![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
myoplasticity |
changes in muscle structure as a result of change in function related to physical training. |
|
|
skeletal muscles are... |
amitotic |
|
|
amitotic |
doesn't undergo mitosis. |
|
|
satellite cells |
like a population of stem cells for muscles. Theycan reproduce. They help repair damaged or injured skeletal muscles. |
|
|
how skeletal muscles change in form is directly related to.. |
how you move them. |
|
|
do skeletal muscles change the number of muscle fibers? |
no. |
|
|
endurance training. |
long distance runners. Swimmers. Long distancecyclists. |
|
|
for endurance training.. how does the motor units respond. |
increased rate in which they are activated |
|
|
endurance training helps with.. but not.. |
longer times. not more weight. |
|
|
how do we tell if a person does endurance training.. |
increased level of oxidative enzymes |
|
|
what type of training is this: increased fatigue resistance |
endurance training. |
|
|
the blood vessel network for endurance training.. |
increased |
|
|
endurance training and use of fatty acids and non-glucose fuels for ATP production are... |
more efficient |
|
|
resistance/ strength training... what is their motor unit activation? |
moderate increase in frequency. |
|
|
strength training does what to force production? |
large increase |
|
|
what do you do with strength training? |
few repetitions. heavier weights. |
|
|
strength training causes (noticable/nonnoticable) |
noticeable. |
|
|
strength training... myofibrils and diameter of muscle fibers |
increase |
|
|
hypertrophy |
number of myofibrils and the diameter of the muscle fibers increase. |
|
|
strength training.. how does it change motor unit activation? |
Moderate increase in frequency of motor unitactivation and large increase in force production. |
|
|
how does your endurance respond to strength training? |
decreased endurance |
|
|
how does strength training change the proportion of mitochondrial proteins and blood supply to the skeletal muscle? |
decreased. with fiber enlargement. |
|
|
muscle atrophy |
decreased muscles. muscles and bones get weaker. |
|
|
sarcopenia |
loss of muscle mass |
|
|
disuse of skeletal muscles causes a... |
decrease in number of myofibrils and the size of fiber and decrease in oxidative enzymes. |
|
|
disuse results as a |
decline in both strength and endurance |
|
|
"Use it or lose it" has to do with |
skeletal muscles |
|
|
atrophy is a problem for.. |
bedridden individuals. or those who have lost the use of limbs. |
|
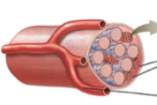
what type of physical training occurred? |
endurance training |
|
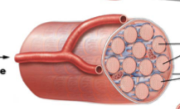
what type of physical training occurred? |
resistance training |
|
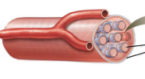
what type of physical training occurred? |
disuse. |
|
|
what physical training causes an increased number of blood vessels? |
endurance training |
|
|
what type of training causes an increased number of mitochondria and their proteins? |
endurance training |
|
|
what type of training causes increased number of myofibrils? |
resistance training |
|
|
what type of training causes increased diameter of muscle fiber and myofibrils? |
resistance training |
|
|
what physical training causes decreased oxidative enzymes? |
disuse |
|
|
what physical training causes decreased number of myofibrils and decreased diameter of muscle fibers? |
disuse |
|
|
fatigue |
the inability to maintain a given level of intensity during activity. |
|
|
depletion of key metabolites involved in ATP production can lead to . |
Muscular fatigue |
|
|
decreased availability of oxygen to muscle fibers can cause |
Muscular fatigue |
|
|
accumulation of some chemicals in the fiber (Ca++, ADP and Phospahte) can cause |
Muscular fatigue |
|
|
extreme heat, sweating in response to heat may cause electrolyte disturbances and cause |
Muscular fatigue |
|
|
recovery period: |
time after exercising to return to pre-exercise state. |
|
|
increased rate of breathing in the recovery period is called |
excess post exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) |
|
|
EPOC is called.. |
excessive post-exercise oxygen consumption |
|
|
what does EPOC do? |
allows the body to recover from exercise induced homeostatic imbalances... |
|
|
what all in included in exercise induced homeostatic imbalance? |
body temp intracellular and extracellular ion concentrations blood pH balances. |

