![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What kind of epithelium covers the surface of the ovary?
|
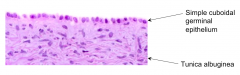
Cuboidal germinal epithelium
|
|
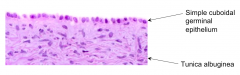
What is the cuboidal germinal epithelium of the ovary continuous with?
|
Serosa of the mesovarium
|
|
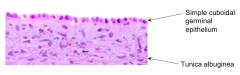
Do cells of the cuboidal germinal epithelium give rise to gametes?
|
No
|
|
|
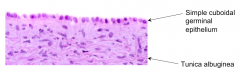
What is the layer of dense fibrous CT just deep to the epithelium?
|
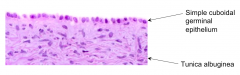
Tunica Albuginea
|
|
|
What is the Tunica Albuginea?
|
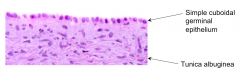
The layer of dense fibrous CT just deep to the epithelium
|
|
|
What are the types of follicles in the ovary?
|
- Primordial follicles
- Primary follicles |
|
|
Where are Primordial follicles located? What kind of cells surround them?
|
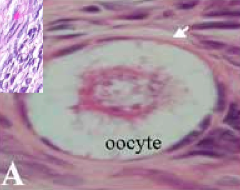
- Primordial follicles located peripherally
- Surrounded by a single layer of SQUAMOUS follicular cells (arrow) |
|
|
What surrounds the Primary follicles?
|
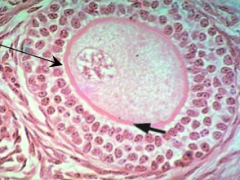
- Cuboidal follicular cells in either a single layer (unilaminar) or multiple layers (multilaminar)
- Zona Pellucida - homogenous, eosinophilic, non-cellular layer of glycoproteins and proteoglycans residing just inside the innermost layer of follicular cells |
|
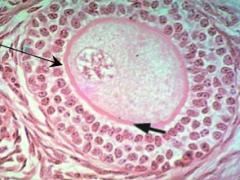
What kind of follicle is this? What do the arrows point out?
|
Primary Follicle
- Arrow points out the Zona Pellucida |
|
|
What is the Zona Pellucida? What kind of follicles is it seen in?
|
- Homgenous, eosinophilic, non-cellular layer of glycoproteins and proteoglycans
- Resides just inside the innermost layer of follicular cells in Primary Follicles |
|
|
Why does it appear that some oocytes lack nuclei?
|
They are very large cells, hence nuclei may be out of the plane of the section
|
|
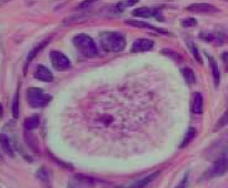
What kind of follicle is this?
|
Unilaminar Primary Follicle
|
|
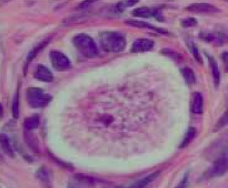
What kind of follicle is this?
|
Multilaminar Primary Follicle
|
|
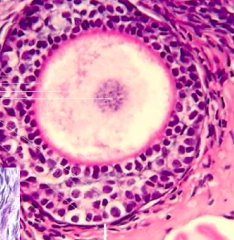
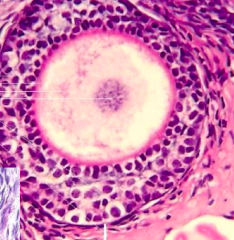
What kind of follicle is this?
|
Primordial Follicle
|
|
What kind of follicle is this?
|
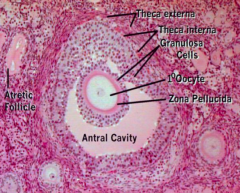
Secondary / Antral Follicle
|
|
|
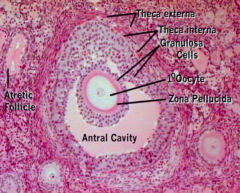
What are the components of a Secondary / Antral Follicle?
|
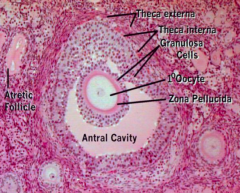
- Membrana Granulosa: follicular cells lining the antrum cavity
- Theca Interna: layers of cuboidal follicular cells bordering the membranous granulosa - Zona Pellucida - Antrum Cavity |
|
|
What is the term for the follicular cells lining the antrum cavity in Secondary / Antral Follicles?
|
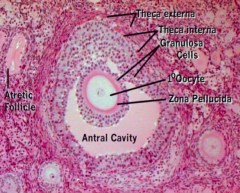
Membrana Granulosa
|
|
|
What is the term for the layers of cuboidal follicular cells bordering the membrana granulosa in Secondary / Antral Follicles? Function?
|
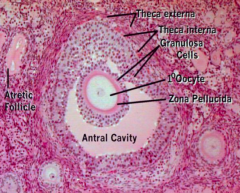
- Theca Interna
- Secrete estrogen precursors |
|
|
What determines which secondary follicles will continue maturation to the point of ovulation?
|
Density of FSH receptors
|
|
|
Which type of follicle bulges from the ovarian surface and can occupy the entire ovarian cortex?
|
Graafian Follicle
|
|
|
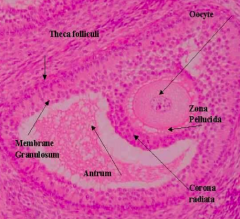
Which What are the components of a Graafian Follicle?
|
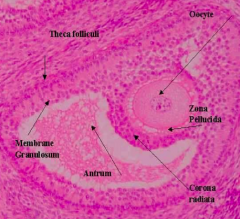
- Zona Pellucida
- Oocyte - Cumulus Oophorus - Corona Radiata - Antrum Cavity - Theca Externa |
|
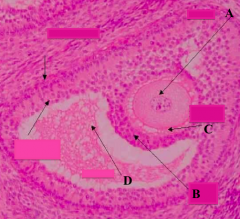
What type of follicle? What is structure A?
|
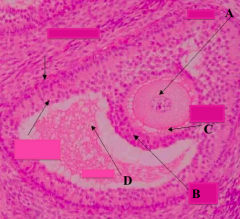
Graafian Follicle:
- Oocyte: nucleus and nucleolus may not be in the plane of section |
|
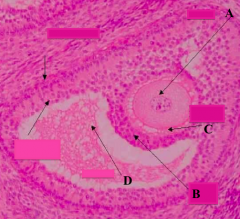
What type of follicle? What is structure C?
|
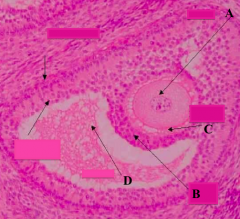
Graafian Follicle:
- Zona Pellucida |
|
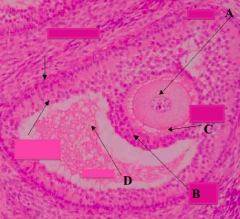
What type of follicle? What is structure B?
|
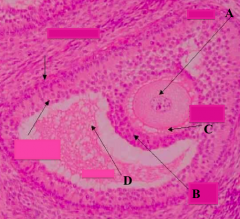
Graafian Follicle
- Corona Radiata (layer of cells just outside the zona pellucida |
|
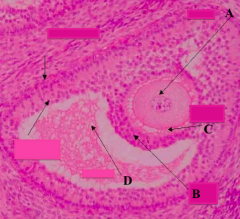
What part of the Graafian follicle is a stalk of cells supporting the oocyte (A) and corona radiata (B)?
|
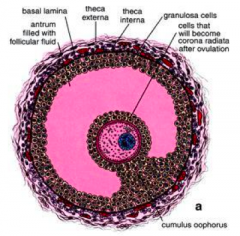
Cumulus Oophorus
|
|
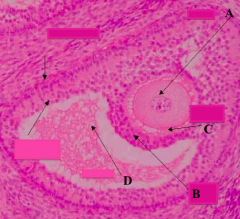
What type of follicle? What is structure D?
|
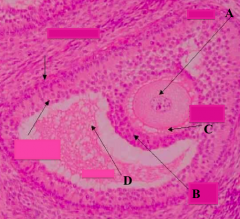
Graafian Follicle:
- Antrum Cavity |
|
|
What is the outer layer of the Graafian follicle? What does it contain?
|
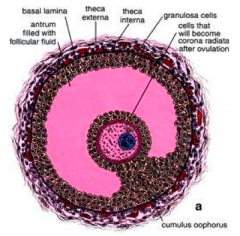
Theca Externa
- Several layers of spindle-shaped smooth muscle and CT cells along w/ collagen fibers just outside the Theca Interna - These cells merge with surrounding ovarian stroma |
|
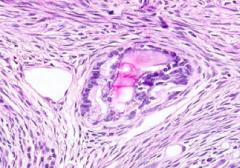
What can Atretic Follicles be derived from?
|
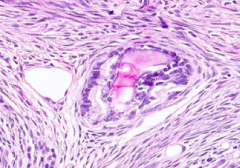
- Primary follicles
- Primordial follicles |
|
|
What are the signs that an atretic follicle (degenerationg) is derived from a Primary Follicle?
|
You will see a Zona Pellucida that is collapsed onto itself, these are easy to identify
|
|
|
What are the signs that an atretic follicle (degenerationg) is derived from a Primordial Follicle?
|
No Zona Pellucida will be evident
|
|
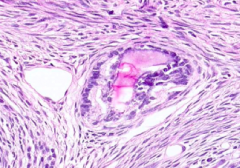
What kind of follicle is this?
|
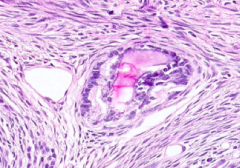
Atretic Follicle (undergoing follicular degeneration)
|
|
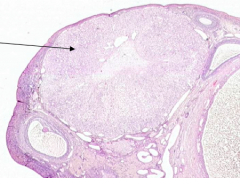
What does the arrow point out?
|
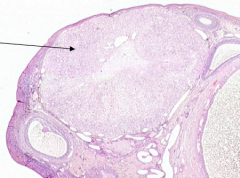
Corpus Luteum
|
|
|
What material occupies the follicular cavity after ovulation?
|
Eosinophilic material composed of CT-type infiltrate
|
|
|
What kind of cells surround the former follicular cavity?
|
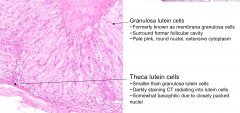
Granulosa lutein cells (formerly membrana granulosa cells); they stain pale pink w/ round nuclei and extensive cytoplasm
|
|
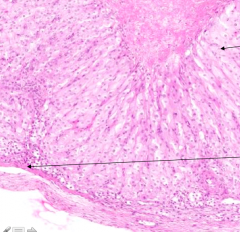
What does the long arrow indicate? Short arrow?
|
- Long arrow: Theca Lutein cells
- Short arrow: Granulosa Lutein cells |
|
|
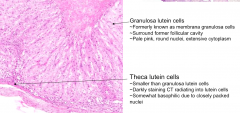
What is the darkly staining CT components radiating into the granulosa lutein cells?
|
Invagination contains Theca Lutein Cells
|
|
|
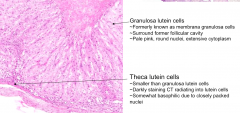
Which are bigger, Theca or Granulosa Lutein cells?
|
Granulosa Lutein Cells are larger
|
|
|
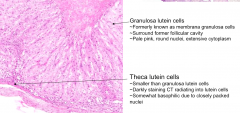
What are the large cells that stain pale pink w/ round nuclei and extensive cytoplasm in the corpus luteum?
|
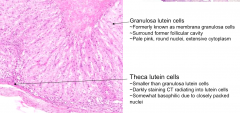
Granulosa Lutein Cells - formerly Membrana Granulosa Cells
|
|
|
What are the smaller somewhat basophilic cells d/t the closely packed nuclei?
|
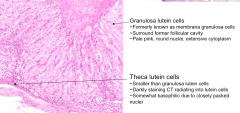
Theca Lutein Cells
|
|
|
What is the function of the Corpus Luteum?
|
Secretes progesterone to maintain the endometrial lining during pregnancy
|
|
|
List two secretory products of the Corpus Luteum?
|
- Progesterone
- Estrogen - Relaxin |
|
|
When a Corpus Luteum is replaced by scar tissue, what does it become?
|
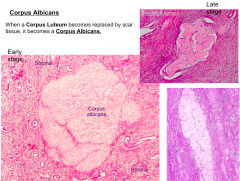
Corpus Albicans
|
|
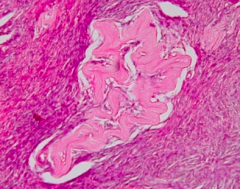
What is this structure?
|
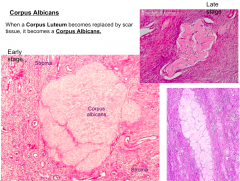
Corpus Albicans - the replacement of the corpus luteum by scar tissue
|
|
|
What is the uterine tube considered proximal and distal in relationship to?
|
In relation to the uterus, not the ovary
|
|
|
What is the funnel-shaped distal end of the uterine tube?
|
Infundibulum
|
|
What are the finger-like projections that extend from the infundibulum?
|
Fimbriae
|
|
|
What is the term for the distal 2/3 of the ovarian tube?
|
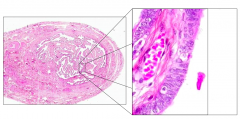
Ampulla
|
|
|
What type of epithelium lines the lumen of the ampulla of the ovarian duct?
|
Ciliated and Non-ciliated Simple Columnar
|
|
|
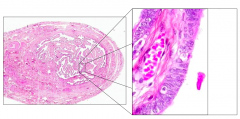
What is the term for the proximal 1/3 of the ovarian tube?
|
Isthmus
(Note: Mucosal folds are less numerous; inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of smooth muscle surround this tube) |
|
|
What is the segment of the ovarian tube that passes through the uterine wall?
|
Intramural part
|
|
|
How does the ampulla compare to the isthmus in the ovarian tube?
|
Ampulla:
- Distal 2/3 - Mucosa is highly folded - Lined by ciliated and non-ciliated simple columnar epithelium - Muscularis has inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of smooth muscle Ampulla - Proximal 1/3 - Mucosal folds are less numerous - Inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of smooth muscle surround this tube |
|
|
What surrounds the muscularis layer of the ovarian tube?
|
Mesosalpinx
|
|
|
What are the types of cells within the lining epithelium of the ovarian tube?
|
Simple columnar cells:
- Ciliated - Non-ciliated |
|
|
What kind of epithelium is found in the exocervix?
|
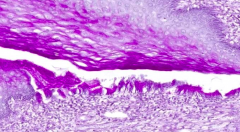
Stratified squamous non-cornified (wet type) epithelium
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is found in the cervical canal (endocervix)?
|
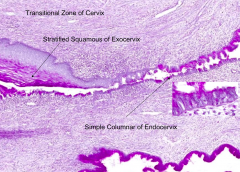
Simple columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What can you see histologically as you transition from the exocervix to the endocervix (cervical canal)?
|
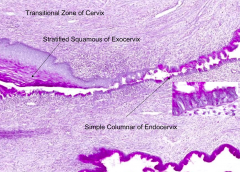
- Exocervix: stratified squamous, non-cornified (wet type)
- Endocervix: simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
What is the clinical significance of the transition from the exocervix to the endocervix?
|
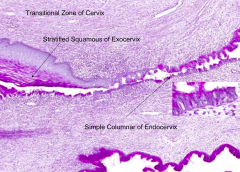
Squamous epithelial cells in this region may develop cervical carcinoma
|
|
|
What type of epithelium lines the wide, branched cervical glands?
|
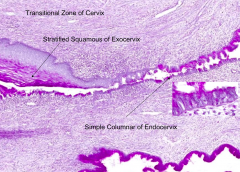
Simple columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What are the phases of the menstrual cycle?
|
1. Menstrual Phase (days 1-4)
2. Proliferative Phase (days 5-14) 3. Early Secretory Phase (days 15-18) 4. Secretory Phase (days 19-24) 5. Late Secretory Phase (days 25-28) |

