![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fentanyl |
MOA: opioid agonist —> analgesia + sedative effects Dose: 25-100 mcg IV q 1-2 hourly EM indications: pain control, sedation adjunct Pitfalls: respiratory depression, vasodilation (hypotension), laryngospasm, preg C |
|
|
Furosemide (Lasix) |
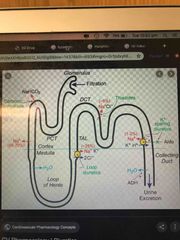
MOA: inhibits Na and Cl réabsorption in the ascending LOH and distal convoluted tubule Dose: 20-40mg IV, reassess, increase to desired effect, max single dose = 200mg EM indications: pulmonary oedema, CHF exacerbation, hyperkalaemia (if making urine) Pitfalls: volume depletion, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, ototoxicity, preg C |
|
|
Ketamine (Ketelar) |
MOA: acts on cortex and limbic system, NMDA receptor antagonist Dose: subdissociative 0.1-0.5 mg/kg IV Procedural sedation 0.5-1 mg/kg IV RSIinduction 2mg/kg IV EM indications: analgesia, sedation, RSI (rapid sequence induction) Pitfalls: emergence reactions (treat with benzos, barbs), laryngospasm, IOP increase, ICP increase, tachycardia, HTN, preg D |
|
|
Furosemide (Lasix) |
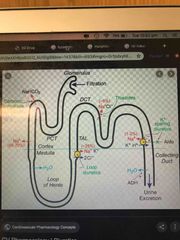
MOA: inhibits Na and Cl réabsorption in the ascending LOH and distal convoluted tubule Dose: 20-40mg IV, reassess, increase to desired effect, max single dose = 200mg EM indications: pulmonary oedema, CHF exacerbation, hyperkalaemia (if making urine) Pitfalls: volume depletion, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, ototoxicity, preg C |
|
|
Diazepam (Valium) |
Drug class: benzodiazepine MOA: enhances inhibitory effects of GABA Dose: 2-10mg PO/IV/IM q 6 hours PRN EM indications: seizure abnormality, alcohol withdrawal, agitation, muscle spasm Pitfalls: respiratory depression, hypotension, preg D |
|
|
Lorazepam (Ativan) |
Drug class: benzodiazepine MOA: enhances inhibitory effects of GABA Dose: usual bolus dose = 1-2 mg IV, usual continuous infusion = 1-10mg/hr EM indications: delirium tremens, status epilepticus, serotonin syndrome, agitation Pitfalls: respiratory depression, hypotension, preg D |
|
|
Magnesium sulfate |
MOA: participates in physiologic process Dose: eclampsia = 2-4 grams IV over 5 min, pulseless torsades = 2 grams IV push, asthma exacerbation= 2 grams IV over 5 min EM indications: torsades, ventricular dysrhythmias, eclampsia, status asthmaticus Pitfalls: respiratory depression, hypotension, preg A |
|
|
Methylprednisolone - SoluMedrol |
MOA: multiple glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid effects —> regulates BP, electrolyte balance, physiologic stress response, reduces inflammation and inhibits immune system Dose: asthma = 1mg/kg IV, hypersensitivity reaction = 1mg/kg IV EM indications: severe asthma, acute hypersensitivity reaction Pitfalls: immunosuppression, preg C
|
|
|
Methylprednisolone (Depo-medrone) + lidocaine 1% suspension for injection |
MOA: anti inflammatory + analgesia Dose: Depo medrol = 40mg/ml, small joint= 0.1-0.25ml, medium joint= 0.25-1ml, large joint 0.5-2ml. Eg at SJRH I performed inj on trochanteric bursitis= 1ml (40mg) + 3ml EM indications: intraarticular (RA, OA), periarticular (epicondylitis), intrabursal (subacromial, prepatellar, olecranon) and tendon sheath (tendinitis) Pitfalls: pull back on syringe to look for synovial fluid/ blood, move joint / area slightly to aid mixing, advise to return if signs of infection |
|
|
Metoclopramide (Reglan IV, Maxolon PO) |
MOA: antagonises dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone Dose: 10mg IV q 6 hours PRN EM indications: vomiting prévention and treatment Pitfalls: tardive dyskinesia, extrapyramidal sx, dystonia, methemoglobinema, preg B |
|
|
Morphine sulfate |
MOA: opioid agonist analgesia with adjunctive sedative effects Dose: 2-10mg IV q 2-6 hours PRN; recommended dose 0.1mg/kg IV EM indications: pain control Pitfalls: respiratory depression, vasodilation (hypotension), preg C |
|
|
Ondansetron (Zofran) |
MOA: antagonises serotonin 5-HT3 receptor, centrally acting antiemetic Dose: 4-8mg IV q 4-6 hourly PRN EM indications: vomiting prévention and treatment Pitfalls: QT prolongation, torsades (rare), preg B |
|
|
Propofol (Diprivan) |
MOA: GABA agonist, Na channel blocker Dose: procedural sedation = 1mg/kg IV bolus then 0.5mg/kg q 3 minutes to effect RSI induction = 1.5-2.5 mg/kg IV x1 EM indications: procedural sedation, RSI induction, ventilator sedation Pitfalls: hypotension, anaphylaxis, bradycardia, apnea, preg B |
|
|
Dobutamine Dopamine |
Drug class: sympathomimetics MOA: mimic agonist actions of E and NE Indication: short term hemodynamic support guided by continuous monitoring. Severe refractory HF with low CO despite adequate treatment. Pearls: Need continuous monitoring of arterial and venous pressure + ECG |

