![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why are plant cells much more regular and have uniformity than animal cells? |
The cell wall |
|
|
What is the main function of the cell wall? |
To provide support and structure to the plant cell. |
|
|
What is the cell wall mostly made of? |
Insoluble cellulose - but it is permeable to everything dissolved in water |
|
|
The presence of which to components affect the permeability of the cell wall? |
- The cell wall can become impregnated with lignin (bark/woody plants) - suberin - in cork tissues These both prevent water and dissolved substances passing through |
|
|
What are the components of the middle lamella (The fist layer formed in cell division) |
Primarily composed of pectin but the negative COOH group in pectin can interact with positive calcium ions to make calcium pectate. This builds up on either side the middle lamella. |
|
|
What is the structure of the primary cell wall? |
Cellulose microfubrils are all orientated in same direction Matrix of calcium pectate |
|
|
How is the secondary cell wall different to the primary? |
It builds once plant ages Cellulose micrifibrils are arranged densely in opposite angles. Hemicellulose can be added to harden it further Lignin added in woody plants |
|
|
What are plasmodesmata? |
Cytoplasmic bridges between cells formed from gaps in the cell wall |
|
|
What is the interconnected cytoplasm called? |
Symplast |
|
|
Describe a technique used to find evidence for the function of plasmodesmata |
Plant grafts - a rose can be grafted onto another plant root and the graft rose will only start growing by cell division once their are plasmodesmata established between the tissues. So shows how the plasmodesmata is important is cell communication and passing substances along. |
|
|
What is the function of the vaculole? |
- control movements of substances in and out - control water potential -allow water into cell via osmosis -storage |
|
|
State 5 substances a vacuole can store. |
1. Pigments e.g. beetroot 2. Lytic enzymes like lysosomes 3.Poisons e.g. foxgloves 4. Waste products and chemicals 5.proteins in seed and fruits |
|
|
How does heating beetroot let pigment out? |
The heat changes the structure of the membrane of the vacuole and the cell, allows pigment to leak |
|
|
What is the tonoplast? |
The specialised membrane surrounding the vacuole, allowing substances to move in and out of cell sap. |
|
|
Name 4 exceptions of plant structures that do not have chloroplasts |
1. Xylem and phloem 2. Root 3. Seeds and flowers 4. Parasitic plants |
|
|
Which unspecified organelles are both the chloroplasts and amyloplasts developed from? |
Leucoplasts |
|
|
What can you find a lot of in potato tubers? |
Amyloplasts |
|
|
What does the amyloplasts store? |
Starch |
|
|
What are the 5 similarities between chloroplasts and mitochondria? |
- Large organelles- biconvex shape - own DNA - have outer membrane - folded inner membrane in which enzyme controlled reactions take place. - endosymbiotic theory |
|
|
What are the features of chloroplasts not present in mitochondria? |
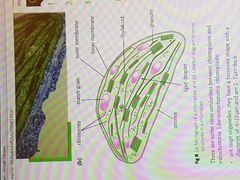
1. Chlorophyll 2. Formed from leucoplasts 3. Site of photosynthesis |

