![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Deamination of Amino Acids |
Glutamic Acid (a.a.) →NAD, H20→a-Ketoglutaric acid (Carbs)+ NH4+ |
|
|
|
Catabolism |
Energy Yielding Metabolism |
|
|
|
Anabolism |
Biosynthetic Metabolism |
|
|
|
Amphibiotic Metabolism |
Can integrate catabolic at anabolic pathways to improve cell efficiency |
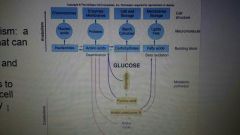
Occurs in Kreb's cycle and Glycolysis |
|
|
Glyceradehyde-3-Phosphate precursor for: |
Carbohydrates & Triglycerides |
Amphibolic Metabolism |
|
|
Pyruvic Acid, start point for: |
Gluconeogenesis and Amino Acid Synthesis |
Amphibolic Metabolism |
|
|
Acetyl CoA is condensed into? |
Hydrocarbon chains to form fatty acids Oxaloacetate and a-ketoglularate are involved in synthesis of some amino acids |
|
|
|
Glycogen Synthesis |
straight Chain is an a-1,4 linkage Branch is a-1,6 linkage |
GlyCogen is stored in liver and muscles |
|
|
Nitrogen Cycle (A LOT of Microbes involved) |
Nitrogen fixation: N2 to NH3 (ammonia)
Nitrification: NH4 → NO2- and NO3- (Nitrifying bacteria: E. Coli)
Ammonification: proteins → ammonia (deaminates)
De nitrification: Ammonia → Nitrates → N2 |
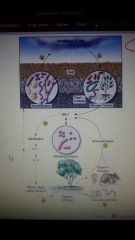
|
|
|
Photosynthesis |
602+12 H2O + Light Energy → C6 HI2 06 +6 02 + 6 H20 Photons visible light spectrum Chlorophylls, carotenoids, phycobilins Catabolic Reactions to Drive Anabolism |
|
|
|
Light Reactions |
Splits water & produces 02 as a byproduct
Absorbed light energy produces NADPH & ATP
Electron Transport produces NADPH
H+ flow produces ATP |
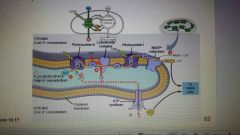
|
|
|
Calvin Cycle (Dark Rxns) 3 phases |
1. Carbon Fixation
2. Energizing C02 (reduction)
3. Regeneration of the C02 acceptor sugar |
|
|
|
what does the Calvin Cycle use to convert CO2 to sugar? Where does it occur? |
Uses ATP and NADPH
Occurs in stroma (fluid portion of Chloroplast) |
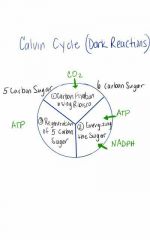
|
|
|
4 Main Elements/Nutrients Microbes Must Obtain (CHON) |
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen |
|
|
|
Microbial Cytoplasm when H20 is removed; is mainly made up of. . . |
50% Proteins (structural & functional molecules) |
|
|
|
2 Main Recylable Energy sources |
l. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids (Carbon) |
Lipids are hydrocarbons |
|
|
Autotroph (self-energy) |
Self Feeders use CO2 in inorganic form |
|
|
|
Heterotroph ("Not of self") |
Other-Feeders use Organic carbon in form of carbohydrate or lipids |
|
|
|
Energy sources for Microbials |
Chemotroph, Phototroph, and Lithotroph |
|
|
|
Chemotroph |
Use Organic Molecules like C&H which can be found immersed in water in the living system. |
Only certain bacteria , such as methanogens, deep-sea vent bacteria |
|
|
Phototroph |
Use light for energy |
Algae, Plants, Cyanobacteria |
|
|
Lithotroph (Purple Bacteria) |
Use inorganic molecules like H2S |
|
|
|
Structure and Metabolism of Carbon Compounds of cells are... |
Organic |
|
|
|
Heterotroph must obtain Carbon in which form? |
Organic Form Nutritionally Dependent on other Living Things) |
Organic - contain C&H |
|
|
What do Autotrophs use as their Carbon source? |
Inorganic CO2 (Not Nutritionally Dependent on other living things |
CO2 is NOT bonded to H which makes it inorganic |
|
|
What 3 things are the primary source of Nitrogen for heterotrophs? |
1. proteins 2. DNA 3. RNA |
amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and have an ammonia group on them that contain Nitrogen. |
|
|
Inorganic Nitrogenous Nutrients like Nitrate are utilized by ... |
Bacteria & Algae |
|
|
|
Nitrogen Fixation |
Small number of bacteria that can take Usable compounds and transform atmospheric N2 into molecules for Protein, DNA, & RNA |
|
|
|
What do you need to synthesize amino acids and other nitrogenous bases/compounds (DNA, RNA) |
Nitrogen Sources must be converted to NH3 (ammonia) to combine with Carbon |
|
|
|
The 4 Major Classes of Organic Compounds |
1. Lipids 2. Proteins 3. Carbohydrates 4. Nucleic Acids |
|
|
|
Oxygen Sources |
Major component of organic compounds |
|
|
|
Oxygen is a common component of ... |
Inorganic salts like Sulfates |
|
|
|
What percent of the atmosphere is made up of Oxygen |
20% |
|
|
|
Hydrogen |
A major element in all organic and several inorganic compounds |
|
|
|
A molecule is organic based on a bond between which two elements? |
H+ and Carbon |
|
|
|
What two places are H+ ions used as an energy source? |
1. Electron Transport System (Oxidation-Reduction reactions of Respiration) 2. Flagella of Prokaryotes
|
|
|
|
What two places are H+ bonds found? |
1. Water molecules 2. DNA zipper that holds 2 strands together
|
|
|
|
Are H + bonds weak or strong? |
Weak |
|
|
|
Maintaining PH with H+ in the cell helps to prevent ... |
Denaturing of proteins |
|
|
|
The inorganic source of phosphorus |
Phosphate (PO43-) |
|
|
|
Phosphate is found in what 3 Main places of a cell ? |
1. Glycolysis production of ATP 2. DNA/RNA (nucleic acids key component) 3. Phospholipid Bilayer |
|
|
|
What gives DNA a negative charge? |
Phosphate |
|
|
|
Sulfur |
• Widely distributed in mineral form • Essential component of some vitamins • Amino Acids that allow an important disulfide bond |
|
|
|
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells can be saprophytic? True or False |
True |
Saprobes (fungi & bacteria) eat off dead decaying matter and metabolize their food externally |
|
|
Chemoheterotrophic is aIso known as as a host? True or False |
True |
|
|
|
Derived nutrients from cells or tissues of a host are caused by a . . . |
Parasite |
|
|
|
Why can parasites be referred to as Pathogens? |
Parasites are referred to as Pathogens because they cause tissue damage on even death |
|
|
|
Ectoparasites |
Live on your body (Normal microbiotia) |
|
|
|
Endoparasites |
Lives in organs & tissues (Normal microbiotia) |
|
|
|
Intracellular Parasites |
Live within cells |
|
|
|
Obligate parasites |
Unable to grow outside of living host "viruses" |
|
|
|
Nutrient Transport requires ... |
a carrier and energy |
|
|
|
What moves easily through phospholipids bilayer? |
small and non polar molecules move easily in out |
|
|
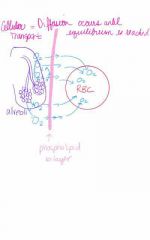
What type of transport is occurring here? |
Cellular Transport: Diffusion |
|
|
|
Active Transport requires... |
Energy |
|
|
|
Diffusion is also known as passive transport. True or False |
True |
|
|
|
Passive Transport is when molecules move from Low → High concentration. True or False? |
False
Molecules move from high → low concentration |
|
|
|
What Channels allow molecules to move through the membrane sac? |
Aquaporins |
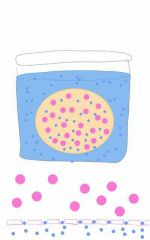
|
|
|
Net gradient will favor Osmosis in membrane sac? T or F? |
True |
|
|

What is occurring in this illustration? |
Osmolysis
Will be able to occur due to lack of cell wall |
|
|
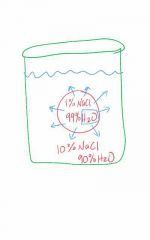
What will happen to cell in this illustration? Is the solution hypotonic or hypertonic? |
Crenation of gram- Cells |
|
|
|
What prokaryote developed a water vacuole as an adaptation of Osmotic Variation |
Amoeba |
|
|
|
How do Halobacteria make their cells isotonic? |
Halobacteiia absorb salt |
|
|
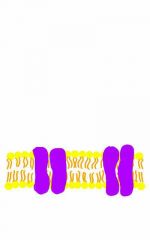
Facilitated Diffusion |
Transport polar hydrophilic molecules with protein carriers & channels |
|
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion flows from high → low Concentration
True or False |
True |
|
|
|
Active Transport requires . . . and moves ......... |
A protein carrier and Requires Energy.
Moves against the gradient. |
|
|
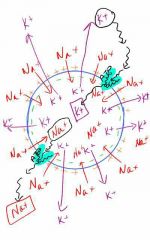
What type of transport is depicted in this illustration? |
Active Transport that uses ATP for energy |
|
|
|
Endocytosis |
Bulk Particles or Cells are engulfed by process of phagocytosis by WBCs |
Amoeba |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
Liquid enters the cell by process of phagocytosis
ex: dissolved glucose, Na+, Amino Acids |
|
|
|
Exocytosis |
Package and Release of Substances (proteins) from a cell (golgi apparatus)
ex: insulin → pancreatic cell → blood |
Requires energy of the cell |
|
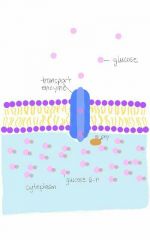
Group Translocation |
An Active Transport that moves molecules across the cell simultaneously as it is converting a useful substance |
composition and location change of a useful substance |
|
|
5 Microbes that thrive in specific temperatures |
1. Psychrophile 2. Psychotroph 3. Thermophile 4. Mesophile 5. Extremethermophile |
|
|
|
Psychrophile |
• Optimum Temperature below 15°C; capable of growth @ 0°C
• Cannot grow above 20°C |
|
|
|
Psychrotrophs |
Grow slowly in cold but have an optimum temperature above 20°C |
|
|
|
Red Snow |
Psychrophile - Algae with red pigment |
|
|
|
Thermophile |
• Microbe that grows optimally at temperatures greater than 45°C
• Temperature Range from 45°C - 80°C |
|
|
|
Extremethermophiles |
grow between 80°C and 120°C (Archae) |
|
|
|
Mesophile |
• Grows @ intermediate temperatures • Optimum growth between 20°C - 40°C • Temperate, Subtropical, and Tropical Regions • Most human pathogens have optima between 30°C - 40°C |
|
|
|
Aerobes |
Use oxygen and uses/needs enzymes to process oxygen products |
|
|
|
Obligate Aerobe |
Cannot grow without Oxygen and have enzymes |
|
|
|
Facultative Anaerobe |
Capable of growth in absence of Oxygen and have enzymes (aerobic respiration) |
|
|
|
Microaerophile |
Doesn't grow @ normal atmospheric concentrations of oxygen but requires a small amount of metabolism and has enzymes |
|
|
|
Anaerobes |
• Lack enzymes for using oxygen in respiration |
|
|
|
Strict or Obligate Anaerobes |
Will die it exposed to Oxygen (clostridium) |
Cloudy @ bottom of test tube |
|
|
Aerotolerant Anaerobes |
Doesn't use Oxygen but can survive and grow to a limited extent in the presence of oxygen |
|
|
|
Obligate Acidophiles |
Euglena mutabilis - Algae that grows between 0-1.0 pH
Thermoplasma - Archae that lives in hot coals 1.0 -2.0 pH; would lyse if exposed to pH 7 |
|
|
|
Microbe and Osmotic Pressure |
Most microbes live either under hypotonic (fresh water) or isotonic conditions |
|
|
|
Osmophiles/Halophiles (halotolerant) |
Live in habitats with high solute concentration
Prefers high concentrations of salt |
|
|
|
Microbial Associations |
Symbiotic and Nonsymbiotic |
|
|
|
Symbiotic Organisms |
* Live in close nutritional relationships; required by One or both members
• Mutualism
• Commensalism
• Parasitism |
|
|
|
Mutualism |
Obligatory, dependent, both members benefit |
protozoan and termites |
|
|
Commensalism |
Satellitism; Commensal benefits; other member isn't harmed (c-diff) |
|
|
|
Parasitism |
Parasite is dependent and benefits; host harmed |
|
|
|
Nonsymbiotic Organisms |
* Organisms are free-living; relationships not required for survival
• Synergism
• Antagonism |
|
|
|
Synergism |
• Members cooperate and share nutrients
• Biofilms created (mixed communities of organism that can exist on their own) |
|
|
|
Antagonism |
• Some members inhibited or destroyed by others
• Some benefit and some destroyed |
|
|
|
Binary fission |
• Asexual process
. growth pattern is exponential • generation time is 30-60 min and can be as short as 10- 12 min |
|
|
|
• Rate of population to complete fission cycle is referenced as |
" Generation" or "Doubling Time" |
|
|
|
Normal Growth Curve Pattern |
• Lag phase • Exponential Growth phase (log phase) • Stationary Growth Phase • Death Phase (some cells remain viable) |
|
|
|
Growth Patterns in microbial control |
Stages of infection |
|
|
|
Turbidometry |
Clear nutrient solution becomes turbid as microbes grow in it |
|
|
|
Genetics |
Study of inheritance • How traits are transmitted • Variations of genes and how they're expressed
• Structure and Function of genes • Gene mutations |
|
|
|
3 Gene Levels |
1. Organismal 2. Chromosomal 3. Molecular |
|
|
|
DNA must be able to ... |
• self-replicate when needed • must be accurately duplicated and separated from each daughter cell |
|
|
|
DNA is independent of Transcription True or False |
True |
|
|
|
Transcription only makes copies of genetic material when needed True or False? |
True |
|
|
|
Viruses can self replicate True or False? |
False |
|
|
|
Genome |
DNA Recipe Book |
|
|
|
Chromosome |
Chapter in DNA Recipe Book |
|
|
|
Gene |
• Page or Recipe in DNA Recipe Book |
|
|
|
Structural Gene |
Codes for Proteins or RNA Molecule |
|
|
|
Regulatory Genes |
• Involved in controlling possession of genotype (genetic constitution of an individual organism)
• Expression of the phenotype (physical traits that come thru)
|
|
|
|
Organisms contain more genes in their genotype than are manifested as |
a phenotype |
|
|
|
How many genes does a Small Virus have? |
4-5 genes |
|
|
|
How many genes do Human cell contain? |
25,000 genes |
|
|
|
Chromosome |
Neatly packed DNA Molecule |
|
|
|
Eukaryotic chromosomes include |
• DNA & Histone • Nucleus • Vary in # few-hundreds • Diploid or Haploid • Appear Linear |
|
|
|
Bacterial chromosomes include |
• Condensed and secured by " histone-like" proteins • Single Circular Chromosome |
|
|
|
DNA consists of what 3 parts |
1. Deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar) 2. Phosphate Group 3. Nitrogenous Base * Purines: Adenines, Guanine * Pyrimidines: Thymine, Cytosine e |
|
|
|
DNA Covalent Backbone |
1 sugar bound to 2 phosphates , 5' to 3' carbon |
|
|
|
RNA Polymerase |
Enzyme that carries out Transcription |
|
|
|
RNA Molecule - Nucleotide A-Adenine is complimentary to... G-Guanine is complimentary to ... |
U -Uracil C-Cytosine |
|

