![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is energy? |
Energy is the capacity to do work. |
|
|
What is the SI unit of energy? |
The SI unit of energy is joule (J) |
|
|
What is potential energy? |
Potential energy is defined as energy that is stored. |
|
|
State 3 types of potential energy. |
Potential energy exists in many forms: 1. Chemical potential energy - The food we eat contains chemical potential energy that can be converted to kinetic energy when we move our bodies. - stored in fossil fuels like coal and oil - a battery storee chemical potential energy that can be converted to electricity when connected to an electrical circuit. 2. Elastic potential energy 3. Gravitational potential energy An object has gravitational potential energy when it is raised to a certain height around the ground. When the object is released, it falls and gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. |
|
|
What is nuclear energy? |
Energy can be released by nuclear bond formation or rearrangement. The energy released in that way is used to produce electricity in nuclear power stations. |
|
|
What is internal energy? |
Internal energy is the sum of the kinetic energy of the molecules and potential energy between these molecules in a substance. In gases, the internal energy is mostly made up of kinetic energy. |
|
|
State 10 forms of energy. |
Forms of energy: GREENSTICK 1. Gravitational potential energy 2. Radiant (from light) energy 3. Elastic potential energy 4. Electrical energy 5. Nuclear energy 6. Sound energy 7. Thermal energy 8. Internal energy 9. Chemical potential energy 10. Kinetic energy |
|
|
State the Principle of conservation of energy. |
Principle of conservation of energy: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed in any process. It can be converted from one form to another or transferred from one body to another, but the total amount remains constant. |
|
|
State the conversion of energy of 1. A driver on a diving board 2. Hammering a nail 3. The burning of fuels such as oil, coal or wood. |
The conversion of energy of : 1. A diver on a diving board: Stored chemical energy in the body of a diver allows the diver to exert a push to bend the diving board. This causes the bent diving board to store elastic potential energy. This energy is then converted to kinetic energy that helps push the diver upwards. 2. Hammering a nail: Gravitational potential energy--> kinetic energy and sound energy and heat energy 3. The burning of fuels such as oil, coal or wood: chemical energy--> thermal energy and light energy |
|
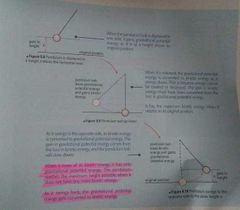
|
Learn |
|
|
Why the oscillating pendulum will eventually come to a stop? |

In the real world, there are frictional fores. As the pendulum swings, some of its total energy is converted to thermal energy due to frictional forces. |
|
|
What is the formula for energy input? |
Energy input = useful energy output + wasted energy output |
|
|
State the formula of efficiency of a machine. |
Efficiency = useful energy output/ energy output ×100% Or Efficiency = useful power output/power input ×100% |
|
|
What is a renewable energy source? |
A renewable energy source is one which can be replaced within a fairly short of time . An energy source that is always present is also a renewable energy source. |
|
|
What is a non-renewable source? |
A non-renewable source is one which cannot be replaced after use. It also includes energy sources that take millions of years to form. |
|
|
State 7 renewable sources of energy. |
Renewable sources of energy: Solar energy Geothermal energy Wind energy Tidal energy Wave energy Hydroelectric energy Biomass |
|
|
State 4 non-renewable source of energy. |
Non-renewable source of energy: Crude oil Natural gas Coal Nuclear (uranium) |

