![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
this is the largest zone of the adrenal gland, and is polyhedral, with large number of lipid droplets in cytoplasm
|
Zona fasciculata
|
|
|
What is Cushing Syndrome? Common cause? Other causes?
|
Hypercortisolism (increased glucocorticoids)
number one cause: exogenous GCs others: 1° hypothalamic – pituitary diseases associated with increased secretion of ACTH hypersecretion of cortisol by adrenal adenoma, nodular hyperplasia or carcinoma secretion of ectopic ACTH by a nonendocrine neoplasm |
|
|
What can be some of the causes of BILATERAL cortical hyperplasia?
|
pituitary adenoma,
ectopic ACTH production, or idiopathic adrenal hyperplasia |
|
|
is malignancy of the adrenal cortex more common in kids or adults?
|
adenomas and carcinomas are equally common in adults
carcinomas > adenomas in children |
|
|
levels of cortisol > with carcinoma or adenoma
|
CARCINOMA
|
|
|
if a pt has sky high levels of a hormone, how can you tell if you have an adenoma or carcinoma, considering that both elevate levels
|
metastatic disease
|
|
|
Ectopic secretion of glucocorticoids is most commonly seen with?
|
small cell carcinoma of the lung
|
|
|
VARIOUS FORMS OF CUSHING SYNDROME?
|
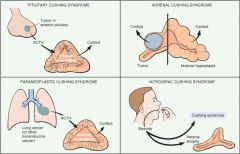
|
|
|
what are some of the main clinical signs of Cushing syndrome?
|
Central obesity – 85-90%
Moon facies – 85% Weakness, fatigability – 85% Hirsutism – 75% Hypertension - 75% Plethora – 75% Glucose intolerance/diabetes 75%/20% Osteoporosis – 75% Neuropsychiatric abnormalities – 80% Menstrual abnormalities – 70% Cutaneous striae – 50% Delayed wound healing |
|
|
this problem in the adrenal cortex causes Na retention, and K excretion...what is it? due to?
|
Primary Hyperaldosteronism
80% of time a solitary adenoma is cause (Conn syndrome) |
|
|
What is Conn syndrome?
*** |
80% of time a solitary adenoma is cause of Primary Hyperaldosteronism
|
|
|
a pt presents with episodic hypertension. After the die, you see a grey-tan color tumor on the adrenal...what is it?
|
PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA
|
|
|
virilization in girls
precocious puberty in boys due to? |
1° gonadal or adrenal disorders
|
|
|
what are the 3 distinctive syndromes associated with adrenogenital syndrome?
|
salt wasting adrenogenitalism – complete absence of hydroxylase activity & resultant mineralocorticoid and cortisol deficiency
--recognized after birth --salt wasting, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia & cardiovascular collapse simple virilizing adrenogenitalism without salt wasting & with incomplete loss of hydroxylase activity nonclassic adrenogenitalism – mild disease which may be asymptomatic or associated only with symptoms of androgen excess during childhood or puberty |
|
|
sudden increase in glucocorticoid requirements in patients with chronic adrenocortical insufficiency can lead to?
|
Adrenal insufficiency
|
|
|
rapid withdrawal of steroids with adrenal suppression 2° to long term glucocorticoid therapy can lead to
|
Adrenal insufficiency
|
|
|
failure to increase steroid doses in adrenalectomized patients during episodes of stress can lead to
|
Adrenal insufficiency
|
|
|
what is Waterhouse--Friderichsen syndrome? more often in what population?
*** |
Uncommon but catastrophic syndrome
overwhelming septicemic infection (usually caused by meningococci – occasionally by pneumococci, gono-cocci, staph) rapid progression to hypotension & shock DIC massive adrenal hemorrhage with insufficiency more often in children - - but may occur at any age ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY- OVERWHELMING SEPSIS WITH DIC |
|
|
TB can lead to what adrenal problem?
* |
Adrenal insufficiency (like Addison's)
look for an HIV or immunosuppressed pt |
|
|
Normal cause of adrenal insufficiency?
|
AUTOIMMUNE
60 – 70% - adrenals may be the only target – circulating antibodies are present 50% of the time |
|
|
what labs would you expect to find with adrenal insufficiency?
|
increased ACTH,
hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, volume depletion |
|
|
how can you distinguish 2ndary adrenocortical insufficiency from primary?
|
distinguished from 1° by:
absence of hyperpigmentation normal (or near normal) levels of aldosterone remember a 2ndary may be caused by any disorder of the hypothalamus or pituitary associated with decreased production of ACTH |
|
|
where do adrenal carcinomas met to?
|
LUNG
|
|
|
a pt presents to you with increased corticosteroids/sex steroids. pt has an xray that shows the left kidney has been displaced downward..what is going on
|
CORTICAL CARCINOMA
|
|
|
most medullary disorders are what?
|
malignant neoplasms
|
|
|
undefinable episodic HTN =?
*** TEST |
Pheochromocytoma
associated with catecholamine production & hypertension 85% arise within adrenal medulla 90% occur sporadically; some occur in familial syndromes von Hippel-Lindau von Recklinghausen Sturge-Weber |
|
|
What is the rule of 10 for pheochromocytoma?
|
10% occur in children
10% are bilateral 10% occur outside the adrenal gland 10% are malignant 10% are familial (MEN II & MEN III) |

