![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Climate |
Long term patterns of temperature and precipitation (NOT THE SAME AS WEATHER!) Usually based off annual variations |
|
|
What Determines Climate |
Global: different amounts of sunlight hitting the Earth |
|
|
Rainfall |
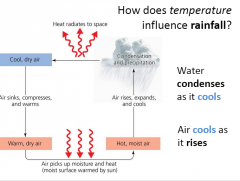
Water condenses as air cools |
|
|
Convection |
The rising and falling of air |
|
|
Convection Cells |
Hadley, Ferrell, and Polar |
|
|
Hadley Cell |
Equatorial Cells |
|
|
Ferrell Cell |
Mid-Latitude Cells |
|
|
Polar Cell |
Upper- Latitude Cells |
|
|
Coriolis Effect |
Spinning of the Earth causes winds to be deflected East and West (curvature of the winds) |
|
|
Prevailing Winds |
Convection and the Coriolis Effect cause wind to move all four directions |
|
|
Doldrums |
Regions of calm wind found near the equator |
|
|
Trade Winds |
the winds moving Southwest and Northwest in the Hadley Cells |
|
|
Prevailing Westernlies |
the winds the winds moving Southeast and Northeast in the Ferrell Cells |
|
|
Ocean Currents |
Wind currents push on the surface of the oceans Create surface ocean currents As surface water moves, deep water moves up to replace it Creating deeper ocean currents |
|
|
Seasons |
are regular, annual fluctuations in temperature, precipitation, or both |
|
|
Weather |
short-lived and local patterns of temperature and precipitation |
|
|
Milankovitch Cycles |
Long-term variations in Earth's climate |
|
|
Anthropogenic |
a human-caused climate change (global warming and greenhouse gases) |
|
|
Global Warming |
Rapid Increase of Global temps due to the excess amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere |
|
|
Greenhouse Gases |
Man-made chemicals that are destroying the atmosphere |
|
|
Leeward Side |
side of mountain in which dry air descends |
|
|
Windward Side |
side of mountain in which water falls as rain or snow |
|
|
Warm Front |
advancing air mass is warming than surrounding air and leads to light precipitation |
|
|
Cold Front |
advancing air mass is cooler than surrounding air and leads to heavy rain and thunderstorms |
|
|
Hurricanes |
the result of vigorously rising air in areas where water is warm and abundant |
|
|
Tornadoes |
caused by dry-air cold fronts colliding with humid warm fronts |
|
|
Axis of Rotation |
Earth is at a 23.5 degree angle that "wobbles" over a 26,000 year cycle which causes the changes in distribution and intensity of sunlight reaching the Earth's surface |
|
|
Jet Stream Hypothesis |
global warming has been more intense in global regions, thus weakening the Northern Hemisphere's jet stream |
|
|
Atmospheric Blocking Pattern |
Warming of the polar regions causes the jet stream to slow down and as it slows the loops of the stream become longer - creating prolonged bouts of weather |
|
|
Outcomes of Climate Change |
Rising Sea Levels |
|
|
Permafrost |
a thick subsurface layer of soil that remains frozen throughout the year, occurring chiefly in polar regions - Global warming is causing it to melt and release peat into the atmoshpere |
|
|
Peat |
dead organic matter covered by permafrost - when it is exposed huge amounts of CO2 and CH4 are released into the atmosphere |
|
|
Phenology Shifts |
warmer spring temperatures cause insects to mature earlier than usual so now bird migration no longer matches the time of peak abundance of food |
|
|
Kyoto Protocol |
Drafted in 1997 but took effect in 2005
Required emission reductions of sixgreenhouse gases back to levels in 1990 |
|
|
Jet Stream |
high altitude hurricane air force that blows air west to east |
|
|
Rising Sea Levels |
Glaciers are melting and oceans are getting warmer |
|
|
Threatened Coral Reefs |
warmer waters cause "bleaching" of coral reefs |

