![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
334 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is in phylum Echinodermata? |
Sea star, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers |
|
|
|
What does Echinoderm mean? |
Spiny skin |
|
|
|
What other animals are Echinodermatas most closely related to? |
Chordates |
|
|
|
What type of symmetry do Echinodermatas have? |
Adults-pentiradial Larvae-bilateral |
|
|
|
What type of body structure do Echinodermatas have? |
Calcareous endoskeleton. Calcium carbonate plates called ossicles. |
Plates derived from mesoderm, held in place by connective tissue, and covered by an epidermal layer. Frequently modified into fixed or articulated spines |
|
|
Echinodermatas: development, body cavities, and tissue organization? |
Deuterostome, coelomate, and triploblastic |
|
|
|
What type of nervous system do Echinodermatas have? |
Nerve net, nerve ring, and radial nerves |
|
|
|
Where is the oral and aboral structures on Echinodermatas? |
Oral-underneath Aboral- on top |
|
|
|
What are the steps for the water vascular system in Echinodermatas? |
Madreporite Stone canal Ring canal Radial canal Lateral canal Ampulla Tube foot |
|
|
|
What is in class asteroidea? |
Sea stars |
|
|
|
What type of symmetry does class asteroidea have? |
Pentiradial. The arms fuse together before reaching the center. |
|
|
|
What class has dermal branchia and what is it used for? |
Class asteroidea. Thin fold of the body wall that extend between ossicles and function in gas exchange |
Skin gills |
|
|
What class has pedicellariae and what is it? |
Class asteroidea. Pincherlike surface that cleans the body surface of debris. |
On the aboral surface |
|
|
What class has the ambulacral groove and what is it? |
Class asteroidea. Runs the length of the oral surface of each arm. Houses radial canal. Tube feet come off of it. |
|
|
|
What does class asteroidea eat? |
Snails, bivalves, crustaceans, polychaeta, corals, etc |
|
|
|
What are the two stomach regions of the class asteroidea? |
Cardiac - receives food Pyloric- gives rise to the ducts that connect to secretory and absorptive structures called Pyloric cecae |
|
|
|
What do asteroidea's use the Pyloric cecae for? |
Absorb nutrients for the body |
|
|
|
Why is having a branched or folded digestive system beneficial? |
Increases surface area for nutrient absorption |
|
|
|
What type of reproduction does class asteroidea have? |
Mostly dioecious |
|
|
|
What is in class ophiuroidea? |
Basket stars and brittle stars |
|
|
|
Which class of Echinodermatas is the most diverse? |
Class ophiuroidea |
|
|
|
How can you tell class asteroidea from class ophiuroidea? |
Asteroidea's arms fuse together before the center. Ophiuroidea are sharply set off from the center |
|
|
|
What is bursae and which class uses it? |
Membranous sacs that diffuse ammonia. Class ophiuroidea |
|
|
|
What is autotomy and which class uses it? |
When an organism can contract muscles that will sever a limb if it is grabbed. Brittle stars in class ophiuroidea |
|
|
|
What is in class Exhinoidea? |
Sea urchins, sand dollars, and heart urchins |
|
|
|
What does class Echinoidea eat? |
Algae, coral polyps, and dead animal remains |
|
|
|
What is Aristotle's lantern and which class uses it? |
A chewing apparatus that can be projected from the mouth. Class Echinoidea |
|
|
|
What is in class holothuroidea? |
Sea cucumbers |
|
|
|
What is respiratory trees and which class uses them? |
Used for gas exchange and removal of nitrogenous waste in class holothuroidea |
|
|
|
What is in class crinoidea? |
Sea lilies and feather stars |
|
|
|
Which class of Echinodermatas is the most primitive? |
Class crinoidea |
|
|
|
What are the four unique characteristics of phylum chordata? |
1)dorsal hollow nerve tube 2)notochord 3)pharayngeal slits or pouches 4)postanal tail |
|
|
|
What was phylum chordata named after? |
The presence of a notochord |
|
|
|
What are pharyngeal slits? |
Series of openings in the pharyngeal region between digestive tract and outside of body. Some use for feeding while others use for gills |
|
|
|
What is the dorsal nerve cord? |
Central nervous system that is associated with the development of complex systems for sensory perception, integration, and motor responses |
|
|
|
What is the postanal tail? |
Supported by notochord or vertebral column |
|
|
|
What is in subphylum urochordata? |
Tunicates (sea squirts) |
|
|
|
What is the lifestyle of sea squirts? |
Sessile as adults. Larvae are free swimming. Can be solitary or colonial |
|
|
|
What is the body wall for subphylum urochordata and what is it like? |
Called the tunic. Appears gel like but is often tough. Translucent |
|
|
|
What does the body of subphylum urochordata possess? |
Two siphons for filter feeding |
|
|
|
What is in subphylum cephalochordata? Why are they so special? |
Lancelets. They possess all five characteristics of chordates |
|
|
|
What do lancelets look like? |
Elongate, latterly flattened and nearly transparent |
|
|
|
What is the lifestyle of lancelets? |
Poor swimmers that spend most of their time in a filter feeding position |
|
|
|
What is the atrium? |
Surrounds the pharayngeal region of the body of lancelets in subphylum cephalochordata |
|
|
|
What does subphylum cephalochordata have that aids in filter feeding? |
Food exits through the atriopore. Cirri initially sorts food particles |
|
|
|
Sexual functions of subphylum cephalochordata? |
Dioecious. External fertilization. (Gonads bulge into the atrium. Gametes are shed into atrium and leave through the atriopore) |
|
|
|
What does all of subphylum craniata have in common? |
All possess a skull that surrounds the brain, olfactory organs, eyes, and an inner ear |
|
|
|
What are the two subclasses in subphylum craniata and what are the distinctions? |
Superclass agnatha-jawless fish Superclass gnathostomata- jawed mouth |
|
|
|
What are the two classes under superclass agnatha? |
Class myxini (hagfishes) Class petromyzontida (lampreys) |
|
|
|
Characteristics of hagfish? |
Head supported by cartilaginous bars. Lack vertebrae and retain the notochord (flexible). Four pairs of sensory tentacles surrounding their mouths and ventrolateral slime glands (on side towards belly). Found in cold-water marine habitats |
|
|
|
Where do hagfish live and what do they eat? |
Live buried in sand and mud. Feed on soft body invertebrates and scavenge dead and dying fish. (Will enter the fish through the mouth and eat the contents of the body, leaving only a sack of skin and bones) |
|
|
|
What mechanism do hagfish use for feeding and self protection? |
Knotting |
|
|
|
What do lampreys eat and where do they live? |
Adults prey on larger fish; larvae are filter feeders. Live in marine and freshwater environments in temperate regions. |
|
|
|
How do the lampreys eat? |
They use their sucker like lips to attach and then uses tongue to remove the scales. Teeth are present in the mouth. Have salivary glands with anticoagulant |
|
|

What animal was preying on this fish? |
Lamprey |
|
|
|
What are the three extant classes in superclass gnathostomata? |
Chondrichthyes-cartilaginous sarcopterygii-lobe finned actinopterygii-ray finned |
|
|
|
What are the cartilaginous fish that are in class Chondrichthyes? |
Sharks, skates, rays, and ratfishes |
|
|
|
Which class is subclass elasmobranchii? |
Chondrichthyes |
|
|
|
What is in subclass elasmobranchii? |
Sharks, skates, and rays |
|
|
|
What type of skin and teeth do sharks have? |
Tough skin with dermal placoid scales. Teeth are modified placoid scales. |
|
|
|
How do the largest live sharks eat? |
They are filter feeders and use pharyngeal - arch modifications to strain plankton |
|
|
|
Which sharks are the fiercest and most feared? |
Great white and mako |
|
|
|
Which shark is the largest and how does it feed? |
Whale shark and it filter feeds |
|
|
|
What is in subclass holocephali? |
Ratfish |
|
|
|
Description of a rat fish? |
Large head with small mouth surrounded by large lips. Has modified teeth that look like large plates for crushing the shells of mollusks. Has operculum which is a gill cover |
|
|
|
What is in class sarcopterygii? |
Lobe finned fish that have muscular lobes associated with their fins and usually use lungs in gas exchange |
|
|
|
What class does the lung fish belong to? |
Class sarcopterygii |
|
|
|
What is aestivation and which animal uses it? |
A low energy state used by lung fish to survive a drought |
|
|
|
What class does coelacanths belong to? |
Sarcopterygii |
|
|
|
What are coelacanths called? |
Living fossils |
|
|
|
What is in class actinopterygii? |
Ray finned fish that lack muscular lobes. |
|
|
|
What do ray finned fish posses that other fish don't? |
Swim bladders |
|
|
|
What is a swim bladder? |
Gas filled sacs along the dorsal wall of the body cavity that regulates buoyancy |
|
|
|
What class do sturgeons belong to? |
Class actinopterygii |
|
|
|
Which fish do caviar come from? |
Sturgeons |
|
|
|
Which class do paddlefish is belong to? |
Class Actinopterygii |
|
|
|
What is teleosts? |
Modern bony fish |
|
|
|
What is special about teleosts? |
They under went adaptive radiation and now have over 24,000 species |
|
|
|
What are gill rakers? |
Found in Herring, paddlefish, and white sharks. Used to filter feed |
|
|
|
What is a lateral line system? |
Consist of sensory pits in the epidermis of the skin that connect two canals that run just below the epidermis. It can detect water currents common movement of predators / prey, and low frequency sounds. |
|
|
|
What is electroreception? |
Detection of electrical Fields the fish or other organisms generate. This is highly developed and rays and sharks. |
|
|
|
True or false: most fishes are oviparous. |
True |
|
|
|
What does oviparous mean? |
Lay eggs outside of the body. Eggs develop outside of the body. |
|
|
|
What are the two important series of evolutionary events during the evolution of bony fishes? |
Evolutionary explosion about a hundred and fifty million years ago that resulted in the vast majority of modernity teleosts. Evolution of terrestrialism. |
|
|
|
What does the evolution of terrestrialism mean? |
Presidents of functional lungs in Lung fishes has led to the suggestion that lung fish lineages may have been ancestral to Modern terrestrial vertebrates |
|
|
|
What is tiktaalik and why is it important? |
A fossil that possessed many tetrapod characteristics. First sarcoptergyian fossil to show evidence of a pectoral girdle and a freely movable neck |
|
|
|
What does class amphibia mean? |
Having a double life. This implies that amphibians either move back and forth between water and land or live on stage in their lives in water and another on land |
|
|
|
What is included in class amphibia? |
Frogs, toads, salamanders, and caecilians |
|
|
|
What is ichthyostega and why is it important? |
A fossil that has been influential in formulating ideas regarding the ancestral animals of stegocephalians looked like. Loss of cranial bones and appearance of a mobile neck. Loss of opercular bones. Reduction of the notochord and replaced with a more rigid vertebral column. Four muscular limbs with discrete digits. Presence of sacral vertebra that fused the vertebral column and the pelvis |
|
|
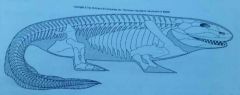
Which important fossil is this? |
Ichthyostega |
|
|

Which important fossil is this? |
Tiktaalik |
|
|
|
Zoologists agree that the extant amphibians are closely related to whom? |
Amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) |
|
|
|
What is in order gymnophiona under class amphibia? |
Caecilians that are worm-like burrowers that feed on worms and other invertebrates |
|
|
|
Why can't caecilians dry out? |
Because the majority of their respiration occurs Across the Skin So the skin must remain moist |
|
|
|
Why can't caecilians dry out? |
Because the majority of their respiration occurs Across the Skin So the skin must remain moist |
|
|
|
What is in order caudata of class amphibia? |
Salamanders Posses a tail throughout life and both pairs of legs (when present) that are relatively unspecialized |
|
|
|
What does caudata mean? |
"Tail & to bear" |
|
|
|
What is in order anura of class amphibia? |
Frogs and toads |
|
|
|
What does anura mean? |
"Without a tail" |
|
|
|
What is a urostyle and which animals posses it? |
Frogs and toads have them. Adults lack tails and caudal vertebrae that fuse into a rodlike structure |
|
|
|
What are the larval stages called for frogs and toads? |
Tadpoles that have well developed tails |
|
|
|
What type of skin do toads have? |
Bumpy dry skin |
|
|
|
What family do toads belong to? |
Bufonidae |
|
|
|
What type of skin do frogs have? |
Smooth and moist skin |
|
|
|
What family do frogs belong to? |
Family ranidae |
|
|
|
Which animals have granular glands and what are they used for? |
Frogs and toads. Grandular secretions aid in protection by keeping skin moist. Helps male cling to females during mating. Produce toxic chemicals to discourage predators |
|
|
|
What are chromatophores? |
Specialized pigment cells that are responsible for skin color and color changes |
|
|
|
What type of respirations do amphibians use? |
Cutaneous, which is used more often than not. Buccopharyngeal accounts for 1-7% of total gas exchange |
|
|
|
What is the disadvantage of the respirations used by amphibians? |
Contributions to total gas exchange is relatively constant. Meaning they cannot maintain a high level of activity for a long time. They cannot increase their respirations |
|
|
|
How do amphibians maintain body temp? |
They are ectothermic, meaning they depend on external heat sources to maintain body temperature |
|
|
|
Salamanders rely on what for courtship and mating? |
Olfactory and visual cues |
|
|
|
Anurans rely on what for courtship and mating? |
Male vocalizations and tactile cues |
|
|
|
When anurans find a suitable mate what do they do? |
Go into amplexus which is where the male stays attached to a females back |
|
|
|
What is an advertisement call used by anurans? |
Used the attract females to breeding area and announce to other males that a given territory is occupied |
|
|
|
What is a release call used by anurans? |
Used to inform a partner that a frog is incapable of reproducing |
|
|
|
What is a defense call used for by anurans? |
Used by both sexes in response to pain or being seized by a predator |
|
|
|
What is the deadly fungus responsible for disappearing numbers of amphibians? |
Chytridomycosis. Affects the skin by causing roughing and ulceration |
|
|
|
Which classes are included in the monophyletic lineage amniota? |
Reptilia, aves, and mammalia |
|
|
|
What is the monophyletic lineage amniota characterized by? |
The presence of an amniotic egg |
|
|
|
Which monophyletic lineage broke ties with water? |
Amniota |
|
|
|
The amniotic eggs of reptiles and birds have.... |
Leathery or hard shells to protect embryo. Albumen to cushion and provide moisture and nutrients to the embryo. And a yolk to supply food to the embryo |
|
|
|
What is synapomorphy? |
A shared derived characteristic |
|
|
|
What is the major synapomorphy that distinguishes reptiles, birds, and mammals from other vertebrates? |
The amniotic egg |
|
|
|
Which class does snyapsida lead to? |
Mammals |
|
|
|
Which class does diapsida lead to? |
Reptilia |
|
|
|
Which characteristics unite birds with reptiles? |
A single occipital condyle. Single ear ossicle. Lower jaw structure. |
|
|
|
What is The Reptilian ear bone? |
Stapes |
|
|
|
What are the three ear bones of mammals? |
Stapes, incus, and malleus |
|
|
|
What is in class reptilia order testudines? |
Turtles |
|
|
|
What is a carapace? |
The dorsal portion that forms from a fusion of vertebrae, expanded ribs, and bones in the dermis of the skin of a turtle. The shell. |
|
|
|
What is a plastron? |
The ventral portion that forms from bones of the pectoral girdle and dermal bone of the turtle |
|
|
|
What kind of mouth do turtles have? |
Keratinized beak rather than teeth |
|
|
|
How many cervical vertebrae do turtles have? |
8 |
|
|
|
Do turtles care for their young? |
No they lay large hatches of eggs and then leave |
|
|
|
What is in class reptilia order crocodilia? |
Alligators, crocodiles, gharials, and caimans |
|
|
|
What type of selection do crocodilians have? |
Stabilizing because they haven't changed much over their 170 million year existence |
|
|
|
What is a secondary palate and who has it? |
The secondary palate separates the nasal and mouth passageways in crocodilians |
|
|
|
What kind of reproduction and parental care do crocodiles have? |
Oviparous and display parental care of hatchlings that parallels that of birds |
|
|
|
How can you tell the difference between an alligator and a crocodile? |
Alligator jaw- U Crocodile jaw- V |
|
|
|
What is in class reptilia order sphenodontida? |
Tuataras. Live in new zealand. Two rows of teeth on upper jaw and single row on lower jaw to produce a shearing bite that can decapitate a small bird |
|
|
|
What is in class reptilia order squamata? And what are the two suborders? |
Suborder sauria-lizards Suborder serpentes-snakes |
|
|
|
What type of reproduction do most lizards |
Oviparous |
|
|
|
Characteristics of a gecko? Which sub order is it included in? |
Nocturnal. Makes clicking vocalizations. Eyes with pupils adapted for night vision. Adhesive discs on their digits that Aid in clinging to trees and walls. Suborder Sauria. |
|
|
|
Characteristics of iguanas? Which suborder is it included in? |
Robust bodies with short necks and distinct heads. Includes the marine iguanas of the Galapagos Islands and the flying dragons of Southeast Asia. Suborder Sauria |
|
|
|
Characteristics of chameleons? And which sub order are they included in? |
Live mainly in Africa and India. Adapted to arboreal Lifestyles and use long sticky tongue to capture insects. Use chromatophores to change color in response to illumination temperature or behavioral state. Suborder Sauria |
|
|
|
What are the only two venomous lizards? |
Gila monsters and Mexican bearded lizards |
|
|
|
How does the Gila monster in Mexican bearded lizard use their venom? |
Venom is released into grooves on the surface of teeth and introduced to the prey as the lizard chews |
|
|
|
Which snakes give birth to live young? |
New World vipers, boas, and cobras |
|
|
|
All Reptiles periodically shed the outer, epidermal layer of skin in a process called? |
Ecdysis |
|
|
|
The tongues of which two animals in class reptilia are non protrusible? |
Turtles and crocodilians |
|
|
|
Which snakes possess hollow fangs? |
Vipers |
|
|
|
How does a neurotoxin work and give an example of snakes that use it. |
Nero toxins attach to nerve centers and cause respiratory paralysis. Coral snakes, cobras, and sea snakes. |
|
|
|
How does a hemotoxin work and give an example of a snake that has it. |
Hemotoxins break up blood cells and attack blood vessel Linings. Vipers |
|
|
|
Where does gas exchange occur for snakes? |
Across internal lungs |
|
|
|
What type of temperature regulation do snakes have? |
Ectothermic |
|
|
|
True or false: temperature determines sex for snake eggs. |
True |
|
|
|
What are the adaptations for flight in class aves? |
Appendages modified his wings. Feathers. Endothermy. High metabolism. Bones are lightened by numerous air pockets |
|
|
|
Which lineage did birds descend from? |
Ancient archosaurs |
|
|
|
Birds are most closely related to whom? |
Therapods from the saurischian lineage |
|
|
|
True or false: feathers predate flight. |
True |
|
|
|
What did early feathers provide? |
Insulation in thermoregulation. Water repellency. Courtship devices. Camouflage. Balance while running. |
|
|
|
What is archaeopteryx and why it is important? |
A pigeon sized fossil that had characteristics of both dinosaurs and birds. Shows the main line between reptiles and birds |
|
|
|
How many orders of birds are there? |
31 orders |
|
|
|
What is in class aves order ciconiiformes? |
Herons, egrets, shorts, and wood ibises |
|
|
|
What is in class aves order anseriformes? |
Ducks, geese, and swans |
|
|
|
What is in class aves order falconiformes? |
Vultures, Hawks, Eagles, Osprey, and Falcons |
|
|
|
What is in class aves order galliformes? |
Grouse, Quail, pheasants, and turkeys |
|
|
|
What is in class aves order cuculiformes? |
Roadrunners and cuckoos |
|
|
|
What is in class aves order columbiformes ? |
Pigeons, doves, and sand grouse |
|
|
|
What is in class aves order strigiformes? |
Owls |
|
|
|
What is in class aves order passeriformes? |
Songbirds. Pretty birds. Swallows, larks, crows, titmice, nuthatches, and many more |
|
|
|
What is plumage? |
The covering of feathers on a bird. |
|
|
|
What are the two primary functions essential for flight from feathers? |
Form the flight surface that provides lift an 8N steering. Prevent excessive heat loss |
|
|
|
What all are feathers used for? |
Flight, roles in courtship, incubation, and Waterproofing. |
|
|
|
What are the two types of feathers? |
Pennaceous and plumulaceous |
|
|
|
What are pennaceous feathers? |
Flattened, tightly closed for those that create aerodynamic surfaces. This includes the flight and contour feathers |
|
|
|
Where are flight feathers? |
Line the tip and trailing edge of the wing and are asymmetrical |
|
|
|
Where are contour feathers? |
Line the body and cover the base of the flight feathers; provide waterproofing, insulation, and streamlining. Are usually symmetrical. |
|
|
|
What are plumulaceous feathers? |
Feathers that have a rudimentary shaft to which a wispy tuft of barbs and barbules is attached. Includes insulating down feathers. These feathers are periodically molted. |
|
|
|
What are bird bills and tongues modified for? |
A variety of feeding habits and food sources |
|
|
|
What are bird bills used for? |
Feeding, preening, nest building, courtship displays, and defense |
|
|
|
Which organ in the bird allows for quick ingestion of large quantities of food? |
Crop |
|
|
|
What are the two regions of the bird's stomach and what do they do? |
Proventriculus-secretes gastric juices that initiate digestion Ventriculus (gizzard)-has muscular walls to crush hard materials |
|
|
|
What gives an owl the element of surprise? |
Their flight feathers have fluted tips |
|
|
|
What are auriculars and which animal has them? |
The owl has loose feathers that cover the external ear openings |
|
|

Which important fossil is this? |
Archaeopteryx |
|
|
|
True or false: vision is important for most birds and olfaction is a minor role. |
True |
|
|
|
What are the mating behaviors of birds? |
Establishing territories, find inmates, constructing Nest, incubating eggs, and feeding young. All are oviparous |
|
|
|
How does a male woodpecker attract a female? |
He drums on trees |
|
|
|
How does a male ruffed grouse attract a female? |
He fans his wings on logs and creates a sound that can be heard for miles |
|
|
|
How does a crane attract a female? |
A courtship dance that includes stepping,bowing, stretching, and jumping displays |
|
|
|
Are most birds monogamous or polygamous? |
Monogamous |
|
|
|
What birds pair for life? |
Swan and penguin |
|
|
|
What does polyandrous mean? |
It's rare. When a female bird mated with multiple males in one breeding season |
|
|
|
What is a group of eggs laid and chicks by a female bird called? |
Clutch |
|
|
|
What is an altricial offspring? |
Birds that are entirely dependent on their parents upon hatching and are often naked. |
|
|
|
What are precocial young? |
Birds that are alert and Lively at hatching. Covered with down and can walk, swim, and feed themselves |
|
|
|
What is migration? |
Periodic round trips between breeding and non breeding areas. |
|
|
|
Why is migration beneficial? |
It allows Birds to avoid climatic extremes and to secure adequate food, shelter, and space throughout the year. Most are annual with nesting areas in the northern regions and wintering grounds in the south |
|
|
|
What influences migration? |
Resource utilization |
|
|
|
What are some examples of annual migrant Birds? |
Fly catchers, thrushes and hummingbirds |
|
|
|
What is a resident bird? |
A bird that does not migrate |
|
|
|
When did the age of mammals begin? |
Approximately 70 million years ago at the beginning of the tertiary period. Which conceited with the extinction of many reptilian lineages |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of pre-mammalian synapsids? |
lack hair, oviparous, Long Gate, ectothermic. |
|
|
|
What are therapsids? |
Synapsids that were successful in the middle of the Permian period. Tooth morphology similar to Modern mammals. Hind limbs directly beneath the body. Changes in size and shape of ribs suggesting the separation of the trunk and to thoracic and abdominal regions. Breathing mechanism similar to Modern mammals. |
|
|
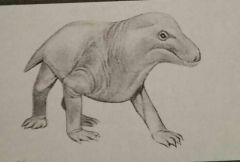
What is this? |
A cyodent therapsid |
|
|
|
When were most of the successful therapsids wiped out? |
During a major extinction at the Permian - triassic boundary. Only a few cyodent therapsids survived along with the archosaurs (dinosaurs, crocodiles, and eventually birds) |
|
|
|
Towards the end of the Jurassic period cyodonts became increasingly what? |
Smaller, probably nocturnal, and more mammal-like. began developing hair and endothermy. |
|
|
|
Which mammalian characteristics evolved during the Jurassic period. |
Teeth specialized to facilitate rapid food processing. Middle ear structure and changes in regions of the brain devoted to hearing and olfaction. First "true mammals" were present- had hair |
|
|
|
What is the chicxulub crater? |
Where a mass extinction occurred about 65 million years ago. Asteroid impact in Central America. Which began the age of mammals |
|
|
|
Characteristics of mammals? |
Hair, mammary glands, diaphragm, three middle ear ossicles, heterodont dentition, sweat glands, sebaceous and scent glands, four-chambered heart, and large cerebral cortex |
|
|
|
What is heterodont dentition? |
Different types of teeth |
|
|
|
What is homodont dentition? |
Same teeth |
|
|
|
What are the two living lineages of mammals? |
Subclass prototheria Subclass theria |
|
|
|
What is included in subclass prototheria? |
Montremes which are oviparous mammals |
|
|
|
What is included in subclass theria? |
Infraclass metatheria which is marsupial mammals. Infraclass eutheria which is placental mammals |
|
|
|
What is a marsupium? |
A pouch used by marsupials in infraclass metatheria in subclass theria in class mammalia |
|
|
|
What does subclass prototheria have that other mammals dont? |
They are oviparous and have a cloaca |
|
|
|
What is in infraclass metatheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Kangaroo, koala, etc. Viviparious, primitive placenta, and young are born early and then carried in a marsupial pouch |
|
|
|
What does Viviparious mean? |
Give birth to live young |
|
|
|
What is in order proboscidea of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? |
Elephants. Born at Advanced stage of development. Long muscular trunk. Second in size or modified into tusks. Has placenta. |
|
|
|
What is in order xenarthra of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Anteaters and sloths. Incisors and canines absent. Hind foot has four toes. Fore foot has two or three toes period limbs specialized for climbing or digging. |
|
|
|
What is in order eulipotyphla of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Hedgehogs and mice. Small mammals with long, narrow mobile snouts. feed on insects and earthworms. |
|
|
|
What is in order chiroptera of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Bats. Found everywhere but especially abundant in the tropics. Bones of the arm and hand are a long and slender. Most are insectivores; some are fruit eaters, Fish Eaters, and blood feeders. Second largest mammalian order |
|
|
|
What is a bat with a long tongue eat? |
Nectar |
|
|
|
What does a bat with large ears eat? |
Insects and uses echolocation |
|
|
|
What do bats with folds on the face eat? |
Fruit. The folds direct the juice of the fruit to the mouth |
|
|
|
What is order carnivora of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Bears, seals, wolves, dogs, cats, leopards, raccoon's, etcetera. Predatory mammals. Highly developed sense of smell and large Brain case. Canines well-developed develop. |
|
|
|
What is in order perissodactyla of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Odd toed ungulates. Hoofed; axis of support through the third digit. Large molars and premolars. Primarily grazers |
|
|
|
What is in order artiodactyla of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Pronghorn, giraffe, hippo, dear, camel. Hoofed; axis of support between 3rd and 4th digits. Digits 1, 2, and 5 reduced or lost. Primarily grazing animals (pigs are the exception) |
|
|
|
What is in order cetacea of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Whales and dolphins. Streamlined and nearly hairless. Insulated by blubber. External naris on top of skull. |
|
|
|
Examples of toothed whales: |
Beaked whales, narwhals, sperm whales, Dolphins, porpoises and killer whales |
|
|
|
Examples of toothless whales: |
Right whales, gray whales, blue whales and humpback whales |
|
|
|
What is baleen? |
Used to filter feed by toothless whales |
|
|
|
What is in order lagomorpha of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Includes rabbits. Incisors our ever-growing and slowly worn down by feeding on vegetation. Possess a diastema. Fenestrated skull. Corophagy |
|
|
|
What does Fenestrated mean? |
Lattice like organization of bone and skull. makes the skull lighter |
|
|
|
What does diastema mean? |
Gap between incisors and molars |
|
|
|
What does Corophagy mean? |
Consumes their own feces to ensure they extract all nutrients |
|
|
|
What is in order rodentia of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Beavers and chipmunks. Largest mammalian order. have ever growing incisors |
|
|
|
What is in order primates of infraclass eutheria of subclass theria of class mammalia? Characteristics? |
Monkeys, baboons Kama chimpanzees, humans, etc. Adaptations for increased agility and arboreal habitats. Omnivores. Unspecialized teeth. Grasping digits with nails |
|
|
|
What is pelage, what does it include? |
A coat of hair that includes guard hairs and under hairs |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of guard hairs? |
Long and protect the skin |
|
|
|
What are under hairs? |
Dense insulating hairs. Which are modified into vibrissae |
|
|
|
What is vibrissae? |
Whiskers |
|
|
|
What are true horns? |
They consist of a covering of keratin and other proteins surrounding a core of live bone. Continue to gray throughout organism's lifetime (except pronghorn) |
|
|
|
What is ossicones? |
Bony projections that are covered with furred skin. Are not shed. Example: giraffe |
|
|
|
What are antlers? |
When fully developed they are dead bone without a horn or skin covering. They shed and regrow every year. Example: moose |
|
|
|
What is a rhinoceros horn? |
Composed of keratin and grow continuously. No bony core |
|
|
|
What are scent or musk glands and where are they located? |
They secrete pheromones that are involved in defense, species and sex recognition, and territorial Behavior. Found around the face, feet, or anus of many mammals. |
|
|
|
What are mammary glands? |
Are functional in female mammals and are present, but non-functional in males. Probably derived from apocrine glands and usually contains substantial fatty deposit. Monotremes have mammary glands that lack nipples |
|
|
|
Describe an incisor: |
chisel like amd used for gnawing or nipping |
|
|
|
Describe a canine tooth: |
Long, stout, and conical; used for catching, killing, and tearing prey |
|
|
|
Describe a premolar tooth: |
Positioned next to canines; used for chewing |
|
|
|
Describe a molar tooth: |
Broad chewing surfaces |
|
|

Phylum & class? |
Phylum Echinodermata Class asteroidea |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? Class? |
Brittle star Phylum Echinodermata Class ophiuroidea |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? Class? |
Basket star Phylum Echinodermata Class ophiuroidea |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? Class? |
Sea dollar. Sand biscuit. Sea urchin Phylum Echinodermata Class Echinoidea |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? Class? |
Sea urchin Phylum Echinodermata Class Echinoidea |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? Class? |
Sea cucumber Phylum Echinodermata Class holothuroidea |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? Class? |
Sea cucumber Phylum Echinodermata Class holothuroidea |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? Class? |
Feather star Phylum Echinodermata Class crinoidea |
|
|
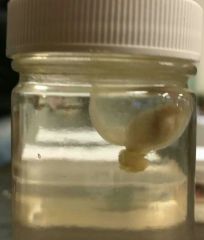
Identify. Phylum? subphylum? |
Tunicate (sea squirt) Phylum chordata Subphylum urochordata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? |
Lancelet Phylum chordata Subphylum cephalochordata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? |
Lancelet Phylum chordata Subphylum cephalochordata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Hagfish Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Subclass agnatha Class myxini |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Lamprey Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Subclass agnatha Class petromyzontida |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Dog fish shark Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class Chondrichthyes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Bonnet head shark Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class Chondrichthyes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Ray Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class Chondrichthyes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Skate Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class Chondrichthyes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
African lung fish Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class sarcopterygii |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Flounder Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class actinopterygii |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Perch Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class actinopterygii |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Catfish Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class actinopterygii |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Alligator Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order crocodilia |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Copperhead Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order serpentes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Rattlesnake Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order serpentes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Bull snake Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order serpentes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Great plains skink Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order squamata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Collard lizard Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order squamata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Spiny crevice lizard Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order squamata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Horned lizard Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order squamata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Alligator skull Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order crocodilia |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Red eared slider Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order testudines |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Snapping turtle Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order testudines |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Ornate box turtle Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class reptilia Order testudines |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Caecilian Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class amphibia Order gymnophiona |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? Family? |
Leopard frog Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class amphibia Order anura Family ranidae |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? Family? |
Bull frog Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class amphibia Order anura Family ranidae |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? Family? |
Great plains toad Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class amphibia Order anura Family bufonidae |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? |
Woodland salamander Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class amphibia Order caudata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Tiger salamander Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class amphibia Order caudata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Scaled quail Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order galliformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Lesser Prarie chicken Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order galliformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Greater road runner Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order cuculiformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
American coot Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order gruiformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Rock dove (pigeon) Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order columbiformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Mourning dove Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order columbiformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Barn owl Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order strigiformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Burrowing owl Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order strigiformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Short eared owl Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order strigiformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Blue Jay Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order passeriformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Red winged black bird Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order passeriformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Bullocks oriole Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order passeriformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Lark sparrow Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order passeriformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Scissor tailed fly catcher Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class aves Order passeriformes |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Duck bill platypus Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order monotremata |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Virginia opposum Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order didelphimorphoa |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Star nosed mole Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order eulipotyphla |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Mole Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order eulipotyphla |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Shrew Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order eulipotyphla |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Pallid bat Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order chiroptera |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Red bat Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order chiroptera |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Cotton tail rabbit Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order lagomorpha |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Cotton rat Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order rodentia |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Kangaroo rat Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order rodentia |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Thirteen lined ground squirrel Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order rodentia |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Wood rat Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order rodentia |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Fox squirrel Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order rodentia |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Pocket gopher Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order rodentia |
|
|
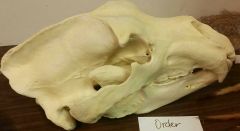
Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Grizzly bear skull Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order carnivora |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Weasel with summer coat Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order carnivora |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Kit fox Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order carnivora |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Mountain lion skull Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order carnivora |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Striped skunk Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order carnivora |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Armadillo Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order xenarthra |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
White tail deer skull Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order artiodactyla |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Goat skull Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order artiodactyla |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Baleen from a whale Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order cetacea |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Porpoise skull Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order cetacea |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? which is male and which is female? |
Gorilla skull Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order primates Left-female. Right-male |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Chimpanzee skull Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order primates |
|
|

Identify. Phylum? subphylum? superclass? Class? Order? |
Baboon skull Phylum chordata Subphylum craniata Superclass gnathostomata Class mammalia Order primates |
|

