![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
150 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are general purpose pumpers used for? |
Firefighting Rescue Salvage Overhaul Forced entry Special hazards |
|
|
|
Who is responsible for the inspection, preparation, maintenance of appliances and equipment |
The driver is responsible for the appliance. But all firefighters are responsible to assist checking the equipment |
|
|
|
When should an appliance be in operational condition |
At all times |
|
|
|
What do all crews need to do at the start of each shift? |
Attend rostered appliance Set riding gear Complete BA check - maintenance procedure A Conduct comprehensive check of appliance as per checksheet M32 Road test appliance Refuel as necessary |
|
|
|
■■ Why do we use pumps in the MFS? |
Control the pressure of water Control the volume or flow of water Transfer water to and from an appliance |
|
|
|
On what form is missing equipment marked? |
M32 B-4 |
|
|
|
What happens if there is an anomaly with the appliance? |
1. It is investigated 2. If minor it can be repaired by on shift crew. If not report to officer in charge of the appliance and then list on the M32-C form |
|
|
|
■■ When should the driver conduct an appliance check? |
1. At the commencement of each shift 2. When changing over an appliance. 3. After a working incident |
|
|
|
Why is it important that firefighters familiarise themselves with each appliance they ride on? |
Equipment location varies from appliance to appliance |
|
|
|
■■ What's on a water gear trolley? |
1. Standpipe 2. Heavy duty plate cover lifter 3. Turncock key and bar 4. Safety torch 5. Combination key |
|
|
|
How full must the petrol be on a truck be to be deemed operational? |
At a minimum 3/4 full |
|
|
|
■■ What 10 things are in a high rise sling? |
1. 38mm hose 2. 10/100 branch 3. Shove knife 4. Wheel valve 5. Door indicators 6. Brass inlet (olive) 7. Square key 8. Hydrant key 9. Door wedges 10. Forestry adaptor |
|
|
|
How many lengths of hose are in a hose box? |
Four 30m lengths of 64mm flaked hose |
|
|
|
■■ List at least 8 items in a tool roll? |
1. Universal shears 2. Clip saw 3. Life hammer 4. Stanley knife 5. Hammer 6. Cable cutter 7. Shifting spanner 8. Spread strap 9. Screw drivers 10. Windscreen removers 11. Square-nose pliers 12. Pointy-nose pliers 13. Multigrips 14. Speed brace and socket |
|
|
|
What side of the truck is near side? |
Curb side or passenger's side (left side) |
|
|
|
What is the fleet number? |
A number individual to the truck like a licence plate to a car |
|
|
|
■■ What is the appliance number? |
The station number and appliance type number. When the appliance is replaced, the new truck will carry over the same appliance number |
|
|
|
■■ How many kpa of pressure is lost with 1m altitude |
10 kpa |
|
|
|
What is thr optimal pressure requirements for the 50/350 branch? |
700 kpa |
|
|
|
■■ How many kpa pressure is lost per length of hose? |
A loss of 100 kpa is lost per 30m of hose |
|
|
|
How many kpa is lost per storey in a building? |
Rule of thumb is a building storey is 3.5m, and it's a loss of 10 ups per metre. Therefore it is a loss of 35 kpa per storey in a building |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of valves used? |
Butterfly - before the pump, low turbulence. Ball valve - delivery side of pump, limited flow control |
|
|
|
What happens if you don't wait 5 seconds after deactivating the pump before changing gears |
You will grind the gears and wreck the appliance |
|
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the centrif pumps? |
Disadvantage: cannot displace gasses and therefore needs a different pump to displace the air in the pump
Advantage: few moving parts, simple to maintain, steady flow, can stop water flow, small/light&compact. |
|
|
|
■■ What are the ways a pump can be damaged? |
1. Cavitation 2. Overheating 3. Water hammer 4. Operator error - not waiting 5 seconds 5. Poor water quality 6. Dry running the pump (running without water) 7. Relief valve left on when not required |
|
|
|
What is a water hammer |
A sudden close of valves that creates shockwaves that pulses through the water and damages the water systems |
|
|
|
What must you do after pumping dirty water? |
Flush with clean or salt water |
|
|
|
What is cavitation? |
When the usage of water is greater than the supply (overrunning) |
|
|
|
What are some signs of cavitation? |
Sudden drop in pressure or capacity loss Increased pump speed without an increase in volume or pressure Vibrations (loud) that can also damage pump seals |
|
|
|
How do you rectify cavitation? |
Increase supply Decrease output pressure Decrease output quantity |
|
|
|
What is an effect of the pump overheating? |
Superheated water turning to steam - can then cause cavitation Hot metals that expand and warp |
|
|
|
How do you rectify an overheating pump? |
Slightly open a valve to ensure its not a closed system Reduce the RPM when deliveries are closed Install a circulating hose from delivery to tank inlet |
|
|
|
What is the RIV? |
Rapid intervention unit or also known as the jaws of life |
|
|
|
What is the hooligan tool used for and where on the appliance is it most commonly found? |
Found on the rear Used in busting pad locks and breaking doors |
|
|
|
What are the steps to engage the pump? |
1. Stop appliance 2. Handbrake 3. Neutral gear 4. Turn on 3rd stage (high pressure) and main pump switches 5. Drive gear |
|
|
|
What are the steps to DISENGAGE the pump. |
1. Shut everything on pump panel and turn off throttle 2. Neutral gear 3. WAIT 5 SECONDS 4. DISENGAGE main pump and 3rd stage (high pressure) 5. Drive transmission 6. Handbrake and drive off |
|
|
|
Why do you wait 5 seconds after putting into neutral before you disengage the pumps? |
It allows the transmission cogs to disengage from the water pump |
|
|
|
How does a centrifugal pump work? |
Energy is created by centrifugal force that is generated by the rotation of the impellers. The spinning creates an area of low pressure (suction) at the eye, thereby drawing water inward. 1. Water is drawn into the eye by the rotational drive 2. Water is spun around 3. Water is thrown out by the vanes |
|
|
|
What part does the volute play in a centrifugal pump? |
Houses the impeller and directs the water spun from the impeller and reduces water velocity, thus reducing water turbulence. |
|
|
|
What is the suggested working pressure for a high pressure line |
2400 kpa
(Main pump must be engaged - high pressure pump is a separate pump buy it is powered by the main pump) |
|
|
|
What will you find on the pump panel? |
Water inlets Water deliveries Throttle Gauges Foam system Relief valve |
|
|
|
■■ What is the purpose of a relief valve? |
The relief valve is a safety mechanism designed to protect the branch operators against surges in pressure when using a 64mm hose.
Ensure relief valve is turned on BEFORE getting to work with a 64mm hose (default is off) |
|
|
|
What can cause surges in water pressure? |
1. Pressurised supply: introduction of supply from mains 2. Fluctuations through mains supply 3. Delivery being shut: when multiple lines are in use and one is shut off |
|
|
|
How do you engage the relief valve? |
1. Ensure throttle is at idle 2. Turn relief valve on 3. Wind pressure knob fully to high/increase 4. The red closed light should be on 5. Open the 64mm delivery 6. Now throttle to increase the RPM to required pressure 7. Wind relief valve pressure knob in direction of low/decrease until green open light comes on |
|
|
|
Why is "off" the default for the relief valve |
Water damage inside the valve when using high pressure hose lines at 2400kpa if turned on. Valve is also to be OFF when relay pumping and booster operations |
|
|
|
■■ What are the 5 principals of friction loss? |
1. Friction loss varies directly with the length of the hose
2. For the same velocity, friction loss decreases directly with the increase in diameter (up diameter = down friction)
3. Friction loss increases directly as the square of the velocity (m/s)
4. Friction loss increases with the roughness of the interior of the hose
5. Friction loss, for all practical purposes, is independent of pressure |
|
|
|
Who is responsible for maintaining the optimal water pressure for firefighting? |
The pump operator |
|
|
|
What are the advantages of using water for fires? |
1. Relatively cheap 2. Relatively available and plentiful 3. Readily absorbs quantities of heat (for pattern) 4. Expands when converted into steam - 1700:1 at 100 degrees Celsius 5. Easily transported in containers |
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of water? |
High surface tension Reactivity with some chemicals (mg in cars = combust) Low viscosity (resistance to flow) Will conduct electricity |
|
|
|
What are some ways you can reduce friction? |
1. Eliminate bends / kinks 2. Use adapter when necessary 3. Keep branches and valves fully open 4. Use gaskets of proper size 5. Use shorter lines as much as possible 6. Use larger diameter hose or multiple lines when flow must be increased |
|
|
|
What is the flow rate of a 50/350 TFT branch at 700kpa? |
900 L/minute |
|
|
|
Why does elevation affect pressure |
Gravity creates a pressure called "head" pressure. There will be a 10 kpa loss/gain per meter elevation up/down (respectively).
Head pressure must be one of considerations of the pump operator when setting pump pressure |
|
|
|
What is jet reaction? |
A reaction equal to and opposite to the force of the jet. It takes place at the nozzle in the opposite direction to the flow Considerations: 1. Size of TFT 2. Changes in pressure 3. Spray pattern |
|
|
|
What is relay pumping? |
Relay pumping consists of a number of appliances spaced at intervals between a water source and the incident. Lines of hose connect the appliance pump at the supply to subsequent appliance pumps and then to the incident ground pump, which then delivers water for fire operations. |
|
|
|
What are the factors to consider when relay pumping? |
Quantity of the water required on the fire ground The distance to the nearest water supply The number and capacities of the available pumps The terrain over which the relay extends (hills = head pressure) |
|
|
|
■■What are the 3 considerations of the pump operator? |
1. Elevation 2. Branch requirements 3. Friction |
|
|
|
In a relay, what is the incident ground pump? |
The first arriving at the scene. Where possible the largest capacity pump should be positioned at the water supply and the smallest capacity pump as the incident ground pump |
|
|
|
In what order do you shut down a relay? |
Starting at the incident ground pump, reducing RPM and closing deliveries; working appliance-by-appliance back to the pump at the water source. Last step is to turn off the hydrant, release the residual pressure from the system and make up equipment. |
|
|
|
What is an open circuit relay? |
Water is delivered into a holding dam or the appliance tank of each appliance in the relay. |
|
|
|
What is a closed circuit? |
Where the water is pumped from the source by the first relay pump to the inlet of the next relay pump. |
|
|
|
What are some considerations for setting up a relay? |
Twinned lines to supply: increased pressure and low friction At least 2 spare lines in case burst lines Distance and elevation between pumps Male coupling (bare threading) towards the fire, female (bit with the spinny bit) towards delivery Spare delivery valve to release air from the system as water advances |
|
|
|
What PPE must be worn when driving an appliance? |
Level 1 worn, level 2 must be in the back |
|
|
|
How many recruits can be in the appliance? |
2 |
|
|
|
What do you need when reversing? |
- beacons on - 2 guides at rear (1 giving directions) |
|
|
|
What is the hand signal for stop? |
One arm raised vertically, palm of hand facing the driver |
|
|
|
What is the hand signal for reversing? |
Palms of both hands are turned to the chest and moving back and forth |
|
|
|
What is the hand signal for turn right/left? |
The arm is held horizontal to the ground at shoulder level indicating what way to turn |
|
|
|
What is the hand signal to indicate distance? |
Using both hands facing each other. The distance between the hands indicates the distance between the vehicle and the obstacle |
|
|
|
What is the protocol for any faults or abnormalities with an appliance? |
Details to be entered on the appropriate M32 form and reported to the officer in charge of the appliance |
|
|
|
What is the blood alcohol limit for driving an appliance |
Zero |
|
|
|
What is the 3 second rule? |
Method of establishing a safe driving distance when driving in a convoy. Another method is to allow one appliance length for every 10 km/h of speed. |
|
|
|
What should you do if you ding the appliance |
Report to recruit instructor IMMEDIATELY |
|
|
|
When can you overtake another appliance |
Only if they pull over. Never overtake a moving appliance |
|
|
|
What are 2 considerations to parking on a hill? |
1. Wheel chocks 2. Wheels angled into the curb |
|
|
|
What are the appliance checks and driving considerations that the driver is responsible for? |
- engine oil - fuel (3/4 minimum) - clean windows, wipers and full washer fluid - bodywork for damage - tyre condition - identify and locate all gauges (changes in each appliance) - change seat position to suit good posture - passengers must wear seatbelts - 2 hands on steering wheel at all times when driving |
|
|
|
What are some hazards when driving an appliance? |
1. Physical - round-a-bouts 2. Other road users - not aware of lights and sirens 3. Factors affecting roads - rain, pot holes 4. 3-second rule = safe driving distance |
|
|
|
What must we do before driving an appliance out of the engine room? |
- ensure echaust fans are on - seatbelts - ensure powerlines are disconnected |
|
|
|
What's the purpose of standard hose and ladder drills? |
To allow recruit firefighters to develop the skills to competently use hose, ladders and other associated equipment These skills will be assessed for competence annually on shift |
|
|
|
Where does each position sit in the appliance? |
Pos 1. Near side back seat Pos 2. Off side back seat Pos 3. Driver Near side front (passenger) seat is OIC |
|
|
|
What does is the command "stand from under" |
The command given by anyone who has to drop or lower equipment from a height, when there is a risk that it might strike someone standing below. |
|
|
|
What is the command "haul away" |
The command given when taking gear aloft with the aid of a rope line |
|
|
|
What is the command "fall in" |
The crew fall into a single line at close intervals, standing at ease, 2 paces to the rear of, and facing away from the appliance |
|
|
|
What is the command "get to work" |
To undertake the drill detailed in a safe and efficient manner |
|
|
|
What is the command "as you were" |
This command cancels the last order given, and the crew resumes their previous positions |
|
|
|
What is the command "still" |
Emergency situation. Yell with force. Everyone stop what you are doing as there might be a hazard or a danger ahead. |
|
|
|
■■ What does the compound gauge display? |
Water pressure entering the pump. It is capable of measuring positive and negative pressures. Negative pressure provides an indication of vacuum present at the pump during priming or when the pump is operating from draft. Positive pressure provides indication of residual pressure (Water pressure left over) when the pump is operating from a hydrant or receiving water through a supply line from another pump |
|
|
|
■■ What does the transfer case do? |
Directs and transfers the engine power between drive wheels to the pump and vise versa |
|
|
|
■■ What does the main gauge display? |
Displays the water pressure leaving the pump before is reaches the individual discharge lines |
|
|
|
■■ What is the purpose of the relief valve? |
A safety mechanism designed to protect the branch operators against surges in pressure on a 64mm hose |
|
|
|
■■ What is a fire? |
Fire is a chemical reaction in which oxygen is combined with a gaseous or vaporous fuel, this rapid oxidation produces heat and light |
|
|
|
■■ What is the fire triangle? |
The fire triangle illustrates the three elements required for fire to exist. The elements are heat, oxygen and fuel. A fire needs all three components to come together under the right conditions for combustion to occur. |
|
|
|
■■ How do we extinguish a fire |
Starve Smother Cool
Remove one of the components in the fire triangle: - remove the heat - remover the oxygen - remove the fuel Interrupt the chemical chain reaction |
|
|
|
■■ What are the 4 stages of fire development? |
Ignition - on a molecular level
Growth - as soon as a flame is present the fire has developed in to the growth stage. Initially the fire develops at a slow rate, but this will increase over time. As long as there is sufficient fuel and oxygen to consume, fire intensity will continue to accelerate during growth stage.
Fully developed - fire has developed as far as the available fuel and oxygen supply will allow. The rate of heat released by the fire reaches a stable point and continues at this point until fuel or oxygen sources begin to delish.
Decay - combustion process begins to slow as it has been limited by either the available fuel or oxygen supply. Without the addition of more fuel or oxygen the fire will extinguish |
|
|
|
What are the 3 ways heat transfers |
Convection - transfer of heat by movement of air or liquid Conduction - transfer of heat from one object to another by direct contact or two objects or an intervening medium (conductor) Radiation - transfer of heat by electromagnetic waves. One of the major sources of fire spread |
|
|
|
What are the 3 basic states of fuel? |
Solid - the smaller the solid, the quicker to combust Liquid - give off vapours when heated Gas |
|
|
|
What is pyrolysis? |
When heated solids start to decompose causing a release of flammable gases |
|
|
|
What is the atmospheric percentage of oxygen? |
20.9, rounded up to 21% O2 is most common supporter of combustion. Oxidising agent |
|
|
|
How do you starve a fire? |
Removal or separation of unburnt fuel. |
|
|
|
How do you smother a fire? |
Removal or dilution of oxygen supply. I.e. cover with fire blanket or an inert gas. Foam, dry chem powder and wet chem extinguishers all smother |
|
|
|
How do we cool a fire? |
Remove the heat source (spray with water) will cool the fire. Water, foam, co2 and wet chemical extinguishers all cool |
|
|
|
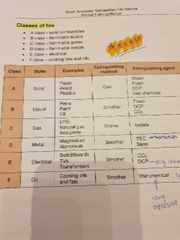
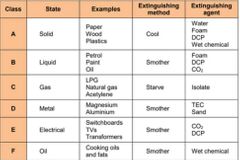
■■ What are the 6 classes of fire? |
Class A - solid combustibles (paper, wood, plastics)
Class B - flammable liquids (petrol, paint, oils)
Class C - flammable gases (LPG, natural gas, acetylene)
Class D - flammable metals (magnesium, aluminium)
Class E - electrical (switchboards, Tv's, transformers)
Class F - cooking fats and oils |
|
|
|
What extinguishing method do you use for LPG gas fire? |
Isolate and starve the fire |
|
|
|
What extinguishing method do you use for switchboard fire? |
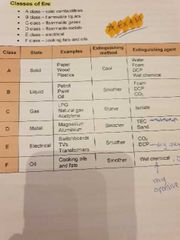
Smother (remover oxygen) using co2 or dcp extinguishers |
|
|
|
■■ What are the 7 causes of structural collapse? |
Fire Impact (MVA, plane etc) Explosions (gas, terrorist) Poor workmanship Flood Earthquake Landslide |
|
|
|
■■ What are the ways chemicals can enter the body? |
Inhalation - resp system Absorption - wounds, skin pores, eyes Injection - sharp objects, syringes Ingestion - enter through mouth |
|
|
|
What are the principles of least exposure? |
Least number of people exposed Least time of exposure Least amount of materials Wear appropriate PPE |
|
|
|
■■ What are the hazards encountered by operational firefighters? |
Wildfire Electrical Radiation Biological Hazardous atmospheres Extreme temperatures Chemicals Flammable liquids and gases Dust Structural collapse |
|
|
|
What are the 5 conditions for a dust explosion? |
1. Combustible dust 2. Dust suspended in the air at a high concentration 3. The dust is confined 4. There is an oxidant (atmospheric oxygen) 5. There is an ignition source |
|
|
|
What are some chemical hazards firefighters have to deal with? |
Asphyxiates - simple & chemical Toxins, chems, poisons Corrosion - acid/base Irritation (asthma) Sensitivity (increases with exposure) Reactive substances (with water) Explosives - pyrotecnic effect Carcinogens - cancer |
|
|
|
What are the effects of acute and chronic chemical exposure? |
Acute: burns, coughing, light-headedness, blurred vision Chronic: resp problems, impaired organ function/failure, cancers |
|
|
|
How do you use a fire extinguisher? |
P. Pin (remove) T. Test A. Aim S. Squeeze the trigger S. Sweep at the base of the fire |
|
|
|
Why is co2 used for class E fires? |
Doesn't conduct electricity. Preferred to use co2 for electrical instead of dcp (messy) |
|
|
|
How do foam extinguishers eliminate fires? |
Cooling (90% H2o) and blanketing (smothering) |
|
|
|
■■ List all the types of extinguishers and the class of fire they are used for |
Water - class A Foam - Class A and B Carbon dioxide - class B and E Dry powder - universal / class B, A & E Wet chemical - class A or F |
|
|
|
■■ How do we service/maintain our extinguishers? |
Check pressure gauges Check maintenance tag Check for obvious faults
Chubb fire does all the servicing and refills of the extinguishers |
|
|
|
What are the considerations for using a fire extinguisher? |
Correct extinguisher for the job Aware of short working duration Keep a safe distance - do a test before advancing Work upwind Retreat backwards / always face the fire |
|
|
|
■■ What stations are in the southern command? |
40 St Mary's 41 Camden 42 O'hallaran hill 43 Christies downs 44 Glen Osmond 45 Brooklyn Park 46 seaford |
|
|
|
■■ What stations are in the central command? |
20 Adelaide 21 Beulah park 24 Woodville 25 Port Adelaide 27 Marine 28 Largs North 37 Prospect
|
|
|
|
■■ What stations are in the northern command? |
22 Paradise 30 Oakden 31 Golden Grove 32 Salisbury 33 Elizabeth 35 Gawler 36 Angle park
|
|
|
|
■■ Where can you find SOP & SAPs? |
On the member's only website (MOW) |
|
|
|
■■ What is the purpose of an SOP? |
Standard operating procedures provide a number of known procedures that allows firefighting crews to operate in a manner that is SYSTEMATIC, EFFICIENT & PREDICTABLE when attending an emergency incident.
Applied when attending & normalising an emergency incident |
|
|
|
■■ What is the purpose of an SAP? |
Service Administrative Procedures provide practical information on the many administrative processes & procedures used by the MFS
Applied in the day-to-day running of the MFS |
|
|
|
■■ What is the safe distance from a downed wire? |
8 metres |
|
|
|
What water pattern do you use for solar panels that are on fire? |
Broken spreay: Fog pattern or bursts of jet |
|
|
|
■■ What are the 4 risk categories in the greater alarm system? |
Category A Category B Category C Specific Risks |
|
|
|
■■ What do you do for a priority 1 & priority 2 response to an incident |
Priority 1: immediate emergency response. Travel using emergency warning devices - LIGHTS & SIRENS
Priority 2: immediate emergency response. Complying with Australian road rules, no emergency devices |
|
|
|
■■ What do you do if there is a fatal casualty near an electrical hazard? |
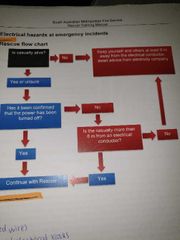
Keep yourself and others at least 8 m away from the electrical conductor, await advice from electricity company |
|
|
|
What causes an electric shock? |
Someone can only recieve a shock when they come in contact with 2 points between which there is a voltage difference |
|
|
|
What are the possible results of electric shock? |
Broken bones Cardiac arrest Involuntary muscle reaction Electric burns Paralysis Difficulty or cessation of breathing |
|
|
|
■■ What is the warning with electrical hazards |
Always treat all downed wires, includingncable TV &telephone wires, as energised until proven otherwise by the relevant authorities |
|
|
|
■■ what is the pump operator responsible for? |
Supplying continuous, reliable and effective water for firefighting |
|
|
|
■■ What do the gauges indicate? |
The condition or the engine, pump and water supply |
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
List 10 items found in the water gear draw |
Washers Suction keys Thimble Storz to london round adaptor Spindle cap Can CRC Can silicone Rake/hoe head Broom heads Hydrant wheel Plate cover key Square key Hydrant key Storz adaptor key Forestry to 64mm storz adaptor Combination key |
|
|
|
What are some signs of structural collapse? |
Cracking in brickwork Movement in floor or roof Concave floors Walls out of alignment Unprotected steel distorting Prolonged burning Intense fire and loud noise |
|
|
|
What are 4 safe handling procedures for dust explosions? |
Use fine spray (fog) not jet Never use water on metal dusts Wear correct PPE handle drums and bins carefully |
|
|
|
What is 'step potential' at electrical hazards? |
If a live downed wire is touching the ground and has created a 'pool' of electricity and you were to place one foot near the point of ground contact and your other foot a step away, the difference in voltage would cause electricity to flow through your body driving by a voltage |
|
|
|
What is 'touch potential'? |
Electricity would flow through your body if you were to place your hand on an energised source while your feet were at some distance from the source |
|
|
|
■■ Can water be applied to extinguish burning solar panels? |
Water can be applied directly onto solar panels using a broken spray pattern and with all personnel a minimum distance of 8m from system components or adjoining conductive material.
It is safe to use fresh water with or without class A foam.
Co2 & DCP extinguishers are suitable for the other components |
|
|
|
Where are the 3 most likely places to find power isolating switches? |
1. Next to panels 2. Next to inverter 3. In the fuse box |
|
|
|
List the appliance types an corresponding numbers |
1 1st GP 2 2nd GP 3 CAPA (combined aerial pumping app) 4 support tender 5. 1st Elevated platform 6 1st BA / HazMat 7 pump / hazmat 8 4x4 medium pump 9. Pump rescue 11 3rd GP 14 4WD grassfire unit 15 2nd elevated platform 16 2nd hazmat H01 1st hooklift 25. Marine vessel 90 1st incident control 92 2nd incident control |
|
|
|
What could cause a negative reading on the compound gauge? |
Indicates a vacuum. Could be seen when overrunning water supply or drafting |
|
|
|
What are the precautions for electrical hazardous sites? |
Utilities shut down Pre- plans may be available Darkness follow BA procedures Re-assess stability increased weight due topooling of water Absorbent materials expands with contact with water Structual collapse walls fall outwards |
|
|
|
What are some electrical hazards? |
Downed wires MVA's with fallen wires (live car) Electricity kiosks Ladders with wires above (conductive) Aerial appliances - entire appliance could be 'live' Wet conditions = enhanced danger Substation fires Fires on pole |
|
|
|
Causes of electrical fires? |
Arching Overheating Faulty electrical wires Electric rail systems |
|
|
|
Can you spray water on a fire on solar panels? |
Water can be applied directly onto solar panels using a broken spray pattern (fog) and from a distance of 8 meters from all system components or adjoining conductive material. |
|
|
|
What are safety considerations for electrical situations? |
8 m Guard against eye injuries from arcs or short circuits Treat all wires as live Do not cut wires Wear full PPE and use insulated tools Care with overhead lines and ladders and other equipment Use back of hand to move wires |
|
|
|
What are the limits of high and low voltage? |
High = 1000 + volts Low = <650 volts |
|

