![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sacculation is charactaristic feature of...
|
the large intestine
|
|
|
the upper portion of the duodenum has numerous clusters of mucous cells called...
|
brunner's glands
|
|
|
insulin is secreted by which type of pancreatic cells?
|
beta cells
|
|
|
carboxypeptidase is an __________ pancreatic enzyme
|
inactive
|
|
|
the most common activator for pancreatic enymes is
|
trypsin
|
|
|
what stimulates the stomach to secrete hydrochloric acid?
|
gastrin
|
|
|
bile is made of...
|
fatty acids & cholesterol
|
|
|
what artery provides vascularization to the cecum and appendix?
|
iliocolic artery
|
|
|
dilation of rectal veins are called....
|
hemorroids
|
|
|
what is an active proteolytic enzyme with a precursor secreted by chief cells?
|
pepsin
|
|
|
is aldosterone a mineralocortioid or a glucocorticoid?
|
mineralocorticoid
|
|
|
What is secreted in urine
|
urea, calcium, phosphates,sodium, water
|
|
|
the left colic artery is a branch of which artery?
|
Inferior mesenteric artery
|
|
|
during chronic stress the body secretes.....
|
corticosteroids
|
|
|
what forms the renal pyramids?
|
collecting tubules
|
|
|
the superior mesenteric vein joins the splenic vein to form the ....
|
hepatic vein
|
|
|
the round ligament of liver was the________________ before birth
|
left umbilical vein
|
|
|
the common bile duct joins with the main pancreatic duct to form the
|
ampulla of vater
|
|
|
rugae are features of the
|
stomach
|
|
|
parsympathetic stimulation to the stomach leads to
|
increased HCL secretion
|
|
|
the styloglossus muscsle is innervated by which cranial nerve?
|
CN XII
|
|
|
A digestive enzyme found in saliva is....
|
amylase
|
|
|
what type of epithelium forms the mucosa of the esophagus?
|
stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
the muscle layer of the stomach has____ layers
|
3
|
|
|
epigastric pain is relieved upon eating in...
|
a gastric ulcer
|
|
|
the main source of blood supply to the stomach is
|
the celiac trunk
|
|
|
what converts pepsinogen into pepsin?
|
HCl
|
|
|
responsible for the majority of gastric ulcer cases is
|
H.pylori
|
|
|
a cell that secretes 5 hydroxytryptamine is
|
enterochromaffin cell
|
|
|
gastric cancer tends to occur in the...
|
greater curvature
|
|
|
what stimulates the contraction of the gallbladder?
|
1 presence of fat in stomach or duodenum
2 enterogastrone reflex |
|
|
the smallest lobe of the liver is the
|
caudate lobe
|
|
|
hepatic veins drain blood into the...
|
IVC
|
|
|
a hypoglycemic agent
|
insulin
|
|
|
hepatocytes secrete
|
1 bile
2 cholesterol 3 albumin 4 prothrombin |
|
|
insulin is secreted by
|
beta cells
|
|
|
capsule of glisson is part of the...
|
liver
|
|
|
majority of gallstones are made of
|
cholesterol
|
|
|
a powerful proteolytic enzyme
|
amylase
|
|
|
porta hepatis does not have
|
hepatic veins
|
|
|
blood in renal vein drains into the
|
IVC
|
|
|
the renal cortex houses
|
glomeruli
|
|
|
most toxins in the blood are retained for release into the urine at the _________ of the nephron
|
convoluted tubules
|
|
|
urine in the renal plevis drains immediately in the
|
ureter
|
|
|
the kidney secretes...
|
erythropoietin & renin
|
|
|
kidney stone is typically the size of
|
a grain of rice
|
|
|
the urethra is connected to
|
the urinary bladder
|
|
|
the renal artery is a branch of the
|
abdominal aorta
|
|
|
the superior pole of the right kidney is in contact with the
|
liver
|
|
|
collecting tubules form the
|
renal pyramids
|
|
|
most common renal disease is
|
pyelonephritis
|
|
|
the________ kidney is higher
|
left
|
|
|
a normal individual has how many nephrons?
|
one million
|
|
|
the most common waste product in urine is
|
urea
|
|
|
promotes the formation of kidney stones
|
protein intake
|
|
|
renal veins drain into the
|
IVC
|
|
|
a hormone that influences the function of the kidney
|
antidiuretic hormone
|
|
|
normally released in urine
|
sodium chloride
|
|
|
________ are not found in the adrenal glands
|
parasympathetic fibers
|
|
|
chronic stress increases secretion of
|
cortisol
|
|
|
layers of the adrenal cortex
|
zona reticularis
zona fasciculata zona glomerulosa |
|
|
hormone relased in acute stress
|
adrenalin (epinephrine/norepinephrine_
|
|
|
what type of gland is the adrenal gland?
|
endocrine gland
|
|
|
adrenal glands has:
|
capsule
cortex medulla |
|
|
adrenal gland regulates
|
1 electrolyte balance
2 carb metabolism 3 protein metabolism 4 fat metabolism 5 ph balance |
|
|
superior part of stomach is
|
fundus
|
|
|
attached to the greater curvature is
|
the greater omentum
|
|
|
primary source of blood supply to the stomach is
|
the celiac trunk
|
|
|
the innermost muscular layer of the stomach is the
|
oblique
|
|
|
intrinsic factor is secreted by which gastric cell
|
parietal cells
|
|
|
in the presence of acid, which enzyme is formed?
|
pepsin
|
|
|
Defiency of __________ leads to pernicious anemia
|
Vitamin b12
|
|
|
sympathetic stimulation to the stomach leads to
|
decreased peristalsis
|
|
|
which gastric secretion can regulate the diameter of gastric blood vessels?
|
5 hydroxytryptamine (seratonin)
|
|
|
parasympathetic nerves to the stomach are found in
|
the vagus nerve
|
|
|
the angular incisure is found in the _______ curvature of the stomach
|
lesser
|
|
|
gastrin trigger the release of
|
HCl
|
|
|
a hyperglycemic agent
|
glucagon
|
|
|
normal blood glucose level
|
90mg/100ml
|
|
|
largest and heaviest organ of body
|
liver
|
|
|
hepatic veins are not found in the _________,they begin in the liver and drain into the _________
|
porta hepatis
IVC |
|
|
rotaion of pancreas =
|
270 degrees
|
|
|
inuslin is a ______ agent, brings blood sugar____
|
hypoglycemic
down |
|
|
glucagon is ________ agent, it brings blood sugar _____
|
hyperglycemic
up |
|
|
blood sugar <60 =
|
hypoglycemic
|
|
|
blood sugar > 200
|
diabetic
|
|
|
blood supply of liver
|
celiac trunk
|
|
|
blood supply of pancreas
|
celiac trunk and superior mesenteric artery
|
|
|
In the ______ sympathetic controls mucous secretion and parasympathetic controls acid secretion
|
stomach
|
|
|
In the _______ the sympathetic controls acid secretion and the parasympathetic controls mucous secretion
|
duodenum
|
|
|
more lymph node aggregation in the ____ thand the _____ because ther bacteria is full blown in the _____
|
ileum
jejunum ileum |
|
|
what are the bacteria in the ileum called?
|
e.coli
|
|
|
vagus nerve ends at the
|
transverse colon
|
|
|
A CARDIA
AB FUNDUS AC BODY AD LESSER CURVATURE AE ANGULAR INCISURE B CARDIAC INCISURE BC PYLORIC SPHINCTR BD PYLORIC CANAL BE PYLORIC ANTRUM C ESOPHAGUS CA GREATER CURVATURE |
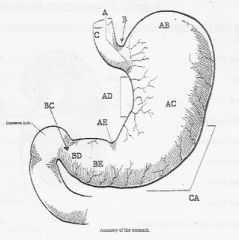
LABEL
|
|
|
A IVC
AB LEFT LOBE AC CAUDATE LOBE AD RIGHT LOBE AE PORTAL VEIN B GALLBLADDER BC COMMON BILE DUCT C QUADRATE LOBE CE HEPATIC ARTERY D FALCIFORM LIGAMENT |
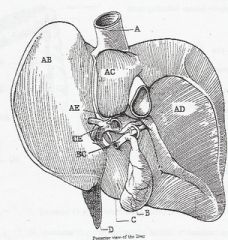
LABEL
|
|
|
A RENAL PYRAMID
AB RENAL PELVIS AC URETER B RENAL CAPSULE BC MINOR CALYX C MAJOR CALYX CD PAPILLA D RENAL SINUS DE RENAL COLUMN E RENAL CORTEX |
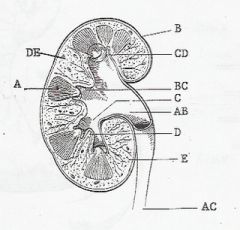
LABEL
|
|
|
A HAUSTRA
AB DESCENDING COLON AC TRANSVERSE COLON AD ASCENDING COLON AE APPENDIX B APPENDICES EPIPLOICEA BC RECTUM BD TENIA COLI C CECUM D SIGMOID COLON E ILEUM |
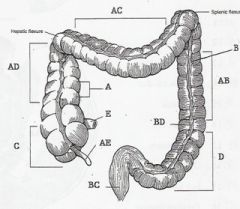
LABEL
|

