![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Examination of the eyes include:
|
*assessment of visual acuity
*extraocular mvmt *internal & external eye structures *visual pathways, fields & reflexs |
|
|
|
Technique for examination of the eyes
|
inspection
palpation |
|
|
|
Eye History Questions to ask your client during Head assessment?
|
-changes in vision?
-wear glasses or contact lenses? -Have you ever had eye injury, eye surgery, blurred vision -Have you ever seen spots or floater, flashes or light of halos around lights? -last eye exam? -hx of frequent or recurring eye infections, styes, tearing or dryness? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hyperopia
|

farsightedness, a refractive error in which rays of light enter the eye and focus BEHIND the retina. Persons are able to clearly see distant objects but not close objects.
|
|
|
|
Myopia
|

snearsightedness, a refractive error in which rays of light enter the eye and focus in FRONT the retina. Persons are able to clearly see close objects but not distant objects.
*Assess using SNELLEN CHART |
|
|
|
Presbyopia
|

impaired near vision or farsightedness in midle-age & older adults caused by loss of elasticity of the lens & assoc. w/ the aging process
|
|
|
|
Screen for Presbyopia by using?
|
Rosenbaum eye chart held 14 inches form clients face. Readings corrletate w/ the Snellen chart/
|
|
|
|
Retinopathy
|
noninflammatory eye d/o resulting from changes in retinal blood vessels.
*Leading cause of Blindness* |
|
|
|
Strabismus
|
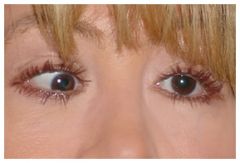
Congenital condition in which BOTH eyes do not focus on an object simultaneously:
*eyes appear crossed *cover/uncover test |
|
|
|
What is the cause of Strabismus?
|
impairment of the extraocular muscles or their nerve supply
|
|
|
|
Cataracts
|
-cloudiness over lens
-develop slowly & progressively after age 35 or suddenly after tramua *Most common eye disorder* |
|
|
|
Glaucoma
|
-intraocular structural damage resulting from ELEVATED Intraocular Pressure
-loss of visual field - |
|
|
|
What is the cause of Glaucoma?
|
-obstruction of the outflow of aqueous humor
-without tx leads to Blindness |
|
|
|
Glaucoma
|
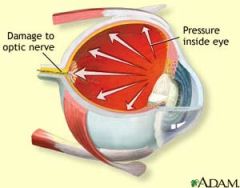
|
|
|
|
Macular Degeneration
|

blurred central vision often occuring suddenly
-Caused by progressive degeneration of the center of the retina -Most common Visual Impairment |
of individuals >50
-Most common cause of Blindness in older adults *There is NO cue* |
|
|
Astigmatism
|
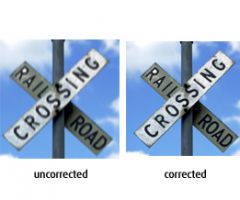
-oblonged of "football" shaped cornea
-generally causes eye-strains, headaches & blurry vision -associated w/ hyperopia(farsightedness) and Myopia (nearsightedness) - |
|
|
|
1.VISUAL ACUITY
|
-ability to see small things
-test central vision |
|
|
|
How do you assess near vision?
|
ask client to read newpaper
|
|
|
|
How do you assess distant vision?
|
Snellen Chart
(test w/o contact 1st & then w/ contacts) |
|
|
|
What does the Standardized #'s at the end of each lines of the Snellen chart? (20/40)
|
-20/ is the distance client stands from the chart
-40 the larger the denominator, the poorer the visual acuity (can read a line that a person w/ normal vision can read 40 ft away) |
|
|
|
Assessment for LIGHT PERCEPTION?
|
-shine a penlight into the eye an then turn off
-If client notes when the light is turned on or off, Light Perception is intact. |
|
|
|
CN controlling Visual Acuity
|
CN-II (Optic)
|
|
|
|
2. Why do you assess EXTRAOCULAR MOVEMENTS?
|
to determine the coordination of the eye muscles (6 small muscles control eye mvmt of each eye)
|
|
|
|
Test used to assess EOM?
|
-6 Cardinal Fields of Gaze
|
|
|
|
Explain the 6 Cardinal Fields of Gaze test?
|
-clients follows finger w/ eyes w/o moving head
-examiner moves finger in a wilde "H" pattern about 20 to 25 cm from clients eye |
|
|
|
As you r performing the 6 Cardinal Fields of Gaze test, what are you looking for ?
|
-smooth and symmetrical eye mvmt w/ no jerky of tremor-like mvmts (nystagmus)
|
|
|
|
CN controlling EOM?
|
-CN III (Oculomotor)
-CN IV (trochelear) -CN VI (Abducens) |
|
|
|
Nystagmus
|
tremor-like mvmts (check for extraocular pressure)
|
|
|
|
3. How do you elevate VISUAL FIELDS
|
-check by your wiggling fingers on each side of the clients face
-Testing to see if client can see objects in the Periphery |
|
|
|
Visual field test is testing for?
|
-Macular degeneration
-glaucoma |
|
|
|
CN controlling Visual Fields?
|
CN II (Optic0
|
|
|
|
Clients with visual field problems are at risk for ?
|
-injury
|
|
|
|
4, EXTERNAL STRUCTURES include assessing?
|
-Position and Alignment- of the eyes in realation to 1 another
-Eyelids- close completely & open -Eyelashs-curve outward/evenly -Conjunctiva (pink/transparent) & Sclera (white) -Corneas (clear) -Lens (clear), Cloudiness= cataracts -PERRLA (CN II & CN III) -Irises |
|
|
|
PTOSIS
|
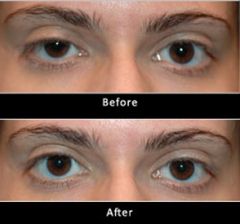
-dropping upper eyelid (covering pupil)
|
|
|
|
EXOPHTHALMOS
|
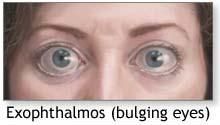
-bulging eyes
-indicates Hyperthyroidism |
|
|
|
STRABISMUS
|
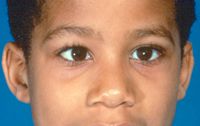
-cross eye
-neuromuscular injury or -inherited |
|
|
|
Tumor or inflammation of the Orbit causes?
|
abnormal eye protrusion
|
|
|
|
Inability to move eyebrows indicates a facial nerve paralysis. Which CN?
|
CN VII (
|
|
|
|
2 causes of Ptosis?
|
-edema
-impairment of 3rd cranial nerve |
|
|
|
In older adults Ptosis results from?
|
loss of elasticity
|
|
|
|
ECTROPION
|
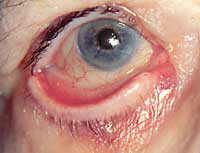
-lid margins turn old
-frequently seen in older adults |
|
|
|
HORDEOLUM
|
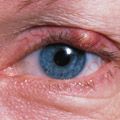
-stye
- inflammation of follicle of an eyelash |
|
|
|
ICTERUS
|
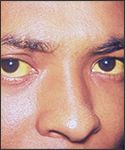
yellow sclera
|
|
|
|
ARCUS SENILIS
|
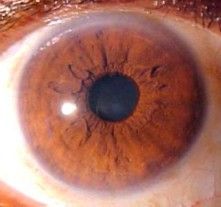
-fatty deposit around the iris
-common with aging but Abnormal in anyone under 40 y/o |
|
|
|
Lacrimal Apparatus?
|
secretes & drains tears, which moisten & lubricate eye structures.
|
|
|
|
lubricates the cornea?
|
blink reflex
|
|
|
|
Presence of redness indicates an allergic or infectious?
|
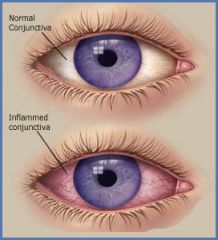
-Conjunctivitis
-highly contagious -easy to spread the crusty drainage (wear gloves) |
|
|
|
Transparent, colorless portion of the eye covering the pupil and iris?
|
-CORNEA
|
|
|
|
What is the Normal size for Pupils?
|
*3 to 7 mm in diameter
|
|
|
|
DILATED pupils are a result of?
|
*glaucoma
*trauma *neurological d/o *eye meds (atropine) * withdrawal from opioids |
|
|
|
What causes Pupil CONSTRICTION?
|
*inflammation of the iris
*use of drugs(morphine, cocaine, pilocarpine) |
|
|
|
Common sign of Opioid intoxication?
|
*Pinpoint Pupils
|
|
|
|
Shinning a light through the Pupil and onto the Retina stimulates which CN?
|
CN III (oculomotor)
|
|
|
|
PERRLA
|
*Pupils
*Equal *Round *Reflect to Light *Accommodation |
|
|
|
How do you test for Light (Pupillary Reflexes)?
|
*dim room
*client looks straight *bring penlight from side of client face, directing the onto the pupil *if client looks at the light, there will be a false reaction to accommodation |
|
|
|
How do you test for Accommodation?
|
*have client gaze at a distant object (far wall), then you hold your finger 4in from bridge of clients nose
*Pupils will dilate to look at an object far away and then converge and constrict to focus on a near object |
|
|
|
Testing for Accommodation is only important if the client has a _____?
|
*Defect in the pupillary response to light
|
|
|
|
What clients are at greatest need for an eye exam?
|
-hypertension
-diabetes -intracranial d/o |
|
|
|
Who does the examination of the Internal Eye Structure exam?
|
*Md
*beyond the scope of new graduate nurses' practice |
|
|
|
Internal Eye Structure exam includes?
|
*retina
*choroid *optic nerve disc *macula *fovea centralis *retinal vessels |
|
|
|
**Client Teaching**
*What are the Teaching Strategies for EYE Assessment? |
* <40 eye exam every 3-5 y
* >40 every 2 years w/ glaucomascreening * >65 every year *describe sx of eye disease *instruct older adult to be cautious driving at night, increase lighting in the room |
|
|
|
Examination of the ears include assessment of the?
|
* External-inspect/palpate
* Middle- inspect w/ otoscope * Internal-Measue clients hearing acuity |
|
|
|
External ear structures consists of ?
|
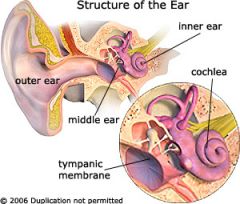
* auricle
* outer ear canal * tympanic membran (eardrum) |
|
|
|
Air-filled cavity containing 3 bony ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes)
|
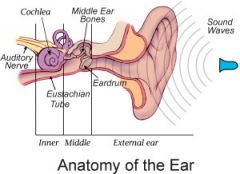
* Middle Ear
|
|
|
|
What connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx/
|
* Eustachian Tube
|
|
|
|
What are some questions the nurse should ask client during EAR assessment?
|
* ear pain, itching, discharge, vertigo, tinnitus(ringing in ears),
* change in hearing * risk for hearing problems (work, family hx,) * hearing aid? * large doses of ASA or ototoxic drugs? * |
|
|
|
Ototoxic drugs (aminoglycoside, furosmide, streptomycin) EFFECTS?
|
HEARING LOSS
|
|
|
|
Ototoxicity
|
injury to the auditory nerve
-resulting from high maintenance doses of antibiotics (aminoglycosides) |
|
|
|
Inspection of the Ear includes:
|
-guarding (children)
-Response to normal voice -does the patient talk loudly? -Auricle of pinna-(equal size & level w/ each other) -objects in ear canal (pink w/ tiny hairs) -drainage (COCA) -use Otoscope |
|
|
|
Appearance of a normal Tympanic Membrane?
|
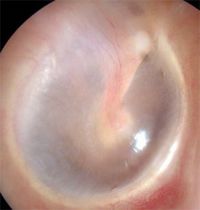
-translucent
-shiny -pearly gray (inspect w/ otoscope) |
|
|
|
3 types of Hearing Loss
|
-Conduction
-Sensorineural -Mixed |
|
|
|
What type of hearing loss Interupts sound waves as they travel from the outer ear to the cochlea of the inner ear?
|
-Conduction Loss
|
|
|
|
What are some examples of causes of Conduction Loss?
|
- swelling of the auditory canal
- tears in the tympanic membrane - listening to loud music - in older adult the bones of the middle ear will get stiff |
|
|
|
What is Sensorineural Loss?
|
- transmission of sound is interrupted at some point beyond the bony ossicles (seen in older adults)
- involves the Inner Ear, Auditory Nerve or Hearing Center of the brain |
|
|
|
What are some questions the nurse should ask client during EAR assessment?
|
* ear pain, itching, discharge, vertigo, tinnitus(ringing in ears),
* change in hearing * risk for hearing problems (work, family hx,) * hearing aid? * large doses of ASA or ototoxic drugs? * |
|
|
|
Ototoxic drugs (aminoglycoside, furosmide, streptomycin) causes?
|
Otitis
|
|
|
|
Ototoxicity
|
injury to the auditory nerve
-resulting from high maintenance doses of antibiotics (aminoglycosides) |
|
|
|
Inspection of the Ear includes:
|
-guarding (children)
-Response to normal voice -does the patient talk loudly? -Auricle of pinna-(equal size & level w/ each other) -objects in ear canal (pink w/ tiny hairs) -drainage (COCA) -use Otoscope |
|
|
|
Mixed loss
|
combination of Conduction and Sensorineural Loss
|
|
|
|
Cerumen
|
yellow, waxy substance
|
|
|
|
Tuning Fork
|
allows for comparison of hearing by Bone Conduction and Air Conduction
|
|
|
|
Weber Test?
|
1. turning fork place on top of client's heard (ask client if sound is heard best in right/left or both ears equally)
|
|
|
|
Expected findings for a negative WEBER Test?
|
Sounds heard equally in both ears
|
|
|
|
What are some questions the nurse should ask client during EAR assessment?
|
* ear pain, itching, discharge, vertigo, tinnitus(ringing in ears),
* change in hearing * risk for hearing problems (work, family hx,) * hearing aid? * large doses of ASA or ototoxic drugs? * |
|
|
|
Ototoxic drugs (aminoglycoside, furosmide, streptomycin) causes?
|
Otitis
|
|
|
|
Ototoxicity
|
injury to the auditory nerve
-resulting from high maintenance doses of antibiotics (aminoglycosides) |
|
|
|
Inspection of the Ear includes:
|
-guarding (children)
-Response to normal voice -does the patient talk loudly? -Auricle of pinna-(equal size & level w/ each other) -objects in ear canal (pink w/ tiny hairs) -drainage (COCA) -use Otoscope |
|
|
|
*Conduction Deafness
|
-vibration heard best in the AFFECTED ear (ear that has the conduction hearing loss)
|
|
|
|
**Sensorineural Deafness
|
vibration is heard best in the UNAFFECTED ear (hear best on the unaffected side)
|
|
|
|
Normal distance for a Watch-Tick Test
|
5 inches
|
|
|
|
Technique for Whisper Test
|
1. 1 ear is occluded & other ear is tested to see if client can hearwhispered sounds w/o seeing examiner's mouth move
2. Repeat w/ other ear (30 cm away) |
|
|
|
Rinne Test?
|
-compares air conduction and bone Bone conduction
-expected findings: AC>BC; 2 to 1 ratio |
|
|
|
Technique for Rinne Test
|
1. Stem of vibrating tuning fork against clients Mastoid process
2. count interval 3 client tell you when she no longer hears the sound (note sec) 5 place still vibrating fork beside ear canal 6. client tells you when she no longer hears should 7. compare # of secs the sounds are heard |
|
|
|
Conduction hearing Loss?
|
AC<BC
(AC is not as long as it should be) |
|

