![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are some reasons that RCTs might not be feasible or ethical
|
if there is already a standard of practice
ethics exposure occurred in the past too expensive/time consuming |
|
|
what are some limitations of RCTs
|
highly selected patients
may be unethical can be expensive |
|
|
what are four basic study designs
|
case series
before and after observational studies meta-analysis |
|
|
what are three types of observational studies... kinda four types
|
case study
cross sectional study cohort hybrid designs (nested case) |
|
|
do hypertensives have a higher risk of MI? What kind of study design would be used
|
cohort
|
|
|
T or F. cohort can be RCT or observational
|
true
|
|
|
when does OR approx equal RR
|
if rare
|
|
|
if your odds are 50% what is the incidence?
|
1/3 because 1/3 / 2/3 is 1/2
|
|
|
what is a way that historical trends might be skewed
|
if definition of a diagnosis were to change, than stats would be affected
|
|
|
draw what you should be looking for in a cohort study
|
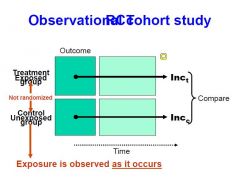
hort -= horizontal
|
|
|
cross product shortcut is a shortcut for what
|
calculating odds ratio in cohort study
|
|
|
what are the pros and cons of a cohort study
|

note the clear temporal relationship
|
|
|
when can you not calculate RR
|
in case control study
|
|
|
what is a cross sectional study
|
a whole population is selected and surveyed. exposure and disease status are ascertained at the same time
|
|
|
what can you calculate with a cross sectional study
|
odds ratio
prevalence ratio |
|
|
what are the benefits of nested case control
|
efficiency of case control
prospective nature of cohort |
|
|
can you calculate incidence in cohort?
|
yes! and RR
|
|
|
if your incidence is 1 per 1000 person years, how many women would you have to study for ten years to get 100 cases?
|
10,000
|
|
|
draw the setup for case control study
|

|
|

what other way can cross section go? why?
|

you can calculate prevalence ratio
|
|
|
name the advantages and disadvantages of case control and cross sectional study
|

|
|
|
is there association?
|
no random error?
|
|
|
is the association real?
|
no bias
|
|
|
is the association causal?
|
no confounding
|
|
|
Is it found in all groups?
|
no interaction
|
|
|
what is the definition of bias
|
systematic error in the methods of the study which result in a tendency to produce results different from the trust
|
|
|
what is the antonym of bias
|
validity
|
|
|
what are two types of validity that you need to be concerned with
|
external and internal
generalizable? observation in convenience samples? selection rpocess? information/classification? |
|
|
name the six types of bias
|
selection
surveillance recall interviewer temporal prevalence incidence |
|
|
what are selection biases in a case control study? cohort study?
|
selection-- how you select your controls.
Cohort-- difference in loss to follow up |
|
|
what is another name for temporal bias
|
reverse causation
|
|
|
explain prevalence incidence bias
|
like race and coronary atherosclerosis
sometimes duration matters! |
|
|
prevalence is about equal to...
|
incidence times duration
|
|
|
___ is an estimated bias of RR
|
prevalence
|

