![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the APGAR score assess? |
Assessment of newborn vital signs following labor, via a 10-point scale evaluated at 1 minute and 5 minutes
- A: Appearance - P: Pulse - G: Grimace - A: Activity - R: Respiration |
|
|
What do the APGAR scores indicate?
|
- ≥ 7 = good
- 4-6 = assist and stimulate - <4 = resuscitate If score remains <4 at later time points, there is increased risk the child will develop long-term neurological damage |
|
|
What is the definition of a low birth weight infant?
|
< 2500 g
|
|
|
What can cause low birth weight (<2500g)?
|
- Prematurity
- Intrauterine growth retardation |
|
|
What problems are associated with a low birth weight (<2500g)?
|
- ↑ Risk of SIDS
- ↑ Overall mortality - Impaired thermoregulation and immune function - Hypoglycemia - Polycythemia - Impaired neurocognitive / emotional development |
|
|
What are the complications of a low birth weight (<2500g)?
|
- Infections
- Respiratory distress syndrome - Necrotizing entercolitis - Intraventricular hemorrhage - Persistent fetal circulation |
|
|
What are the motor, social, and verbal/cognitive milestones from birth to 3 months?
|
- Motor: rooting reflex, holds head up, Moro reflex disappears
- Social: social smile - Verbal/cognitive: orients and responds to voice |
|
|
What are the motor, social, and verbal/cognitive milestones from 7-9 months?
|
- Motor: sits alone, crawls, transfers toys from hand to hand
- Social: stranger anxiety - Verbal/cognitive: responds to name and simple instructions, uses gestures, plays peek-a-boo |
|
|
What are the motor, social, and verbal/cognitive milestones from 12-15 months?
|
- Motor: walks, Babinski sign disappears
- Social: separation anxiety - Verbal/cognitive: few words |
|
|
What are the motor, social, and verbal/cognitive milestones from 12-24 months?
|
- Motor: climbs stairs, stacks 3 blocks at 1 yr, 6 blocks at 2 yr
- Social: rapprochement (moves away from and then returns to mother) - Verbal/cognitive: 200 words and 2-word phrases at age 2 |
|
|
What are the motor, social, and verbal/cognitive milestones from 24-36 months?
|
- Motor: feeds self with fork and spoon, kicks ball
- Social: core gender identity, parallel play - Verbal/cognitive: toilet training ("pee at 3") |
|
|
What are the motor, social, and verbal/cognitive milestones from 3 years?
|
- Motor: Rides tricycle (3-cycle at age 3) and copies lines or circle drawings
- Social: comfortably spends part of day away from mother - Verbal/cognitive: 900 words and complete sentences |
|
|
What are the motor, social, and verbal/cognitive milestones from 4 years?
|
- Motor: use buttons and zippers, grooms self (brushes teeth), hops on 1 foot, makes simple drawings (stick figures)
- Social: cooperative play, imaginary friends - Verbal/cognitive: can tell detailed stories and use prepositions |
|
|
What are the sexual changes that occur in elderly men?
|
- Slower erection and ejaculation
- Longer refractory period |
|
|
What are the sexual changes that occur in elderly women?
|
Vaginal shortening, thinning and dryness
|
|
|
What are the sleep changes that occur in the elderly?
|
- ↓ REM and slow wave sleep
- ↑ Latency and awakenings |
|
|
What age group has the highest suicide rate?
|
Men 65-74 years of age have the highest suicide rate in the US
|
|
|
What physiologic changes occur in the elderly?
|
- ↓ Vision, hearing, immune response, bladder control
- ↓ Renal, pulmonary, GI function - ↓ Muscle mass and ↑ Fat - Presbycusis: high-frequency hearing loss d/t destruction of hair cells at the cochlear base (preserved low-frequency hearing at apex) |
|
|
What are the characteristics of normal grief and bereavement?
|
- Shock
- Denial - Guilt - Somatic symptoms - May experience delusions - Lasts up to 1 year |
|
|
What are the characteristics of pathologic grief and bereavement?
|
- Excessively intense grief
- Grief that is delayed, inhibited, or denied - May experience depressive symptoms, delusions, and hallucinations - Prolonged grief lasting >2-6 months |
|
|
What are the types of sexual DESIRE disorders?
|
- Hypoactive sexual desire
- Sexual aversion |
|
|
What are the types of sexual AROUSAL disorders?
|
Erectile Dysfunction
|
|
|
What are the types of ORGASMIC disorders?
|
- Anorgasmia
- Premature ejaculation |
|
|
What are the types of sexual PAIN disorders?
|
- Dyspareunia
- Vaginismus |
|
|
What does a differential diagnosis for sexual dysfunction include?
|
- Drugs (eg, anti-hypertensives, neuroleptics, SSRIs, ethanol)
- Diseases (eg, depression, diabetes) - Psychological (eg, performance anxiety) |
|
|
What drugs can cause sexual dysfunction?
|
- Anti-hypertensives
- Neuroleptics - SSRIs - Ethanol |
|
|
What diseases can cause sexual dysfunction?
|
- Depression
- Diabetes |
|
|
What psychological state can cause sexual dysfunction?
|
Performance anxiety
|
|
|
How do you calculate BMI?
|
BMI = weight in kg / (height in meters)^2
|
|
|
How do you classify the BMI scores?
|
< 18.5 is underweight
18.5 - 24.9 is normal weight 25.0 - 29.9 is overweight > 30.0 obesity > 35.0 severe obesity > 40.0 morbid obesity > 45.0 super obesity |
|
|
What are the stages of sleep?
|
- Awake (eyes open)
- Awake (eyes closed) - Stage N1 - Stage N2 - Stage N3 - REM |
|
|
How do you remember the EEG waveforms that correspond to the progressive stages of sleep?
|
At night, BATS Drink Blood
- β (Beta) - Awake (eyes open) - α (Alpha) - Awake (eyes closed) - 𝚹 (Theta) - Stage N1 - Sleep spindles and K complexes - Stage N2 - δ (Delta) - Stage N3 - β (Beta) - REM |
|
|
What is happening during the awake (eyes open) stage? EEG waveform?
|

- Alert, active mental concentration
- β (highest frequency, lowest amplitude) At night, (B)ATS Drink Blood |
|
|
What is happening during the awake (eyes closed) stage? EEG waveform?
|

α waves
At night, B(A)TS Drink Blood |
|
|
What is happening during the N1 stage? EEG waveform? Percent of total sleep time in young adults?
|

- Light sleep
- Theta waves - 5% of total sleep At night, BA(T)S Drink Blood |
|
|
What is happening during the N2 stage? EEG waveform? Percent of total sleep time in young adults?
|
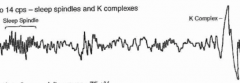
- Deeper sleep, bruxism (teeth grinding)
- Sleep spindles and K complexes - 45% of total sleep At night, BAT(S) Drink Blood |
|
|
What is happening during the N3 stage? EEG waveform? Percent of total sleep time in young adults?
|

- Deepest, non-REM sleep (slow-wave sleep)
- Sleepwalking, night terrors, bed-wetting - Delta waves (lowest frequency, highest amplitude) - 25% of total sleep At night, BATS (D)rink Blood |
|
|
What is happening during the REM stage? EEG waveform? Percent of total sleep time in young adults?
|

- Dreaming, loss of motor tone
- Possibly a memory processing function - Erections - ↑ Brain O2 use - Beta waves - 25% of total sleep At night, BATS Drink (B)lood |
|
|
What percentage of the total sleep does each of the sleep stages take?
|
- Stage N1 (5%)
- Stage N2 (45%) - Stage N3 (25%) - REM (25%) |
|
|
What brain structure is key to initiating sleep?
|
Serotonergic predominance in the raphe nucleus
|
|
|
How do you treat sleep enuresis (bed-wetting)? Mechanism?
|
Oral desmopressin acetate (DDAVP)
- Mimics vasopressin (ADH) - Preferred over imipramine because fewer side effects |
|
|
Which drugs affect the quality of sleep? How?
|
Alcohol, benzodiazepines, and barbiturates:
- Reduced REM and delta (N3) sleep |
|
|
How do you treat night terrors and sleep-walking?
|
Benzodiazepines
|
|
|
How often does REM sleep occur? How long does it last?
|
- Occurs every 90 minutes
- Increases in duration throughout the night - 25% of the total sleep time |
|
|
What neurotransmitters are involved in REM sleep?
|
- ACh is the principal NT in REM sleep
- NE reduces REM sleep |
|
|
What are the findings of REM sleep?
|
- ↑ and variable pulse and BP
- Extraocular movements during REM sleep d/t hyperactivity of PPRF (paramedian pontine reticular formation / conjugate gaze center) - Penile/clitoral tumescence (swelling) - Paradoxical sleep (REM sleep has the same EEG pattern as wakefulness |
|
|
How can you remember the changes that occur during REM sleep?
|
REM sleep is like sex:
- ↑ Pulse - Penile / clitoral tumescence (swelling) - ↓ Frequency with age |
|
|
What causes the extraocular movements during REM sleep?
|
Hyperactivity of PPRF (paramedian pontine reticular formation / conjugate gaze center)
|
|
|
What are the sleep patterns of depressed patients?
|
- ↓ Slow-wave sleep
- ↓ REM latency - ↑ REM early in sleep cycle - ↑ Total REM sleep - Repeated nighttime awakenings - Early-morning awakening (important screening question) |
|
|
What is narcolepsy?
|
- Disordered regulation of sleep-wake cycles
- Excessive daytime sleepiness |
|
|
When can hallucinations occur in patients with narcolepsy?
|
- Just before sleep (hypnagogic)
- Just before awakening (hypnapompic) |
|
|
What happens during the sleep cycle in a patient with narcolepsy?
|
Patient starts off with REM sleep
|
|
|
What symptoms do some patients with Narcolepsy experience?
|
- Hypnagogic (just before sleep) or hypnopompic (just before awakening) hallucinations
- Cataplexy (loss of all muscle tone following a strong emotional stimulus) |
|
|
How do you treat narcolepsy?
|
- Daytime stimulants (amphetamines, modafinil)
- Nighttime sodium oxybate (GHB) |
|
|
What brain structure drives the Circadian Rhythm?
|
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) of Hypothalamus
- Controls ACTH, prolactin, melatonin, and nocturnal NE release - SCN → NE release → Pineal Gland → Melatonin - SCN is regulated by environment (eg, light) |
|
|
What characterizes sleep terror disorder?
|
- Periods of terror with screaming in the middle of the night
- Occurs during slow wave sleep - Most common in children - Occurs during non-REM sleep (no memory of arousal) - Triggers may include emotional stress during previous day, fever, or lack of sleep - Usually self-limited |
|
|
What characterizes nightmares?
|
Occurs during REM sleep (memory of a scary dream)
|
|
|
What are the common causes of death (US) for patients < 1 year old?
|
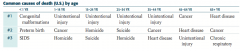
1. Congenital malformations
2. Preterm birth 3. SIDS |
|
|
What are the common causes of death (US) for patients 1-14 years old?
|
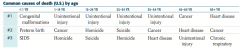
1. Unintentional injury
2. Cancer 3. Homicide |
|
|
What are the common causes of death (US) for patients 15-24 years old?
|
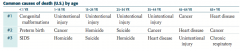
1. Unintentional injury
2. Homicide 3. Suicide |
|
|
What are the common causes of death (US) for patients 25-34 years old?
|
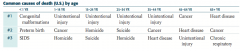
1. Unintentional injury
2. Suicide 3. Homicide |
|
|
What are the common causes of death (US) for patients 35-44 years old?
|
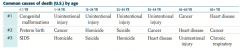
1. Unintentional injury
2. Cancer 3. Heart Disease |
|
|
What are the common causes of death (US) for patients 45-64 years old?
|
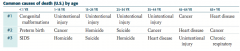
1. Cancer
2. Heart disease 3. Unintentional injury |
|
|
What are the common causes of death (US) for patients 65+ years old?
|
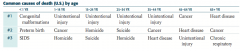
1. Heart disease
2. Cancer 3. Chronic respiratory disease |

