![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Label 1-16 |
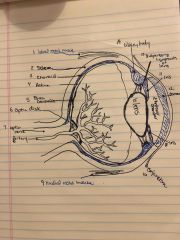
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Lateral rectus |
Moves the eye away from the nose |
|
|
Medial rectus muscle |
Most powerful of extraocular muscles, turns eye toward the nose |
|
|
Fovea centralis |
Area in the macula where visual acuity is sharpest. Contains high number of cones |
|
|
Iris |
Colored part of the eye |
|
|
Lens |
Transparent structure of the eye that focuses light by the curvature of its surface. |
|
|
Optic disk |
Portion of the optic nerve that is formed by meeting all the retinal nerve fibers. Insensitive to light, corresponds to blind spot. |
|
|
Optic nerve |
Carries impulses from retina to brain. Transmits the signals from rods and cones to brain. |
|
|
Retina |
Seeing part of the eye. Retina lines the sclera and is the place where light coming into the eye is focused. |
|
|
Sclera |
White portion of the eye that gives shape and structure to the eyeball |
|
|
Vitreous humor |
Thick clear jelly-like substance that fills the eye btn the lens and retina. Supports the retina and keeps the eye round. |
|
|
What are Rods and cones? |
Photoreceptors. Rods-black and white vision and nighttime vision as well as peripheral and motion detection Cones-color vision and daytime vision and clear central vision |
|
|
Suspensory ligaments |
Long thin fibers that connect the crystalline lenses to the ring of ciliary muscles |
|
|
Fundus |
Bottom/base of an organ. For the eye t refers to the interior surface of the eyeball |
|
|
Choroid |
Blood vessels that nourish the retina so that it can function. Located between the sclera and retina |
|
|
Ciliary muscle |
Muscle that alters the shape of the crystalline lens. It has direct control over focusing ability of the eye. |
|
|
Conjunctiva |
Clear cellophane like tissue that covers the sclera and inside surface of the eyelids. |
|
|
Cornea |
Transparent tissue located on the very front of the eye. Most powerful refractive media of the eye and provides most of the eyes ability to focus light. |
|
|
Anterior chamber |
Located behind the cornea and in front of the iris. It’s filled with fluid called aqueous humor |
|
|
Aqueous humor |
Watery Fluid produced by ciliary body and provides nutrients for the lens and posterior cornea and carries away waste. Maintains intraocular pressure. |
|
|
Crystalline lens |
Provides focusing power to the eye. Allows adjustments from distance to near objects and is the second most powerful refractive medium. |

