![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Commonly Active sites can be
|
Bound metal ions (Mineral) -- Bound organic groups (vitamins) --- Specific amino acids
|
|
|
Co-enzyme vs Co-factor
|
Organic (Vitamin) vs Inorganic (Ca-P)
|
|
|
Apoenzyme (inactive)
|
ezn wo its prostethic group or metal group (co factor)
vitamin (coenz) and prostethic ezn (permanent -- heme) |
|
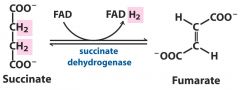
1. Oxido-reductase --- FAD - riboflavin B2
|
Add or remove electrons (and commonly also hydrogen) ---
|
|
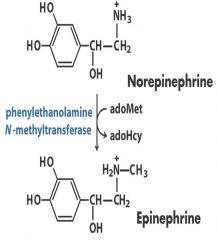
2. Transferase: Norepi -- Epi - CH3
|
Transfer one group from one molecule to another -- CH3
|
|
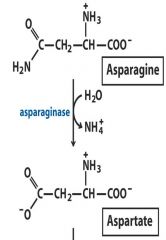
3. Hydrolase: Asparagine (NH3) --- Aspartate (COO)
|
Hydrolysis of functional group by water
|
|
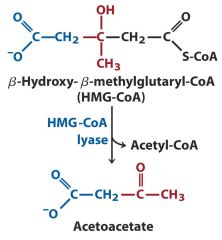
4. Lyase: HMG-CoA ---- Acetoacetate (double bond)
|
Addition or removal of double bonds when adding or removing a functional group
|
|
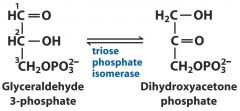
5. Isomerases: G3P --- DHAP
|
changing to new isomer
|
|
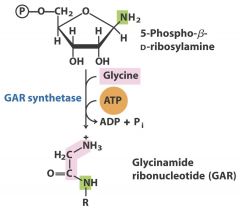
6. Ligase: Glycine - GAR
|
Creates C-C, C-N, C-O, C-S bonds usually with the assistance of ATP
|
|
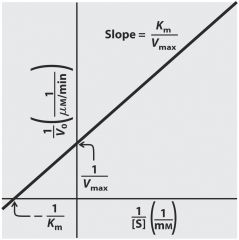
Michaelis-Menten plot can predict and calculate Km - Vm base on substrate concentration
|
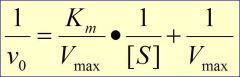
use 1/S ---> x-int= -1/Km ----- y-int= 1/Vm ----- slope = Km/Vmax (reciprocal of Km/Vm)
|
|
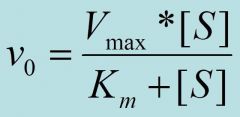
Km
|
is the concentration of substrate that half saturates the enzyme. The lower the Km the higher the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate
|
|
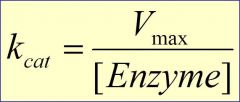
Kcat
|
is how fast this enzyme can go compared to other enzymes
|
|
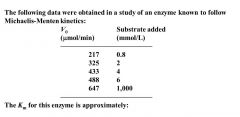
Find Km
|
Find Vm = 647 --- Calc 1/2 Vm = 325 ---> determine Km= 2nM (conc substrate needed to be 1/2 Vm)
|
|
|
Suicide inhibitor
|
Suicide enz bind and inativate the act of enz --> not letting go --> Aspirin acetyl bind into
|
|
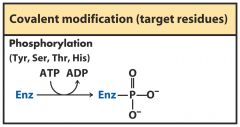
covalent modification
|
Phosphorylation
|
|
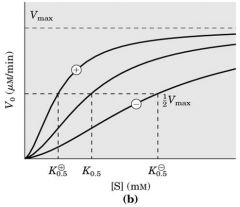
Enz cooperativity (Positive and negative regulation)
|
Vmax is the same --- can increase of decrease Km
|
|
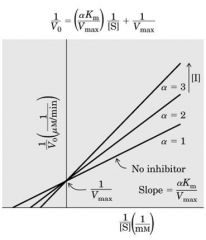
Competitive Inhibition: Methotraxate (cancer) bind to DHFR (DNA synthesis) and compete with folic acid B9 to inhibit DNA synthesis
|
Amt of DHFR is unchange (V max is the same) ---- if Meth increase (while Vm same) need MORE DHFR (substrate conc=Km) to have the same speed of action ----------------- if conc inc -----> Slope inc --- Vm same - Km increase
|
|
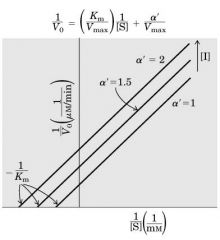
Un-competitive Inhibition (un --- parallel)
|
Inibitor binds only after substrate has already bound, but slows down conversion to product. ----- CONC inc --> Slope same --- Vm dec - Km dec (1/2-1/3)
|
|
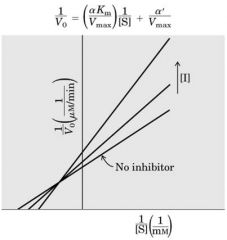
Mixed Inhibition --- tert Comp
|
Inhibitor binds at any time -- CONC inc ---> Slope inc --- Vm dec - Km increase
|
|
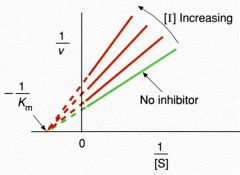
Non-competitive Inhibition
|
CONC inc --> slop inc ----- Vm dec ---- Km same
|
|
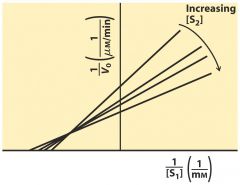
Ternary Complex ---- mixed
|
random order -- order both sub bind the same time --
|
|
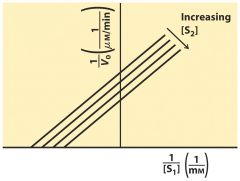
Ping-Pong Kinetics ---- un--compete
|
1st bind first then 2nd come in --> ATP first to bind P then glucose come in to use P parallel
|
|
|
Name some of the common amino acids and other “non-amino acid” chemicals that can be found at an active site.
|
Glu-Asp ----- Lys-Arg ----- Cys ---- His -------- Ser ----- Tyr
|
|

Feedback Inhibition
|
s the product of many the rxn down the line to stop the beginning rxn (to save energy to make too many middle guys)
|

