![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the primary concern of pt presenting with chest pain?
|
what is the origin of the pain?
You need to know if the pain is cardiac or not! |
|
|
What are the causes of chest pain in OFFICE setting most likley?
|
most commonly due to musculoskeletal, GI, and cardiac causes
|
|
|
What can cause rib fractures?
|
metastatic cancers
|
|
|
What are 3 major differentials you should have for a person complaining of chest pain?
|
muscular chest pain
costochondritis rib fracture (if trauma related) |
|
|
A 45 yr old male presents with severe chest pain. Upon questioning he says he ate some spicy Indian food. He says the pain is more SUBSTERNAL. What is the Dx most likley?
|
GERD
esophageal motility is a common cause of chest pain and can be indistinguishable from cardiac chest pain |
|
|
A 23 yr old women presents with chest pain. You palpate her upper right quandrant and she complains of severe tenderness which radiates to her chest. She describes the pain as a substernal pain. What is the likely dx?
|
cholelithiasis or cholecystitis
|
|
|
What is the underlying pathology behind chest pain?
|
insufficient oxygen supply to myocardial tissue usually from coronary artery disease
|
|
|
What is the initial step in coronary artery disease?
|
atherosclerotic plaque is formed by a fatty streak, this calcifies and forms a plaque impairing blood flow and decreasing oxygen
|
|
|
What causes anginal chest pain?
|
If the plaque does NOT rupture the narrowing of the lumen causes anginal chest pain.
This is typically brought on by exertion as the myocardial oxygen demand exceeds the supply |
|
|
What causes pain from pneumonia or PE?
|
inflammation or irritation of the parietal pleura
|
|
|
A pt presents with chest pain to the urgent care. He says the pain started a couple of days age and has not gone away. You perform the necessary workup and everything is normal. The same comes back to your office a week later and now complains of severe pain on his chest and has a rash. What is the most likley dx?
|
herpes zoster - shingles
|
|
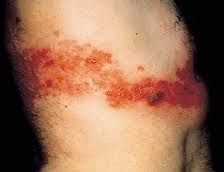
What is this rash?
|
herpes zoster
|
|
|
A 35 yr old male who has a Hx of anxiety presents to your office. He complains of chest pain. What symptoms do you suspect he will have?
|
psychological diseases such as anxiety and panic disorder can present with a variety of chest symptoms - palpitations, dyspnea, chest pain
This is complex..... |
|
|
What type of pain is usually described as substernal chest tightness or pressure that radiates to the left arm, shoulders, or jaw? The pt may also complain of diaphoresis, shortness of breath, nausea, or vomiting
|
myocardial pain
|
|
|
What type of pain presents from onset of exercise, eating, or emotional excitement?
Hint: this pain usually disappears with rest or nitro |
anginal pain
|
|
|
If a person has chest pain for less than 1 minute or longer then 30 minutes is this anginal pain?
|
Nope
anginal pain is usually: 1min < X < 30min |
|
|
What type of pain is often sharp, severe, relieved by sitting up, breathing, lying back, or coughing may make the pain worse?
|
pericardial pain
|
|
|
What type of pain presents more anterior and severe. Has a ripping or tearing quality and may radiate to the back or felt in the abdomen?
|
aortic dissection
|
|
|
What type of pain is a burning pain in the upper sternal area and may be associated with a productive cough?
|
tracheobronchitis
|
|
|
What type of pain has a diffuse chest pain and is aggraveted by breathing and coughing?
|
pneumonia
|
|
|
A young man who smokes presents with sharp pain that is unilateral, and complains of shortness of breath. WHat is this most likely?
|
pneumothorax
|
|
|
A 7 yr old has chest pain. Her mother said she had a viral illness last week. The pain is described as sharp pleuritic.
|
pleurisy
|
|
|
A 67 yr old male complains of chest pain after he eats large meals and then lays down for a nap. He says the pain radiates into his sternum?
|
GERD
|
|
|
What is an added benefit of giving someone nitro for chest pain and GERD?
|
nitro relaxes smooth muscle so for both GERD and angina spasm it can help
|
|
|
What type of pain is reproduced on palpitation. The pt may also be afraid to take a deep breath?
|
musculoskeletal pain
|
|
|
A 32 yo female presents with nonspecific chest pain. She has an overwhelming fear that someone is watching her but is not sure who or why. She complains of palpitations, breathlessness, and is tachycardic. What is going on?
|
most likley has some sort of anxiety disorder
|
|
|
When listening to the heart of person with myocardial ischemia what might you hear?
|
audible S4 = myocardial ischemia
audible S3 = congestive heart failure |
|
|
What might cause a friction rub or pulsus paradoxus?
|
pericarditis
|
|
|
What is Beck's Triad?
|
jugular venous distention
muffled heart sounds decreased blood pressure all suggest CARDIAC TAMPANODE |
|
|
A pt presents with hypotension, absence of peripheral pulses, and an aortic insufficiency murmur. What is this?
|
aortic dissection
|
|
|
A pt presents with chest pain, crackles on inspiration, dullness on percussion of the thorax, and egophpny dullness, all show consolidation. What is this?
|
pneumonia
|
|
|
A pt presence with chest pain, has hyper-resonance to percussion of the thorax, tracheal deviation, decreased breath sounds, and decreased tactile and vocal fremitus. What is the Dx?
|
pheumothorax
|
|
|
Which side will the trachea deviate with a spontaneous pneumothorax?
|
ipsilateral side
|
|
|
Which side will the trachea deviate with a tension pneumothroax?
|
contralateral side
|
|
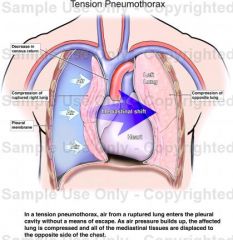
What is this?
|
Tension pneumothorax
|
|
|
A pt presents with nl auscultation findings of the thorax, tachycardia, and has lower extremity edema. What is the most likley dx?
|
Check for PE!
|
|
|
Although an EKG may be nl in a pt with heart dz, what might an ST-segment elevation or depression indicate?
|
myocardial ischemia
|
|
|
What does a diffuse ST segment elevation mean?
|
could mean pericarditis
|
|
|
What can Q wave changes indicate?
|
new or old MI
|
|
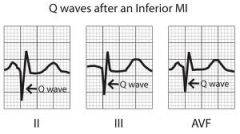
What is this?
|
Q-wave changes
|
|
|
What cardiac markers are sensitive for an MI?
|
creatine phosphokinase
troponin myoglobin all are intracellular cardiac macromolecules released from cells when damage occurs |
|
|
What is the 1st enzyme to rise and remain elevated with an MI?
How long are they elevated? |
troponins
elevated for 5-14 days |
|
|
When do CPK-MB become sensitive for MI?
|
begin to rise within 4hrs and peak in 24 hrs after an MI
8 hrs after the onset of symptoms and up to 95% of pts will have a positive test for CPK-MB or troponins |
|
|
A person is having chest pain but has negative troponin levels, what is this?
|
A negative troponin level between the time of 6 and 72 hrs after the onset of chest pain is strong evidence against an MI and acute coronary syndrome
esp if the EKG is NL!!!!!!! |
|
|
If a person is unable to perform a cardiac stress test what can you do pharmacology wise?
|
chemical stress test
use either adenosine or dobutamine to achieve a target heart rate |
|
|
What is the main reason for a thoracic chest x-ray and chest pain?
|
pneumonia
pneumothorax lung pathology |
|
|
What does it mean if a person has a nl D-dimer in a low risk patient?
|
Strong evidence AGAINST a PE
|
|
|
What drug alone has been shown to reduce mortality by more than 20% in MI pts?
|
aspirin!
give 2 81mg aspirin to people suspected of an MI |
|
|
What can you give someone who is allergic to aspirin?
|
clopidogrel
|
|
|
What is the ideal systeolic blood pressure to maintain?
|
between 100-120 mmHg
|
|
|
What is the nl heart rate for a person?
|
60bpm
|
|
|
When should you consider administering thrombolytics?
|
if the pt is below 75
ST segment elevations within 6hrs of chest pain |
|
|
What can be added with heparin in pts with unstable angina and non-Q-wave infarctions?
|
glycoproteins
|
|
|
what drugs can be given to people who have angina despite maximal therapy?
|
beta blockers
nitrates calcium channel blockers |
|
|
What is the LDL level goal for a person with coronary artery disease?
|
<100 mg/dL
newer evidence now suggest <75 |
|
|
What drugs can improve pericarditis?
|
NSAIDS or aspirin
Steroids can be given in severe cases |
|
|
What is the tx for costochondritis?
|
NSAIDS
|
|
|
4 key points in cadiology
|
4 key pts:
1. most common emergent cases of chest pain are: MI unstable angina aortic dissection PE pneumothorax 2. cardiac chest pain that lasts more then 30 minutes is most probably 2nd to infarction 3. Beck's traid: jugular venous distention, muffled heart sounds, decreased BP = cardiac tamponade 4. pt who presents with cardiac pain should be given O2, nitro, and morphine for pain control |

