![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bioregion |
Region defined by resources and the natural environment - watershed - soil - wildlife - plants - culture / history |
|
|
Levels of how we use our resources |
Exploit: overuse conserve: use wisely preserve: not use |
|
|
How/ why the environment changed over time/ 4 eras |
The 4 waves First wave: (1901-1909) Second wave: (1933-1941) Third Wave: (1960-1980) Fourth wave: (1980-present) |
|
|
Explain the first wave |
(1901-1909) Roosevelt created White House Conference on Natural Resources. He started this cuz of severe depletion of timber in the Great Lakes state. Result of meeting: National Conservation Commission - led to people in foreign countries also conserving |
|
|
Explain the second wave |
(1933-1941) FDR created the National Resources Board- it identified resource problems Examples of Roosevelts Programs: -The Prairie States Forestry Project -Civilian Conservation Corp ( CCC ) -Soil Conservation Service - Tennessee Valley Authority - The North American Wildlife and Resource Conference |
|
|
Explain the Prairie States Forestry Project |
¤Prairie States Forestry Project : Goal to establish shelter belts of trees and shrubs on farmland to reduce soil erosion from wind |
|
|
Explain the Civilian Conservation Corp |
Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) : constructed fire lanes, remove fire hazards, fought forest fires, controlled pests, and planted millions of trees. Also made lake and stream improvements and participated in flood control projects. Also constructed bridges improved roads and built hiking trails |
|
|
Explain the Soil Conservation Service |
Conducted soil conservation demonstrations to show farmers the techniques and importance of erosion control |
|
|
Explain the Tennessee Valley Authority |
Experiment to integrate the use of resources (water, soil, forests, and wildlife) an entire river basin |
|
|
Explain the North American wildlife and resources conference |
Set out to develop an inventory of the nation's wildlife resources and a statement on wildlife and other conservation problems, including policies by which those problems would be solved |
|
|
Explain the third wave |
(1960-1980) Gaylord Nelson and Denis Hayes came up with Earth day -books alerted the public to some of the nation's problems -like pesticides giving off ddt -laws were made to make resources last -formed the environmental protection agency |
|
|
Explain the fourth wave |
(1980-present) -shifts toward sustainable solutions -world commission on Environmental and Development - commission to address the issues and propose actions to promote a sustainable future - United Nations Conference on environmental and development aka earth summit: largest international meeting of the environment in the history of human civilization |
|
|
What has led to an environmental crisis? |
1. A large and rapidly growing human population 2. Excessive resource consumption and depletion 3. Local, regional, and global pollution |
|
|
How many in the human population currently and what are the trends and effects of each era? |
6.67 billion as of 2008 Expected 8 billion by 2025 ☆As population goes up pollution goes up and resources go down |
|
|
Renewable vs Non-renewable Resources |
Renewable - resources that can be renewed by natural processes Non-renewable - occur in fixed amount |
|
|
What are energy inputs and outputs |
Inputs: includes the commodities that companies need to produce goods and services, including raw materials, labor, and energy Outputs: include goods and services |
|
|
Command Economy |
The state or government manages the economy it makes all decisions about the distribution of income who gets what and what the economy produces and how much is produced |
|
|
Market economies |
The production, distribution, and price of goods and services are made by private individuals based upon their own and their customers interests |
|
|
Law of supply and demand |
Describes the market relationship between buyers and sellers |
|
|
GNP |
(Gross national product) The value of all goods and services produced by nation's economy, including all government expenditure and business activities occurring in other countries -measure of all goods and services |
|
|
GDP |
(Gross domestic product) All economic activity within the borders of a nation |
|
|
Sustainable ethics |
Hold that the the earth has a limited supply of resources -Earth's resources should be managed carefully -earth's resources are not for the exclusive use of humans |
|
|
Aldo Leopold |
Proposed a land ethic which held that humans are part of a larger community that includes the soil, water, plants, animals - which he referred to as the land |
|
|
Oil Producing and Exporting Countries (OPEC) |
Impose an embargo on oil, cutting back on exports and drastically raising the price |
|
|
What is the major source of energy in the industrialized world? |
Fossil fuel |
|
|
Energy conservation |
Cutting back of consumption, for example, by shutting off lights and turning down the thermostat |
|
|
Energy efficiency |
Employed technologies that allow us to get the most from the energy we consume, for instance, driving efficient cars or using efficient refrigerators |
|
|
When is peak oil? |
The US production peaked in 1971 extraction rates will continue to fall from the peak point |
|
|
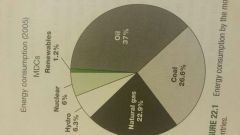
For each category what is the percent of energy consumed Hydropower Natural gas Coal Oil Renewable Nuclear |
|
|
|
What did Dr H M Hubbard say |
By 2030 50% of US energy supplies could come from renewable resources |
|
|
LED lights |
Uses 90% less electricity than flourecent light bulbs |
|
|
The National Appliances Energy Conservation act of 1987 |
Act called on manufacturers to produce appliances that use 20% less energy than 1987 models |
|
|
Green lights program |
Initiated by the epa -a nationwide energy conservation program aimed at reducing electrical demand by the nation's largest corporations and by gov't buildings |
|
|
Energy star program |
Calls on manufacturers of computers, printers, and monitors to reduce the energy demand of their machines, primarily by providing power down options |
|
|
Active solar systems |
Used to heat water for domestic use -can also be used to heat homes and other buildings -can provide 50-100% of a person's hit water needs -cost a little more than hot water heated by natural gas |
|
|
Passive solar systems |
-designed for space heating -don't require collectors or pumps or fans to move heat around |
|
|
Municipal solid waste -how much is produced |
Garbage -in 2005 221 million metric tons of solid waste |
|
|
What does most of the waste from US cities consist of? |
Paper Yard waste Food waste Some metal, glass, plastics |
|
|
Main ways to manage municipal solids |
▪Reduction approach ▪Reuse and recycle approach ▪Model recycling approach ▪Deepening our commitment to sustainable waste management ▪Promoting collection ▪increasing remanufactoring and procurement ▪creating a much more environmentally friendly recycling system |
|
|
End-point seperation |
Recyclable materials can be extracted from municipal trash at central recycling stations |
|
|
Source seperation |
Recyclables can be separated at the source - at homes and factories -and picked up by recyclers or delivered to recycling centers by producers |
|
|
Composting |
Occurs when organic matter is allowed to decompose to a stable, humus- like material |
|
|
Cocomposting |
Compost can be mixed with sewage sludge |
|
|
Incineration |
Burning municipal solid waste -can burn unseperated trash -the heat produced is often used to generate electricity and sometimes the steam is used for industrial processes and heating buildings |
|
|
Open dumps |
Piles of trash |
|
|
Sanitary landfills |
An excavation or hollow in the ground where garbage is dumped, compacted, and covered daily with dirt |

