![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Membranes Definition |
membranes that surround the organelle or cell itself |
|
|
Cell Membrane Big Picture |
all membranes in the cell have a shared/same basic structure, vary by tissue type, and surrounding |
|
|
Fluid-Mosaic Model |
1) cell membrane is made up of different molecules associated with each other 2) cell membranes are flexible & allow for molecules move around within membrane > fluid |
|
|
Molecule Type & Function |
Lipids -phospholipids: forming a separating layer -cholesterol: allows for stability of membrane Proteins: -attachment protein: allows for attachment of cell/organelle -receptor protein: send/receive messages -channel proteins: allow for transport/movement of molecules/ions across membrane -active transport protein: allow for transport/movement of molecules/ions across membrane -junction proteins: allow for connections to be made between membranes -glyco proteins: allow cell/organelle recognition -enzymes: enzymatic activities > aid chemical reactions
|
|
|
Concentration Grading |
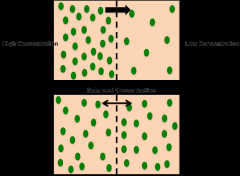
-will eventually reach equilibrium -gradient: any physical difference between adjoining regions ex: temp, conc) -passive transport relies upon the existence of concentration gradients allow for diffusion Diffusion: movement of particles from high > low concentration (does not use energy) Equilibrium: no difference between spaces equilibrium > gradient disappears in resource to diffusion/osmosis osmosis: movement of water from low concentrations |
|
|
Rate of Diffusion Influenced By |
1) concentration difference 2) temperature 3) permeability |
|
|
Transport Across Membrane |
3 main ways 1) passive transport 2) active transport 3) endocytosis/exocytosis |
|
|
Passive Transport |
process where molecules, ions, or other substances move across a membrane without using energy (relies upon diffusion/osmosis) a) simple diffusion: no proteins involved, particles move across lipid bilayer b) facilitated diffusion: proteins helping/faciliating, channels proteins or carrier proteins |
|
|
Active Transport |
process where molecules, ions, and other substances move across a membrane using energy (in form of ATP) (moves against concentration gradient > establishes concentration) |
|
|
Endocytosis/Exostosis |
process where the membrane to envelope or surround the particles creating a vesicle, that transports particles into/out of the cell |
|
|
Cell Theory Principles |
a) every living organism is made up of cells b) all cells arise/come from other cells |
|
|
Common Cell Functions |
-obtain energy -obtain nutrients -make proteins, and other molecules -grow & repair -eliminate waste -reproduce -interact with other cells |
|
|
Cell Types |
Prokaryote: -lack most organelles -ribosomes -typically smaller -genetic material organized in nucleoid & plasmids -domains= bacteria & archaea -always unicellular Eukaryote: -have organelles -ribosomes -typically larger -genetic material organized in nucleus -domains= eukarya > animals, plants, fungi, protists -unicellular or multicellular |
|
|
DRAW PROKARYOTE |
LOOK AT NOTES, YELLOW POST IT |
|
|
DRAW ANIMAL CELL |
LOOK AT NOTES, YELLOW POST IT |
|
|
Contrast Plant & Animal Cell |
Plant: Cell wall & Chloroplast, no intermediate filament of cytoskeleton, central vacuole, plasmodesmata, no lysomes, or centrosomes Animal: no cell wall or chloroplast, intermediate filament of cytoskeleton, no central vacuole, no plasmadesmata, lysomes, and centrosomes |
|
|
DRAW CHLOROPLAST |
LOOK AT YELLOW STICKY NOTE IN NOTES |
|
|
DRAW MITOCHONDRION |
LOOK IN NOTES, YELLOW POST IT |
|
|
How is protein made? |
When the cell needs to make protein, mRNA is created in nucleus, and sent to ribosomes. The ribosomes start protein synthesis and a protein is made. |
|
|
Eukaryotes Big Picture |
1) extremely diverse
-across organisms -within multi-cellular organisms 2) organelles -membrane enclosed structures |
|
|
Things A Cell Has To Do: |
-genetic control -manufacturing, distribution, and breakdown -energy processing -structural support, movement, and communication between cells |
|
|
Endosymbiont Theory |
explanation for the evolution of chloroplasts and mitochondria |
|
|
Life & Energy Flow Big Picture |
life is a series of chemical reactions, which involves energy |
|
|
Chemical Reactions Definition |
processes that form or break chemical bonds |
|
|
Chemical Bonds |
all chemical reactions use energy |
|
|
Types of Chemical Reactions & Big Picture |
Exergonic: reactants have more energy than products, energy going out (image #1) Endergonic: reactants have less energy than products, energy coming in Big Picture: cell metabolism= collections of chemical reactions in a cell |
|
|
Coupled Reaction |
LOOK AT NOTES, YELLOW POST IT |
|
|
Cells Need A Way To: |
-collect and move energy from exergonic reactions -provide the energy for endergonic reactions |
|
|
Energy Carrier Molecules Are Molecules That: |
1) move and collect energy from exergonic Rxns 2) deliver energy to the endergonic Rxns |
|
|
ATP Circle |
LOOK AT NOTES, YELLOW POST IT |
|
|
Enzymes |
-proteins -catalyze (speed up) Rxns -are not actually consumed or permanently altered -usually Rxn specific -lots of enzymes -some enzymes use "helper" coenzymes -structure determines function -can build & break bonds -enzyme activity can be influenced by -temperature -pH }environment -inbibitors |
|
|
Active Site |
DRAW IT, YELLOW POST IT |
|
|
Why do we care about Photosynthesis? |
-supports life as we know it (food & oxygen) -bioinspiration (energy conservations; solar cell engineering) |
|
|
Big Picture of Photosynthesis |
-plants (other photosynthesizers) harvesting suns energy and placing that energy in the form of chemical bonds |
|
|
Equation For Photosynthesis |
6CO2 + 6H20 > 6O2 + C6H12O6 |
|
|
Two Parts of Photosynthesis |
1) Light Rxns -happens in thylakoids (chloroplast) -H20 used -02 released 2) Calvin Cycle -occurs in stroma (fluid in chloroplast) -CO2 used -sugar released |
|
|
Groups of Photosynthesizers |
1) most plants 2) some protists (algae) 3) cyanobacteria (bacteria) |
|
|
Leaf Big Picture |
YELLOW POST IT |
|
|
? |
? |

