![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
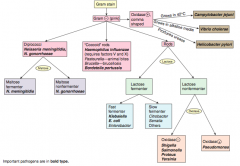
Which bacteria causes mesenteric adenitis that can mimic Crohn disease or appendicitis? Transmission?
|
Yersinia enterocolitica |
|
|
What disease does Yersinia enterocolitica cause? Transmission?
|
- Mesenteric adenitis that can mimic Crohn disease or appendicitis
- Transmitted from pet feces (eg, puppies), contaminated milk, or pork |
|
|
Which bacteria causes gastritis and peptic ulcers (especially duodenal)?
|
Helicobacter pylori
|
|
|
Characteristics of Helicobacter pylori?
|
G- comma shaped rods
- Oxidase (+) - Catalase (+) - Urease (+) - can use urea breath test or fecal antigen test - Creates alkaline environment |
|
|
What does Helicobacter pylori cause?
|
- Causes Gastritis and Peptic Ulcers (especially duodenal)
- Risk factor for gastric adenocarcinoma - Risk factor for lymphoma |
|
|
How do you treat Helicobacter pylori infection?
|
Triple therapy:
- Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) - Clarithromycin - Amoxicillin or Metronidazole |
|

What is the name for spiral-shaped bacteria? Types? Visualization?
|
Spirochetes: BLT -
- Borrelia (big size - only spirochete that can be visualized using aniline dyes (Wright or Giemsa stain) with light microscopy) - Leptospira - Treponema (visualized with dark-field microscopy) |
|
|
Which type of bacteria can be visualized with dark-field microscopy?
|
Treponema (type of spirochete)
|
|
|
Which type of bacteria is found in water contaminated with animal urine?
|
Leptospira interrogans
|
|
|
What diseases are caused by Leptospira interrogans infection?
|
Leptospirosis
- Flu-like symptoms - Jaundice - Photophobia - Conjunctival suffusion (erythema without exudate) Weil Disease (icterohemorrhagic leptospirosis) - Severe form with jaundice and azotemia from liver and kidney dysfunction - Fever - Hemorrhage - Anemia |
|
|
What is the cause and symptoms of Leptospirosis?
|
Leptospira interrogans
- Flu-like symptoms - Jaundice - Photophobia - Conjunctival suffusion (erythema without exudate) |
|
|
What is the cause and symptoms of Weil Disease?
|
Caused by Leptospira interrogans
AKA icterohemorrhagic leptospirosis - Severe form of leptospirosis with jaundice and azotemia from liver and kidney dysfunction - Fever - Hemorrhage - Anemia |
|
|
Who is more likely to get infected with Leptospira interrogans (which causes leptospirosis and Weil disease)?
|
Prevalent among surfers and in tropics (eg, Hawaii)
|
|
|
What causes Lyme Disease?
|
* Borrelia burgdorferi, which is transmitted by the tick Ixodes (also vector for Babesia)
- Natural reservoir is the mouse (important for tick life cycle) |
|
|
Where is Lyme disease more common?
|
NE United States
|
|
|
What are the initial symptoms of Lyme Disease (Borrela burgdorferi)?
|
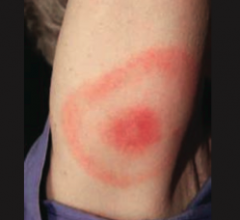
- Erythema chronicum migrans - expanding bulls eye red rash (picture)
- Flu-like symptoms - +/- Nerve palsy |
|
|
What are the later symptoms of Lyme Disease (Borrela burgdorferi)?
|
- Monoarthritis (large joints)
- Migratory polyarthritis - Cardiac - AV nodal block - Neurologic - encephalopathy, facial nerve palsy, polyneuropathy |
|
|
What mnemonic can you use to remember the symptoms of Lyme Disease?
|
FAKE a Key LYME pie:
- Facial nerve palsy (typically bilateral) - Arthritis - Kardiac block - Erythema migrans |
|
|
How do you treat Lyme Disease (Borrelia burgdorferi)?
|
Doxycycline and Ceftriaxone
|
|
|
What bacteria causes Syphilis?
|
Treponema pallidum (spirochete)
|
|
|
What are the stages of Syphilis?
|
- 1° Syphilis
- 2° Syphilis - 3° Syphilis - Congenital Syphilis |
|
|
What are the signs of 1° Syphilis?
|
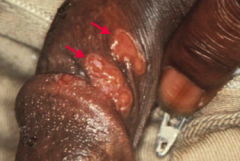
Localized disease, presents with PAINLESS chancre
|
|
|
What are the microscopic and lab findings of 1° Syphilis?
|
- Dark-field microscopy can visualize treponemes in fluid from chancre
- Serologic testing: VDRL/RPR (non-specific), confirm diagnosis with specific test (eg, FTA-ABS) |
|
|
What are the signs of 2° Syphilis?
|
- Disseminated disease / Systemic
- Constitutional symptoms - Maculopapular rash (palms and soles) - Condylomata lata (wart like lesions on the genitals) |
|
|
What are the microscopic and lab findings of 2° Syphilis?
|
- Dark-field microscopy can visualize treponemes
- Serologic testing: VDRL/RPR (non-specific), confirm diagnosis with specific test (eg, FTA-ABS) |
|
|
Following the systemic (2° stage) of syphilis, what happens?
|
Latent syphilis stage
- Positive serology without symptoms |
|
|
What are the signs of 3° Syphilis?
|
- Gummas (chronic granulomas)
- Aortitis (vasa vasorum destruction) - Neurosyphilis (tabes dorsalis, "general paresis") - Argyll Robertson pupil (constricts w/ accommodation but not reactive to light) - Broad-based ataxia - (+) Romberg's test - Charcot joint (progressive degeneration of a weight bearing joint, marked by bony destruction, bone resorption, and eventual deformity) - Stroke without hypertension |
|
|
What are the lab findings of 3° Syphilis?
|
For neurosyphilis: test spinal fluid with VDRL or RPR
|
|
|
What are the signs of congenital syphilis?
|
- Saber shins
- Saddle nose - CN VIII deafness - Hutchinson teeth - Mulberry molars (spreads typically after first trimester) |
|
|
How do you prevent syphilis and congenital syphilis?
|
*Treat with Penicillin G
- Prevent congenital syphilis: treat mother early in pregnancy, as placental transmission typically occurs after 1st trimester |
|
|
What is the "Prostitute Pupil"? AKA? Sign of?
|
Argyll Robertson Pupil
- Pupil constricts with accommodation but is not reactive to light - Associated with 3° syphilis |
|
|
What is the VDRL test used for? Utility?
|
Detects non-specific antibody that reacts with beef cardiolipin; widely used for syphilis (quantitative, sensitive, but not specific)
False positives can be caused by: - Viruses (mono, hepatitis) - Drugs - Rheumatic fever - Lupus and leprosy |
|
|
What is the term for flu-like syndrome that begins after antibiotics are started? Why?
|
Jarish-Herxheimer Reaction
- Due to killed bacteria releasing pyrogens (produces fever) |
|
|
What is the Jarish-Herxheimer Reaction?
|
- Causes flu-like syndrome that begins after antibiotics are started
- Due to killed bacteria releasing pyrogens (produces fever) |
|
|
What is the term for infectious disease transmitted between animals and humans?
|
Zoonosis
|
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by Ixodes ticks? Source? Disease?
|
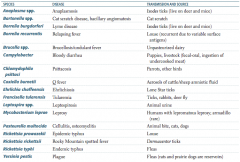
Anaplasma species
- Live on deer and mice - Causes anaplasmosis Borrelia burgdorferi - Lives on deer and mice - Causes Lyme disease |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by a cat scratch? Disease?
|
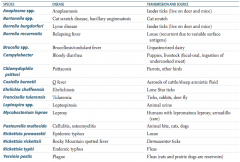
Bartonella species
- Cat scratch disease, bacillary angiomatosis |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by louse? Disease?
|
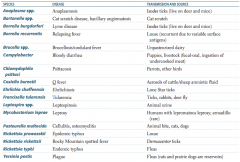
Borrelia recurrentis
- Relapsing fever - Recurrent due to variable surface antigens Rickettsia prowazekii - Epidemic typhus |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by unpasteurized dairy? Disease?
|
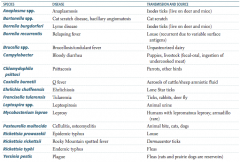
Brucella specia
- Brucellosis / undulant fever |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by puppies and livestock? Source? Disease?
|
Campylobacter
- Fecal-oral transmission via ingestion of undercooked meat - Bloody diarrhea |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by parrots and other birds? Disease?
|
Chlamydophila psittaci
- Psittacosis |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by aerosols of cattle / sheep amniotic fluid? Disease?
|
Coxiella burnetii
- Q fever |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by lone star ticks? Disease?
|
Ehrlichia chaffeensis
- Ehrlichiosis |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by rabbits? Disease?
|
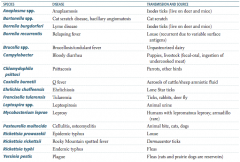
Francisella tularensis (also via ticks and deer fly)
- Tularemia |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by animal urine? Disease?
|
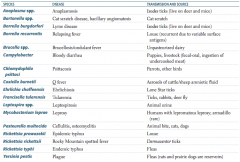
Leptospira species
- Leptospirosis |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by armadillos? Disease?
|
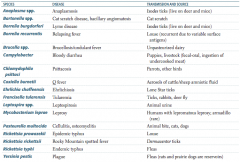
Mycobacterium leprae
- Leprosy - Also spread by humans with lepromatous leprosy |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by animal bites (cats, dogs)? Disease?
|
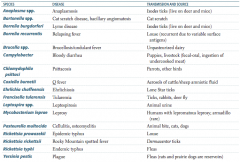
Pasteurella multocida
- Cellulitis and osteomyelitis |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by Dermacentor ticks? Disease?
|
Rickettsia rickettsii
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever |
|
|
Which zoonotic species is transmitted by fleas? Disease?
|
Rickettsia typhi
- Endemic typhus Yersinia pestis - Plaque - Rats and prairie dogs are reservoirs |
|
|
Which zoonotic species has a reservoir in rats and prairie dogs? Disease?
|
Yersinia pestis
- Causes the plague - Transmitted by fleas |
|
|
Which bacteria presents as a gray vaginal discharge with a fishy smell?
|
Gardnerella vaginalis
|
|
|
Characteristics of Gardnerella vaginalis?
|
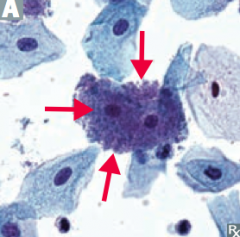
- Pleomorphic
- Gram-variable rod - Involved in vaginosis - CLUE cells or vaginal epithelial cells covered with Gardnerella bacteria are visible under the microscope (arrow) |
|
|
What causes Gardnerella vaginalis?
|
* Not sexually transmitted
- Associated with sexual activity - Overgrowth of certain anaerobic bacteria in vagina |
|
|
How is Gardnerella vaginalis treated?
|
Metronidazole or (to treat anaerobic bacteria) Clindamycin
|
|
|
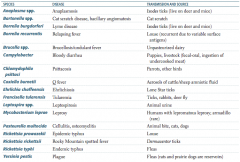
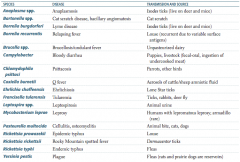
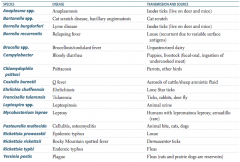
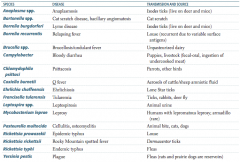
What are the vector-born illnesses? Vector?
|
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever - tick is vector and carries Rickettsia rickettsii
- Typhus - endemic vector is fleas (R. typhi) and epidemic vector is human body louse (R. prowazekii) - Ehrlichiosis - tick is vector and carries Ehrlichia - Anaplasmosis - vector is tick and carries Anaplasma - Q fever - no arthropod vector, Coxiella burnetii spread via tick feces and cattle placenta |
|
|
How do you treat all Rickettsial diseases and vector-borne illnesses?
|
Doxycycline
|
|
|
In which Rickettsial diseases and vector-borne illnesses is a rash common?
|
Rash common:
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever (Rickettsia rickettsii - tick) - Typhus (R. typhi - fleas (endemic); R. prowazekii - human body louse (epidemic)) |
|
|
In which Rickettsial diseases and vector-borne illnesses is a rash rare?
|
Rash rare:
- Ehrlichiosis (Ehrlichia - tick) - Anaplasmosis (Anaplasma - tick) - Q fever (Coxiella burneii - tick feces and cattle placenta) |
|
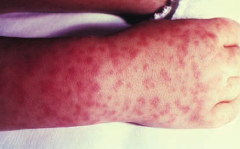
Which bacteria causes a rash that typically starts at wrists and ankles and then spreads to trunk, palms, and soles? Where is it more common?
|
Rickettsia rickettsii (Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever)
- Primarily in S. Atlantic states, especially N. Carolina |
|
|
Characteristics of Rickettsia rickettsii?
|
Obligate intracellular organisms
- Requires CoA and NAD+ because they can't synthesize ATP |
|
|
What is the classic presentation of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
|
Triad: headache, fever, rash (vasculitis)
|
|
|
In which infections is there a "palms and soles" rash?
|
CARS = you drive CARS using your palms and soles
- Coxsackievirus A infection (hand foot and mouth disease) - Rocky mountain spotted fever - 2° Syphilis (systemic) |
|
|
What are the different causes of Typhus? How do they differ?
|
Rickettsia typhi
- Endemic - Spread by fleas Rickettsii prowazekii - Epidemic - Human body louse |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Typhus?
|
Rash starts centrally (trunk) and spreads out, SPARING the palms and soles
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Ehrlichiosis?
|
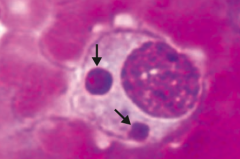
- Caused by Ehrlichia - vector is tick
- Monocytes with morulae (berry like inclusions) in cytoplasm (picture) - Rarely presents with a rash |
|
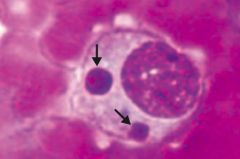
Which disease is pictured: monocytes with morulae (berry-like inclusions) in cytoplasm?
|
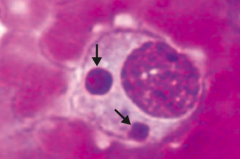
Ehrlichiosis - caused by Ehrlichia (vector is a tick)
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Anaplasmosis?
|
- Caused by Anaplasma, vector is tick
- Granulocytes with morulae in cytoplasm - Rarely presents with rash |
|
|
Which disease is characterized by granulocytes with morulae in cytoplasm?
|
Anaplasmosis - caused by Anaplasma (vector is tick)
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Q fever?
|
- Caused by Coxiella burnetti (can survive outside in its endospore form)
- No arthopod vector - Tick feces and cattle placenta release spores that are inhaled as aerosols - Presents as pneumonia - Rarely presents with rash |
|
|
Which bacteria has Elementary bodies and Reticulate bodies?
|
Chlamydiae
|
|
|
What are the requirements of Chlamydiae?
|
Obligate intracellular organisms - cannot make their own ATP
- Cytoplasmic inclusions seen on Giemsa or fluorescent antibody-stained smear - Chlamydial cell wall is unusual in that it lacks muramic acid |
|
|
What kind of infections does Chlamydiae cause?
|
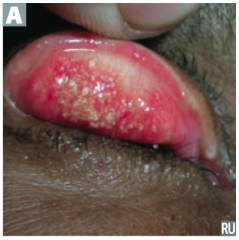
Mucosal infections
- C. trachomatis causes reactive arthritis (Reiter syndrome), follicular conjunctivitis (picture), non-gonococcal urethritis, and PID - C. pneumoniae and C. psittaci cause atypical pneumonia (aerosol transmission) |
|
|
What are the two forms of Chlamydiae?
|
- Elementary Body (small dense) is "Enfectious" and "Enters" cells via "Endocytosis" where it transforms into a Reticulate Body
- Reticulate Body "Replicates" in cell by fission; "Reorganizes" into Elementary Bodies |
|
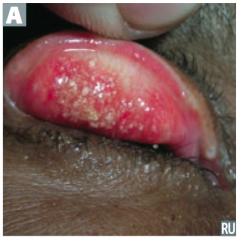
Which bacteria causes reactive arthritis (Reiter syndrome), follicular conjunctivitis (picture), non-gonococcal urethritis, and PID?
|
Chlamydiae trachomatis
|
|
|
Which bacteria causes atypical pneumonia and is transmitted by an aerosol?
|
Chlamydiae pneumoniae and Chlamydiae psittaci (notable for an avian reservoir)
|
|
|
How do you treat Chlamydiae infections?
|
Azithromycin (favored because one time treatment) or Doxycycline
|
|
|
How do you diagnose Chlamydiae infection?
|
Lab: cytoplasmic inclusions seen on Giemsa stain or fluorescent antibody-stained smear
|
|
|
What are the Chlamydiae trachomatis serotypes?
|
- Types A, B, and C
- Types D-K - Types L1, L2, and L3 |
|
|
Which serotypes of Chlamydiae trachomatis cause chronic infection and can cause blindness due to follicular conjunctivitis? Other characteristics?
|
Types A, B, and C
- Africa - Blindness - Chronic Infection |
|
|
Which serotypes of Chlamydiae trachomatis cause urethritis / PID, ectopic pregnancy, neonatal pneumonia (staccato cough), and neonatal conjunctivitis?
|
Types D-K (everything else)
- Neonatal disease can be acquired during passage through infected birth canal |
|
|
Which serotypes of Chlamydiae trachomatis cause Lymphogranuloma Venereum? Symptoms?
|
Types L1, L2, and L3
- Small, painless ulcers on genitals - Swollen, painful inguinal lymph nodes that ulcerate (buboes) - Treat with doxycycline |
|
|
Which bacteria is the classic cause of atypical "walking pneumonia"?
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (more common in patients < 30 years old; common outbreaks in military recruits and prisons)
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of "walking pneumonia"? When is this more common? Cause?
|
- Insidious onset
- Headache - Non-productive cough - Patchy or diffuse interstitial infiltrate - X-ray looks worse than patient - More common in patients < 30 years old - Frequent outbreaks in military recruits and prisons - Cause: Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
|
|
What are the lab results for a patient with "walking pneumonia" caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae?
|
- X-ray looks worse than patient (patchy or diffuse interstitial infiltrate)
High titer of cold agglutinins (IgM), which can agglutinate or lyse RBCs - (remember it is cold in Moscow) - Grows on Eaton agar |
|
|
How do you treat "walking pneumonia" caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae?
|
Macrolide, Doxycycline, or Fluoroquinolone
(penicillin ineffective since Mycoplasma have no cell wall) |
|
|
Why will penicillin be ineffective in a case of walking pneumonia?
|
Typical cause is Mycoplasma pneumoniae (which has no cell wall so penicillin will be ineffective)
|
|
|
Characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae?
|
- No cell wall
- Not seen on Gram stain - Bacterial membrane contains sterols for stability |

