitance as the voltage applied to its terminals varies? |
Varactor diode
|
|
|
3-24C6
What is the principal characteristic of a tunnel diode? |
Negative resistance region
|
|
|
3-25C1
What is the meaning of the term “alpha” with regard to bipolar transistors? The change of: |
Collector current with respect to emitter current
|
|
|
3-25C2
What are the three terminals of a bipolar transistor? |
Base, collector and emitter
|
|
|
3-25C3
What is the meaning of the term “beta” with regard to bipolar transistors? The change of: |
Collector current with respect to base current
|
|
|
3-25C4
What are the elements of a unijunction transistor? |
Base 1, base 2, and emitter
|
|
|
3-25C5
The beta cutoff frequency of a bipolar transistor is the frequency at which: |
Emitter current gain has decreased to 0.707 of maximum
|
|
|
3-25C6
What does it mean for a transistor to be fully saturated? |
The collector current is at its maximum value
|
|
|
3-26C1
A common base amplifier has: |
More voltage gain than common emitter or common collector
|
|
|
3-26C2
What does it mean for a transistor to be cut off? |
There is no current between emitter and collector
|
|
|
3-26C3
An emitter-follower amplifier has: |
More current gain than common emitter or common base
|
|
|
3-26C4
What conditions exists when a transistor is operating in saturation? |
The base-emitter junction and collector-base junction are both forward biased
|
|
|
3-26C5
For current to flow in an NPN silicon transistor’s emitter-collector junction, the base must be: |
At least 0.7 volts positive with respect to the emitter
|
|
|
3-26C6
When an NPN transistor is operating as a Class A amplifier, the base-emitter junction: |
Is forward biased and the collector-base junction is reverse biased
|
|
|
3-27C1
What type of bias is required for an LED to produce luminescence? |
Forward bias
|
|
|
3-27C2
What determines the visible color radiated by an LED junction? |
The materials used to construct the device
|
|
|
3-27C3
What is the approximate operating current of a light-emitting diode? |
20 mA
|
|
|
3-27C4
What would be the maximum current to safely illuminate a LED? |
20 mA
|
|
|
3-27C5
An LED facing a photodiode in a light-tight enclosure is commonly known as a/an: |
Optoisolator
|
|
|
3-27C6
What circuit component must be connected in series to protect an LED? |
Series resistor
|
|
|
3-28C1
What describes a diode junction that is forward biased? |
It is a low impedance
|
|
|
3-28C2
Why are special precautions necessary in handling FET and CMOS devices? |
They are susceptible to damage from static charges
|
|
|
3-28C3
What do the initials CMOS stand for? |
Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor
|
|
|
3-28C4
What is the piezoelectric effect? |
Mechanical vibration of a crystal by the application of a voltage
|
|
|
3-28C5
An electrical relay is a: |
Remotely controlled switching device.
|
|
|
3-28C6
In which oscillator circuit would you find a quartz crystal? |
Pierce
|

