![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
103 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Which histone protein NOT IN the nucleosome? |
H1 |
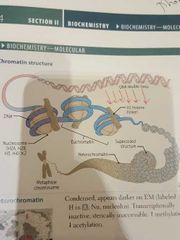
|
|
|
DNA - - - - - charge |
Phosphate groups |
|
|
|
Histone ++++++ charge |
Lysine + arginine |
LYAR |
|

|

|
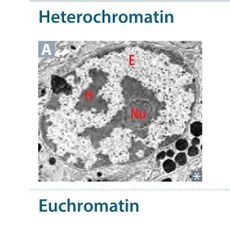
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
DNA METHYLATION |

|
|
|
|
HISTONE METHYLATION |

|
|
|
|
HISTONE ACETYLATION |

|

|
|
|
NucleoSide |
Ribose + Sugar |
|
|
|
NucleoTide |
Ribose + sugar + phosphaTe |
|
|
|
Purines |
Adenine guanine |
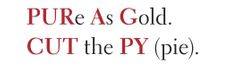
|
|
|
Pyrimidines |
Cytosine - - uracil - - thymine |
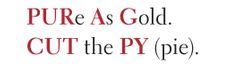
|
|
|
Guanine - - cytosine |
3 H BONDS |
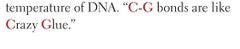
|
|
|
Adenine - - thymine |
2 H BONDS |
2 AT ım var |
|
|
Methylation of uracil makes thymine |
THYmine has a meTHYl |
|
|
|
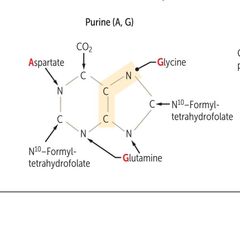
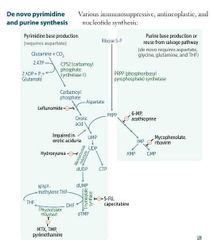
Amino acids necessary for PURINE synthesis |

|
|
|
|
LEFLUNOMIDE |
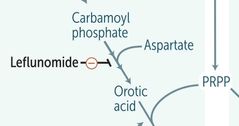
|

|
|
|
METHOTREXATE |
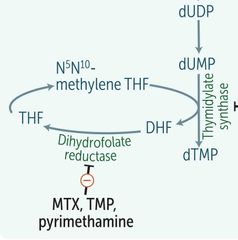
|
HUMANS |
|
|
TRIMETHOPRIME - - TMP |
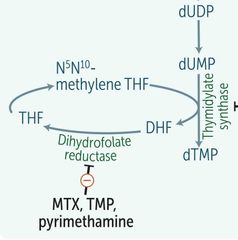
|
BACTERIA |
|
|
PYRIMETHAMINE |
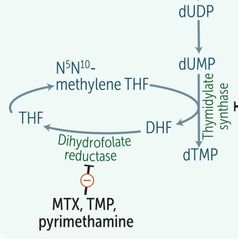
|
PROTOZOA |
|
|
5-FU - - - - CAPACITABINE |
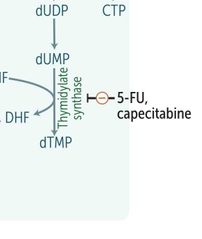
|
|
|
|
6-MP---AZATHIOPURINE |
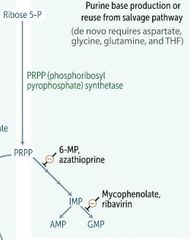
|

|
|
|
MYCOPHENOLATE - - RIBAVIRIN |

|
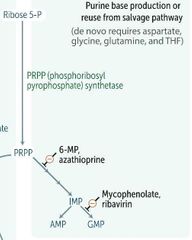
|
|
|
HYDROXYUREA |
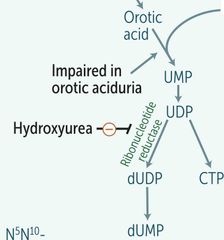
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
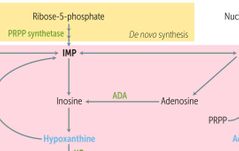
ADENOSINE DEAMINASE (ADA) DEFICIENCY |
Autosomal recessive Lymphotoxicity SCID |
|
|
|
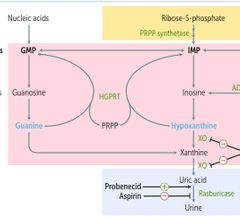
LESCH-NYAN SYNDROME |
HGPRT deficiency X-linked |
|
|
|
LESCH-NYAN SYNDROME SYMPTOMS |

|
|
|
|
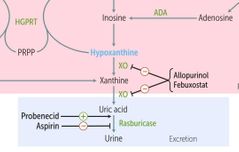
LESCH-NYAN SYNDROME TREATMENT |
ALLOPURINOL FEBUXOSTAT (2 ND LINE) |
|
|
|
1 amino acid 1 codon |
METHIONINE AUG TRYPTOPHAN UGG |
|
|
|
HELICASE deficiency |
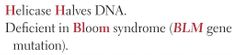
|
|
|
|
IRINOTECAN - - TOPOTECAN |
inhibits TOPOISOMERASE 1 Eukaryotes |
|
|
|
ETOPOSIDE - - TENIPOSIDE |
inhibits TOPOISOMERASE 2 Eukaryotes |
|
|
|
FLUOROKINOLONES |
Inhibits TOPOISOMERASE 2 ( DNA GYRASE) and TOPOISOMERASE 4 Prokaryotes |
|
|
|
DNA POLYMERASE III |

|
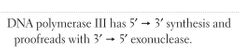
|
|
|
DNA POLYMERASE I |
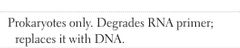
|
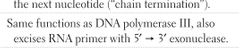
|
|
|
DNA LIGASE |

|
|
|
|
TELOMERASE |

|
|
|
|
mRNA STOP CODONS |
UAA - - - UAG - - - UGA |

|
|
|
mRNA START CODON |
AUG |
|
|
|
RNA PROCESSING |

|
|
|
|
POLYADENYLATION SIGNAL |
AAUAAA |
|
|
|
RNA POLYMERASE I Eukaryotes |
rRNA present only in NUCLEOLUS |
|
|
|
RNA POLYMERASE II Eukaryotes |
mRNA small nuclear RNA (snRNA) opens DNA at promoter site |
|
|
|
RNA POLYMERASE III Eukaryotes |
5SrRNA tRNA |
|
|
|
Alfa-AMANITIN |
inhibits RNA POLYMERASE II |
|
|
|
Actinomycin D |
inhibits RNA POLYMERASE in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes |
|
|
|
Rifampin |
inhibits DNA DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE in prokaryotes |
|
|
|
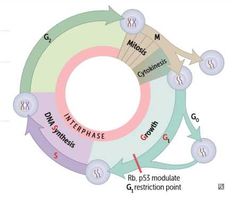
SHORTEST PHASE of cell cycle ; |
M PHASE Mitosis + cytokinesis |
|
|
|
PERMANENT cells |
Neurons Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Red blood cells |
Remain in G0 |
|
|
STABLE (QUIESCENT) |
Hepatocytes Lymphocytes Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) Periosteal cells |
Enter G1 from G0 when stimulated |
|
|
LABILE |
Bone marrow Gut epithelium Skin Hair follicles Germ cells |
Never go to G0 |
|
|
. |
|
|
|
RICH IN ROUGH ER |
Mucus-secreting goblet cells of small intestine Antibody secreting plasma cells |
|
|
|
RICH IN SMOOTH ER |
Liver hepatocytes Steroid hormone producing cells of adrenal cortex Gonads |
|
|
|
PEROXISOME |
Membrane-enclosed organelle involved in: - β-oxidation of very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) - α-oxidation (strictly peroxisomal process) - Catabolism of branched-chain fatty acids, amino acids, and ethanol - Synthesis of cholesterol, bile acids, and plasmalogens (important membrane phospholipid, especially in white matter of brain) |
|
|
|
ZELLWEGER SYDROME |
PEX mutation Autosomal recessive |
Hypotonia Seizures Hepatomegaly Early death |
|
|
REFSUM DISEASE |
Disorder of ALFA OXIDATION Autosomal recessive |
Phytanic acid NOT TO pristanic acid |
|
|
REFSUM DISEASE |
Scaly skin Ataxia Cataracts/night blindness Shortening of 4th toe Epiphyseal dysplasia |
Treatment Diet Plasmapheresis |
|
|
ADRENOLEUKODYSTROPHY |
ABCDI gene mutation X-linked recessive Disorder of BETA OXIDATION |
VLCFA build up in Adrenal glands White matter of brain Testes |
|
|
I (inclusion) CELL DISEASE Mucolipidosis Type II |
Failure of Golgi to phosphorylate mannose residues on GP |
|
|
|
KARTAGENER SENDROM 1 ciliary diskinesia |
Dynein arm defect |
Autosomal recessive |
|
|
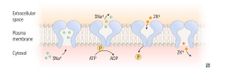
OUABAIN Cardiac glycoside |
inhibits by binding to potassium site |
|
|
|
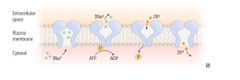
DIGOKSIN DIGITOKSIN |
Direct inhibition of Na/K ATP ase |
|
|
|
. |
|
|
|
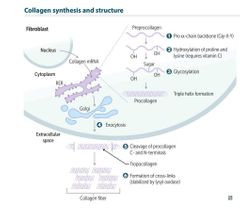
OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA |
COL1A1 and COL1A2 gene defects Problem forming triple helix Type 1 collagen Autosomal dominant |

|
|
|
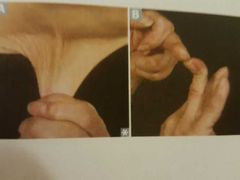
EHLER DANLOS CLASSICAL TYPE |
COL5A1 and COL5A2 mutation Type V Collagen Can be AD or AR |
|
|
|
EHLER DANLOS VASCULAR TYPE |
COL3A1 gene mutation Type III procollagen |

|
|
|
MENKES DISEASE |
Defective MENKES protein (ATP7A) impaired copper absorption and transport Decreased activity of lysyl oxidase XLR |
Brittle kinky hair Growth retardation Hypotonia |
|
|
Alfa-1 antitrypsin |
inhibits ELASTASE - break down elastin |
|
|

|
. |
|
|

|
. |
|
|
|
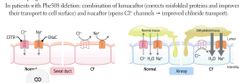
CYSTIC FIBROSIS |
CFTR gene mut on chromosome 7 Commonly a deletion of Phe508 |
|
|
|
CFTR Gene |
ATP gated Cl- channel Secretes Cl- in lungs and GI tract Reabsorbs Cl-in sweat glands |
|
|
|
CYSTIC FIBROSIS DIAGNOSIS |
Increased Cl- concentration in pilocarpine induced sweat test |
|
|
|
CYSTIC FIBROSIS NEWBORN SCREENING |
Increased immunoreactive trypsinogen |
|
|
|
TREATMENT IN PHE508 DELETION |
|
|
|
|
X-LINKED RECESSIVE DISORDERS |

|

|
|
|
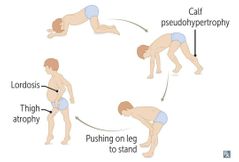
DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY |
Dystrophin prt mutation Frameshift del or nonsense mut Loss of dystrophin myonecrosis Increased CK and aldolase GSGNTST Onset before 5 years of age Dilated CMP common cause death |
|
|
|
GOWERS SIGN DMD |
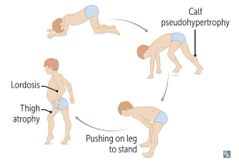
|
|
|
|
BECKER MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY |
Dystrophin gene mut Non-frameshift del Less severe than DMD Onset in adolescence or early adulthood |
|
|
|
TRINUCLEOTIDE REPEAT EXPANSION DISEASES |

|

|
|
|
TRINUCLEOTID REPEAT EXPANSION DISEASES CHART |
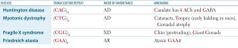
|
|
|
|
GENETIC DISORDERS BY CHROMOSOME |
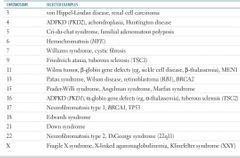
|
|
|

|
. |
|
|
|
EDWARDS SYDNROME TRISOMY 18 |

|
|
|
|
PATAU SYNDROME TRISOMY 13 |

|
|
|
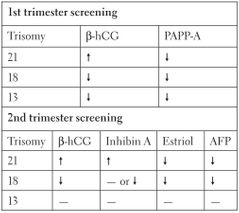
|
. |
|
|
|
CRI DU CHAT |

|
|
|
|
WILLIAMS SYNDROME |

|
|
|
|
ROBERTSONIAN TRANSLOCATION |
Chromosomal translocation Commonly involves chromosome pairs 13. 14. 15. 21. 22 |
|
|
|
FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS |
A. D. E. K. |
|
|
|
WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS |

|
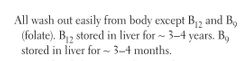
|
|
|
VITAMIN A - RETINOL DEFICIENCY |

|
|
|
|
VITAMIN A - RETINOL EXCESS |

|
|
|
|
RETIN-A |
Topically for wrinkles and acne |
|
|
|
ISOTRETINOIN |
Orally to treat severe cystic acne Teratogenic |
|
|
|
all-TRANS RETINOIC ACID |
To treat acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) |
|
|
|
VITAMIN B1 - THIAMINE FUNCTION |

|
|
|
|
VITAMIN B1- THIAMINE DEFICIENCY |

|
|
|
|
GLUT-1 |
RBC Brain |
|
|
|
GLUT-2 |
Liver Kidney Pancreatic beta cells |
|
|
|
GLUT-4 |
Insulin dependent Muscle Adipose tissue |
|

