![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
493 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
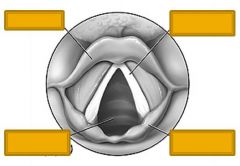
|
Epiglottis
Vocal cords Trachea Cartilage |
|
|
ACLS: to establish an aw:
-flex or extend neck? |
Extend neck (head tilt)
Flexing to chest will close aw |
|
|
ACLS: trauma pt without aw:
-perform head tilt/chin lift? |
No - may have C-spine injury
*Perform jaw thrust instead |
|
|
ACLS: trauma pt w/out aw:
-perform jaw thrust? |
Yes
Avoid head tilt/chin lift since may have C-spine injury |
|
|
ABCs: what is next step to establish aw:
-difficult time with ventilation using position and BVM alone |
Aw adjunct (oro or naso aw)
|
|
|
Oropharyngeal airway: where should flange end up (in relation to patient)?
|
Flange at lips
|
|
|
Facial trauma/significant head injury: which better to establish aw?
Oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal adjunct? |
Oro
Avoid naso if head trauma |
|
|
Intubate pt if GCS what value?
|
<8 --> intubate
|
|
|
RSI: pre-oxygenation:
-preO2 for how long? what %O2? -buys you how much time before desat? |
100% O2 x 5 minutes
Buys you 8 MINUTES before you see desat <90% |
|
|
RSI:
-pre-treat all pts? -what drug if head injury? -what drug if peds pt? |
Pre-treatment falling out of favor
Head injury: lidocaine or fentanly Peds: atropine |
|
|
RSI: induction or paralytic?
Etomidate |
Induction
|
|
|
RSI: induction or paralytic?
Propofol |
Induction
|
|
|
RSI: induction or paralytic?
Versed |
Induction
|
|
|
RSI: purpose of induction agent?
|
To sedate pt --> prepare for paralysis
|
|
|
RSI: induction or paralytic?
Succinylcholine |
Paralytic
|
|
|
RSI: what INDUCTION agent is fast on/off?
|
Succinylcholine
|
|
|
Succinylcholine:
-slow or fast on? -slow or fast off? |
Fast on & off
|
|
|
RSI: non/depolarizing?
Succinylcholine |
Depolarizing
|
|
|
RSI: non/depolarizing?
Vecuronium |
Non-depol
|
|
|
RSI: non/depolarizing?
Rocuronium |
Non-depol
|
|
|
Induction agents: which has higher risk of S/E hyperkalemia?:
Succinylcholine or Rocuronium |
Succinylcholine (depolarizing)
|
|
|
Induction agents: which is longer acting?
Succinylcholine or Rocuronium |
Roc
|
|
|
RSI: which better position?
Sniffing (head tilt/chin lift) or jaw thrust? |
Sniffing (oropharynx & trachea in line)
-however cannot do in trauma, obesity, kyphosis |
|
|
Mac blade: tip in what anatomical location?
|
Velecula --> indirectly lift up epiglottis
|
|
|
Miller blade: tip in what anatomical location?
|
Epiglottis --> lift directly (contrast Mac blade)
|
|
|
What intubation blade:
-directly lift epiglottis -lift velecula |
Direct: Miller
Indirect: Mac |
|
|
Intubation blade:
Which type preffered in peds? |
Miller (straight)
|
|
|
RSI: sweep tongue to L or R?
|
PATIENTS LEFT
|
|
|
Endotracheal tube sizing:
-DIAMTER in adult F - adult M - peds |
adult F: 7.5-8.0mm
adult M: 8.0-8.5mm in adult men Peds - Winters formula (age/4) + 4 |
|
|
WINTERS FORMULA
-used when? -what is it? |
To determine DIAMETER of endotrach tube in peds
Length (mm) = (age/4) + 4 |
|
|
RSI: where should tube be located in relation to carina?
|
2 cm above carina
|
|
|
RSI: how estimate LENGTH of ETT?
-common length F? -M? -Peds? |
Mouth corner to sternal notch
F: 21 cm long, 7.5-8mm wide M: 23 cm long, 8-8.5 mm wide Peds: wide: (age/4) + 4 Length: 3 x width |
|
|
Chest pain: BIG 5 (fatal causes of CP)
|
1. Esophageal rupture
2. Ao dissection 3. Tension PTX 4. PE 5. MI |
|
|
Acute coronary synds:
What % pts with ACS presenting to ED will end up surviving to discharge? |
6%
|
|
|
What % MIs are silent?
|
30%
|
|
|
MI: are cardiac risk factors (e.g. smokers) good predictors of MI?
|
NO - NOT IN ED
*presence of chest pain outweighs all other risk factors in terms of predicting MI |
|
|
ACS: is physical exam helpful to distinguish "cardiac" vs "noncardiac" etiology of chest pain?
|
NO
(unless obvious other dx, e.g. PTX) |
|
|
MI: what % pts have S3?
|
20%
(i.e. few) |
|
|
MI: what % pts have "chest wall tenderness"?
|
15%
(i.e. cannot say 'chest wall tenderness = chostochondr) |
|
|
MI: single best test to determine MI
|
EKG
|
|
|
MI & EKG:
-what % MI pts have ST elev? -what % have initial normal EKG? -what % unstable angina has normal EKG? |
ST elevation: only 50%
Initial normal: 5% Unstable angina with normal EKG: 5-20% |
|
|
National guideline: it pt p/w possible ACS --> must obtain EKG w/in how many minutes?
|
10 minutes
|
|
|
ACS:
Is Troponin a standard of care? |
Yes
|
|
|
Troponin:
What % sensitivity to detect MI? (initial troponin) |
Detects 40% MIs
(i.e. serial enzymes much better) |
|
|
Troponin:
Normal in unstable angina? |
Yes - normal in most unstable angina
|
|
|
CK-MB:
-detect what % MI at presentation? -what % have 5-6h MI? |
50% at present --> 90% after 5-6h
|
|
|
What cardiac marker:
peaks at 12h (fastest marker) |
Troponin T
|
|
|
Troponin T:
Peaks how many hrs s/p MI? |
12h
(fastest) |
|
|
CK-MB:
Peaks how many hrs s/p MI? |
18-24h
(slowest; Trop T peaks at 12h) |
|
|
Which elevated longer s/p MI:
Trop T or CK-MB (what is duration elevated each) |
Trop T: 5-14d
CK-MB: 2d |
|
|
MI: which decreases mortality the most?
ASA or streptokinase |
SAME - 23%
|
|
|
CP r/o MI:
What dose ASA? |
325 mg
|
|
|
MI: ASA works via what mxn?
|
Inh thromboxane A2 --> no plt agg
|
|
|
What drug:
Inh thromboxane A2 --> no plt agg |
ASA
|
|
|
Nitrates: decrease pre- or afterload?
|
BOTH
|
|
|
MI: are nitrates safe if pt has underlying....
-CHF -HTN |
YES - EXCELLENT FOR BOTH
|
|
|
Nitrates: do not use if MI in what area of heart?
|
RV
|
|
|
Unstable angina: give what drugs?
|
ASA 325
PLUS HEPARIN (or enox) |
|
|
What drug:
Binds AT-III --> inactivates thrombin |
Hep
|
|
|
Heparin: mxn of action
|
Binds AT-III --> inactivates thrombin
|
|
|
AMI: what drugs?
|
ASA 325
Hep BETA-BLOCKER |
|
|
Cocaine-induced CP:
Tx with what drugs? |
ASA
Nitrate Benzo (tx HTN, tachy) +/- heparin +/- CEB AVOID B-blockers |
|
|
Cocaine-induced CP: avoid what drug class when treating
|
Beta-blockers
(CEBs are safe) |
|
|
Aortic dissection: disset what BV layer?
|
Tear intima --> blood enters media
|
|
|
Aortic dissection:
#1 location (anatomical) |
Ligamentum arteroisum (ASC ao)
|
|
|
What dz:
Stanford Classification |
Aortic dissection
(A asc +/- desc; B desc only) |
|
|
Aortic dissection:
-What system to classify? -What does A vs. B indicate? which more common? |
Stanford Classific.
A: 80%; ascending (+/- desc) B: desc only |
|
|
Pregnant + CP: what is fatal etio?
|
Aortic dissection
(preg --> increased risk dissect) |
|
|
Aortic dissection:
Increased risk in what connective tissue disease(s)? |
Marfan
AND Ehler-danos |
|
|
Aortic dissection: does SURGERY improves outcomes in:
-type A -type B |
A: decrease mortality from 75% --> 20%
B: no change (30%) |
|
|
What disease:
Tearing/ripping acute pain b/w scapulae |
Ao dissect
|
|
|
Aortic dissection:
See DULL/PRESSURE-like pain? |
POSSIBLE
(not always ripping/tearing) |
|
|
Aortic dissection:
n/v, diaphoresis common? |
YES
(resembles MI) |
|
|
Aortic dissection:
-common/rare to see normal lung & cardiac exam -what % have murmur (Ao insuff) -what % have unequal/absent pulses? |
Common to have normal exam
20% have murmur Only 50% have changes in pulses |
|
|
Aortic dissection:
What % have some abn on CXR? |
85%
|
|
|
Aortic dissection:
If suspect dissect --> order EKG? |
Yes
IVs --> EKG |
|
|
Aortic dissection:
Tx - lower BP? (goal BP?) |
Yes -- decrease pressure on intima
Goal SBP: 100-110 |
|
|
Aortic dissection:
Initial meds? |
NIPRIDE + ESMOLOL
|
|
|
#1 non-surgical peripartum maternal death
|
PE
|
|
|
PE: due to DVT in what %?
|
80-90%
UE in 10% |
|
|
#1 risk factor PE
|
previous DVT or PE
|
|
|
PE: what % pts have no identifialbe risk?
|
10-15%
|
|
|
PE: #1 sign OR symptom
|
RR > 16 (90%)
(dyspnea 85%, pleuritic CP 75%) |
|
|
PE: what % have ST or T wave abns?
#1 EKG finding? |
only 40%
#1: sinus tachy |
|
|
PE:
-CLASSIC EKG finding? -what % pts have this finding? |
S1Q3T3
6% pts |
|
|
PE:
Normal A-a gradient = (formula) |
Normal = 10 + 0.1(age)
|
|
|
PE:
What % pts have normal A-a gradient? |
>20%
|
|
|
PE: CXR shows atelectasis in what % pts?
|
50%
|
|
|
What is:
-Hampton's Hump -Westermark's sign |
Hump: wedge-shaped infiltrate (PE)
Westermark: prox-dilated pulm art w/abrupt cutoff (PE) BOTH RARE |
|
|
PE: name for:
-wedge-shaped infiltrate -proximally dilated pulm art |
Wedge = Hampton's Hump
Dilated art = Westermark sign |
|
|
PE: if suspect:
-order imaging study OR anticoag 1st? -What meds & dose to anticoag? |
if high pre-test --> ANTICOAG FIRST!
low pretest --> image 1st Heparin 80 U/kg i.v. bolus; 18 U/kg/hr i.v. drip |
|
|
Spont PTX-
-what % occur w/exertion? |
only 10% with exertion
|
|
|
Spont PTX:
-what % pts have pleuritic CP? - % have >24 rr? -hyperressonance? |
WOOOOAH!!!
pleuritic CP: 95% Tachypnea: ONLY 5% Hyperresonance: <1/3 |
|
|
Spont PTX: observe for how long s/p decompression/CT?
|
6h
|
|
|
Ao dissection: can you use labetalol to lower the bp?
|
YES
(or nipride + esmolol) (NOT nipride alone) |
|
|
Dyspnea: what fraction pts have cardiac or pulm etio?
|
2/3
|
|
|
Hyperpnea: definition
|
hyperventilation, minute ventilation in excess of metabolic demand; deep, rapid or labored respirations
|
|
|
#1 chronic dz of childhood
|
asthma
(not DM) |
|
|
Asthma: is BRONCHOSPASM the mxn of asthma or only a symptom?
|
ONLY A SYMPTOM
(mxn is INFLAMMATION) |
|
|
Asthma: irreversible changes?
|
If chronic & untx --> can see irrevers worsening
|
|
|
Asthma: care about baseline peak flow from ED standpoint?
|
Yes -- ask
|
|
|
Asthma: risk factors for death:
->___ hosps in past year -> ___ ED visits past year -> ___ MD canisters in 1 mo |
2+ hosps
3+ ED visits 2+ MDI canisters Also poor px: difficulty perceiving severity of aw obstrxn |
|
|
Asthma: do you hope to hear a silent chest (no wheezing)?
|
NO --- REALLY BAD
Means not enough air moving to produce a wheeze |
|
|
Asthma: which is better estimate of severity of attack:
-Pt report OR peak flow measure? |
PEAK FLOW --- use these in ED!
|
|
|
Asthma exacerb: order a CXR?
|
Not unless suspect 2' comp (PTX, PNA)
|
|
|
Asthma: order ABG?
|
May be useful
-tachyp --> should see decreased PCO2 - if elevated PCO2 --> suspect fatigue |
|
|
Asthma: general classes of ED tx
|
1. B-agonists
2. Steroids 3. Anticholinergics 4. Severe: magnesium, mech vent |
|
|
B2-agonists: dlilate LARGE or SMALL aws?
|
SMALL
(contrast anticholinergics) |
|
|
Albuterol: which better
-Nebulized or MDI? -what dose & freq each? |
SAME
Neb: 5 mg q 20 minutes MDI: 6-12 puffs q 20 minutes |
|
|
B2-agonists: what S/E?
|
Tachy
HTN HA Tremor |
|
|
Anticholinergics: dilate LARGE or SMALL aws?
|
Large central aws
(contrast B2-agonists: small) |
|
|
What drug class:
Competitively antagonize ACh at neurogang jxn |
Anticholinergics
|
|
|
Anticholinergics: mxn of action
|
Comp inh ACh at NMJ
|
|
|
Asthma: how deliver anticholinergics?
|
MDI or neb
|
|
|
Asthma: anticholinergics have what S/E?
|
Dry mouth
Thirst Irritability |
|
|
Asthma: deliver steroids w/in how long after presenting to ED --> decrease admit rates
|
Deliver w/in <1h
|
|
|
Asthma: steroids:
-better to deliver IV or PO? -dose in adult? -child? |
IV & PO equally effective (clinical picture)
Adult: 125 mg methylpred IV or 60 mg pred po Child: 1 mg/kg methylpred IV or 1mg/kg pred po 5d (NO TAPER REQ) |
|
|
Asthma: what dose Mg?
|
1-3g IV
|
|
|
Asthma: benefit to POSITIVE PRESSURE aw?
|
Yes - CPAP & BiPAP shown to improve outcomes
|
|
|
Asthma:
-if decide ETT --> what is best induction agent? |
Ketamine -- bronchodil & resp stimulant
|
|
|
Asthma: if ETT --> allow hypoventilation?
|
YES - if maintains sat >90%
|
|
|
Asthma: when admit?
|
1. No improve s/sx
2. Peak flow <50% |
|
|
Asthma: give steroids to which pts presenting to ED?
|
ALL PATIENTS
(no req taper if 5d; yes if 10-14d) |
|
|
PNA:
Suspect what pathogen if HEMATOGENOUS spread (rather than inhaled)? |
Staph aureus
|
|
|
PNA:
ID pathogen in what % pts? |
50%
|
|
|
PNA:
#1 pathogen |
Strep pneumo
|
|
|
PNA:
3 atypicals |
Mycoplasma
CHlam Legionella |
|
|
PNA:
Is CP related to resp? |
YES - pleuritic CP
|
|
|
ATYPICAL PNA:
-fever? -productive cough? |
LOW fever; non-productive cough
(contrast typical) |
|
|
Indicates what process (physically what's going on):
-Inspiratory rales -Bronchial breath sounds - Rhonchi |
Rales: = alveolar fluid
Bronchial breath sounds= consolidation Rhonchi= Bronchial congestion |
|
|
Pneumococcal PNA: what 2 pt pops?
|
1. Extreme ages
2. Chronic ill (e.g. HIV) |
|
|
What SPECIFIC dz:
Sudden onset of rigors, bloody sputum, high fevers, chest pain |
PNEUMOCOCCAL pneumonia
|
|
|
Pneumococcal PNA: pleural effusion in what %?
|
25%
|
|
|
What PNA pathogen presents with ELEVATED LFTs?
|
Pneumococcal PNA
|
|
|
Pneumococcal PNA: see resistant strains?
|
Increasing
|
|
|
Staph aureus PNA: acute or insidious?
|
INSIDIOUS/GRADUAL
(contrast pneumococcal: acute onset) |
|
|
Staph aureus PNA: see focal OR multiple infiltrates?
|
MULTIPLE
(remember - hematogenous spread) |
|
|
What type of PNA (pathogen):
-EtOHics |
Klebs
|
|
|
Klebsiella PNA: gradual or acute f/c & cp?
|
ACUTE
(sim pneumococcus) (contrast staph - gradual) |
|
|
Pseudomonas PNA: mild or severe?
|
SEVERE - confusion, syst illness
|
|
|
PNA: suspect what pathogen
Bilater lower lobe infiltrates |
PSEUDOMONAS
|
|
|
Pseudomonas PNA: risks?
|
hospitalized, recent abx or steriods
|
|
|
Haemophilus PNA:
-what pt pops? - how does CXR appear? |
Elderly, lung disease, alcoholics
Pleural effusions, multilobar infiltrates |
|
|
PNA: what pathogen?
-transplant pts |
LEGIONELLA
|
|
|
PNA: what pathogen?
common in SUMMER months |
Legionella
|
|
|
PNA: what pathogen?
p/w GI sxs! (n/v/d, abd pain) |
Legonella
|
|
|
Legionella PNA:
-what time of year? -how appear CXR? |
Summer
PATCHY INFILTRATES |
|
|
PNA: what pathogen
-also p/w sore throat, mild fever, non-prod cough |
Chlamydia OR mycoplasma
(mycoplasma also see rash) |
|
|
PNA: what pathogen:
May p/w RASH |
Mycoplasma
|
|
|
PNA: CXR confirms dx in what % pts?
|
only 50%
|
|
|
PNA: suspect what pathogen:
LOBAR INFILTRATES |
PNEUMOCOCCUS
|
|
|
PNA: a/typical:
Hilar adenopathy |
Atypical
|
|
|
PNA: what 3 pathogens more likely in ETOHICS?
|
1. Klebs
2. Pneumococc 3. Haemophilus |
|
|
PNA: DM pts:
-what is increased risk of PNA? -what 3 pathogens? |
3-4 increased risk (vs. non-DM)
Staph aureus, gram negatives, Mucor |
|
|
PNA & pregnancy:
-what birth comps? -suspect what pathogen if resp distress in mom? -what pathogen if AIDS mom? |
low bw & preterm
Resp distress --> think VZV AIDs: PCP pneumonia in preg |
|
|
PNA in elderly: common to see normal/low WBC?
|
yes
|
|
|
PNA: #1 pathogen in HIV pt
|
Pneumococcus (same as gen pop)
|
|
|
PNA in HIV pt: suspect what type (bact vs. viral vs. fung) if:
CD4>800 CD4 250-500 CD4< 200 |
CD4>800: Bacterial more common
CD4 250-500: TB, cryptococcus, histoplasma CD4< 200: PCP, CMV |
|
|
PNA: 3 drugs for OUTPT tx
|
Doxycycline
Macrolide (azythromycin) Fluroquinolone (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin) |
|
|
PNA: what pathogen in CF pt? tx w/what drug?
|
Pseudomonas
Cefepime or ciprofloxacin |
|
|
PNA: how tx INPATIENT? (3 options)
|
3rd gen cephalo
pen w/lactamase inh + macrolide Fluoroquino |
|
|
What % CAP does NOT req admit?
|
75%
|
|
|
What dz:
Barrel chest |
COPD
|
|
|
What is the only cause of death in US that is INCREASING?
|
COPD
|
|
|
COPD:
-#1 risk |
Smoking
(developing world: cooking in confined space) |
|
|
What % smokers develops COPD?
|
only 15%
|
|
|
What dz:
Part of pathogenesis is Protease-Antiprotease Imbalance |
COPD
|
|
|
What dz:
Tripod |
COPD
|
|
|
What dz: CXR shows:
Hyperinflation Flattened diaphragms Increased AP diameter Increased parenchymal lucency Attenuation of vascular shadows |
COPD
|
|
|
COPD: EKG shows deviation in what direction?
|
RAD
|
|
|
Suspect what dz: EKG with:
Wandering pacemaker, multifocal atrial tachy, low voltage |
COPD
|
|
|
2 signs of hypercapnia
|
1 altered MS
2. Hypopnea (NOT tachyp, tachyc, htn) |
|
|
COPD:
-danger of suppl O2 -goal sat |
Supp O2 --> decrease hypoxia & resp drive (despite fact that you are retaining CO2) --> resp arrest
90-92% |
|
|
COPD: what initial drug therapy in ED?
|
Alb-ATROVENT (antichoin) neb ---> THEN alb alone
(IMPORTANT) |
|
|
COPD flair: give abx? steriuds? PPV?
|
YES - doxy --> small improve in outcome
STeroids --> improved outcomes & longer time to relapse CPAP/BiPap --> decreased need for ETT (note: pt must be able to cooperate) |
|
|
CHF: after develop pulm edema --> what % pts survive past 1 year?
|
<50%
|
|
|
CHF:
-CXR changes may lag behind clin picture by how much time? |
6h
|
|
|
CHF: what % pts have pulm congestion on CXR?
|
only 60%
--> do NOT base tx on CXR alone |
|
|
CHF: initial drug tx --> then what drug?
can you give morphine? |
Nitroglycerin sublingual or IV drip --> nitroprusside drip (if BP still elevated)
Morphine good! venodilator --> decreases preload |
|
|
CHF: goal to in/decrease:
-preload -after |
Decrease both
|
|
|
BNP: release via what mxn? what # considered negative?
|
STretch VENTRICLES
<100 is negative |
|
|
CHF: affect mortality?
-BiPAP -CPAP |
BiPAP: decrease ETT; no change mortality
CPAP: higher rates MI |
|
|
What % abd pain is NONSPECIFIC?
|
25%
|
|
|
Abdominal pain: diagnostic accuracy of physicians?
|
50%
|
|
|
Abd pain: awhat % require surg?
|
15-30%
|
|
|
Abd pain: top 4 etios in elderly
|
1. Acute cholecystitis (25%)
2. Malignant disease 3. Ileus 4. NSAP |
|
|
Abd pain: top 2 SURGICAL etiologies
|
1. Acute appendicitis
2. SBO (cholecystitis is LOW - 5%) |
|
|
Cholecystitis: what % have localized RUQ pain?
|
40%
|
|
|
Appendicitis: what % pts do NOT have anorexia?
|
>10%
|
|
|
Acute abd pain: what % have TYPICAL presentations?
|
60-70%
(30% present in ATYPICAL way) |
|
|
What portions of duodenum are intra-abd but EXTRA-peritoneal?
|
2-4
(only 1st is intra-peritoneal) |
|
|
Intra- or extra-peritoneal?:
Pancreas |
Extra
|
|
|
Visceral or somatic pain?:
Autonomic sensory fibers |
Visceral
|
|
|
Visceral or somatic pain?:
Bilateral innervation --> midline perception |
Visc
|
|
|
Visceral or somatic pain?:
Vague, deep, poorly localized |
Visc
|
|
|
Midline visc abd pain: what nerves supply?:
EPIGASTRIC pain |
celiac sympathetic plexus; some parasymps
|
|
|
Midline visc abd pain: what nerves supply?:
Periumbilical |
Celiac symp plexus
Superior mesenteric ganglia |
|
|
Midline visc abd pain: what nerves supply?:
HYPOGASTRIC |
inferior mesenteric ganglia
Pelvic parasymps |
|
|
Visceral or somatic pain:
Unilat innvervation (periph nerves) |
Somatic (peritoneal)
|
|
|
Visceral or somatic pain:
Sharp, localized |
Somatic (peritoneal)
|
|
|
Visceral or somatic pain:
INVOL GUARD & REBOUND |
Somatic (peritoneal)
|
|
|
Rectocecal appendix: pain in which quadrant?
|
UPPER LEFT!
|
|
|
SBO: acute or gradual onset?
|
GRADUAL
|
|
|
Abd pain: exam pt in RECLINED or FLAT position?
|
FLAT!
|
|
|
Eponynms: what is it & what does it indicate?:
Cullen's sign |
Blue umbilicus
Retroperitoneal hemorr (pancreatitis, AAA) |
|
|
Eponynms: what is it & what does it indicate?:
Kehr's sign |
Severe L shoulder pain
splenic rupture, ectopic preg rupture |
|
|
What eponynm:
Severe L shoulder pain due to splenic/ecoptic preg rupture |
Kehr's sign
|
|
|
Eponynms: what is it & what does it indicate?:
Iliopsoas sign |
extend R hip --> abd pain
Append |
|
|
Eponynms: what is it & what does it indicate?:
Obturator sign |
Int rotate (flexed) R hip --> pain
Append |
|
|
Eponynms: what is it & what does it indicate?:
Palpate LLQ --> pain in RLQ |
Rovsing's sign
Append |
|
|
Peritoneal signs: common to see with:
- extra-abd disease? - intra-abd, extraperitoneal disease (e.g. pancreatitis)? |
NO!
Almost always due to intra-abd, intra-peritoneal dsease Exceptions: SBO, mesenteric isch |
|
|
Microscopic hematuria:
Defin: how many RBCs per hpf? |
3+ RBCs/hpf
(contrast pyuria: 5+ WBCs) |
|
|
Microscopic hematuria:
How SENSITIVE for acute ureteral calculus? |
>90%
|
|
|
Pyuria:
Defin: how many WBCs per hpf? |
5+ WBCs/hpf
(contrast hematuria: 3+) |
|
|
Abdominal pain: what % plain films ordered will have abnormality? Change management in what % pts?
|
Only 10% will have abn
Change managements in 10% |
|
|
Abdominal PLAIN film: 2 uses
|
1. Free air
2. Obstruction |
|
|
Abdom PLAIN film: can see what VOLUME (how many ccs) of free air? which view (PA or lat) is more sensitive?
|
1 cc detectable
Lat most sensitive |
|
|
Acute abdominal series: includes what views? (3)
|
upright CXR
Supine abd Upright abd |
|
|
Suspect what dz:
RUQ U/S negative, HIDA scan positive |
Acalculous cholecystitis
|
|
|
AAA: what % rupture into retroperitneum?
|
75%
|
|
|
AAA: classic triad
|
1. abd pain
2. pulsatile mass 3. hypoT |
|
|
What should be 1st thought:
Old man with back pain |
AAA
|
|
|
AAA: #1 mis-dx
|
Renal colic
|
|
|
Mesenteric ischemia: what % pts have occlusion:
-SMA -IMA -no occlusion |
SMA: 50% (50% thrombosis, 50% embolus)
IMA: 25% non-occlusive: 25% |
|
|
Mesenteric ischemia:
common to see abd findings before irrevers injury? |
NO -- may have irrevers injury before any findings
|
|
|
What dz:
abd XR: thumbprinting, bowel wall thickening, gas in bowel wall |
Mesenteric ischemia
|
|
|
Mesenteric isch: how affect WBC?
|
Increase WBC
|
|
|
Perform angiography?:
-AAA -mesenteric ischm |
AAA: no- usu too unstable; do CT
Mes Isch: YES - dx & therapteutic |
|
|
Appendicitis:
What is lifetime risk (%) |
7%
|
|
|
Appendicitis:
Perforation rate highest in young, adult, or elderly? |
ELDERLY have highest perf
|
|
|
Appendicitis:
-overall mortality -mortality in elderly |
<1% overall
5-15% in elderly |
|
|
#1 surg emerg in preg
|
Appendicitis
|
|
|
Appendicitis:
What % exlaps are negative? |
15-20%
|
|
|
What dz:
Alvarado score |
Appendicitis
|
|
|
Suspect what dz:
RLQ --> sudden improvement |
Perforated appendix
(feels good at first!!!) |
|
|
Ectopic preg: triad
|
1. Abd pain
2. Amenn 3. Vag spotting (70% pts) |
|
|
Ectopic preg: common to see preg on U/S?
|
No
|
|
|
Heterotopic pregnancy:
-overall risk -risk if s/p in vitro drugs |
1:3,000
1:300 |
|
|
IUP: see pregnacny at WHAT HCG level? how many weeks?
-transvaginal -transabd |
TV: 5 weeks, 1,200-2,000
TA: 6 weeks, 6,000 |
|
|
Acute surgical abdomen: common to see pain OR vomit first?
|
pain --> vomit
(except in elderly - may not have pain) |
|
|
#1 surg emergency in kids >1yo
|
Appendicitis
|
|
|
Does a NORMAL acute abd series r/o perforation?
|
NO
|
|
|
U/S: linear or curved probe:
higher freq |
Linear
|
|
|
U/S: linear or curved probe:
Shallow penetration |
Linear
(higher freq --> shallow pen) |
|
|
U/S: linear or curved probe:
DVT |
Linear
(high freq --> shallow pen) |
|
|
U/S: linear or curved probe:
SubQ abscess |
Linear
(high freq- shallow pen) |
|
|
U/S: linear or curved probe:
Occular |
Linear
(high freq --> shallow pen) |
|
|
U/S: linear or curved probe:
Low freq |
Cuved
|
|
|
U/S: linear or curved probe:
Chest, abd & pelvic scans |
Curved
|
|
|
U/S: linear or curved probe:
higher resolution |
Linear
(high freq) |
|
|
What is dx?
|
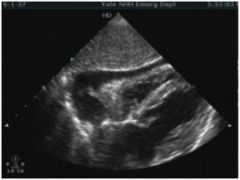
Pericarditis
|
|
|
Which higher incidence:
Upper of lower GIB |
UPPER
|
|
|
GI bleed: more common in:
-M or F? -adult or elderly? |
M, elderly
|
|
|
Upper GI bleed: anatomical definition
|
Prox to ligament Treitz
|
|
|
#1 etio upper GIB
|
PEPTIC ULCER DZ
|
|
|
Gastric ulcers:
-#1 location -which type most likely to rebleed |
Duodenal #1
Gastric most likely to rebleed |
|
|
What dz:
Bright red hematemesis s/p repeated retching/cough/sz |
MW syndrome
|
|
|
#1 etio Lower GIB
|
*upper GIB mistaken as lower!
|
|
|
Intestinal AVMs: most common location
|
R colon
|
|
|
Prox or distal lesion:
Hematochezia |
Distal (colorectal)
|
|
|
GI bleed: what is initial fluid resuscit?
|
2L NS --> then consider transfusion (if not improved)
|
|
|
Significant GI bleed:
-lavage all pts? -does negative lavage r/o upper source? |
ALL pts
negative does NOT r/o upper source (intermittent, pyloric spasm, etc) |
|
|
GI bleed tx: what is last ditch med?
|
Vasopressin (vasocon) + IV nitro (prevents MI)
|
|
|
GI bleed: does pt req stable hct to be discharged?
|
YES - hct >30%
|
|
|
Volvulus: small bowel twists around which artery?
|
SMA --> compromise midgut
|
|
|
Volvulus in neonate: assoc with which 2 CONGENITAL anomalies?
|
1. Ladd's bands
2. Duodenal atresia (50% will have malrotation at some point) |
|
|
Volvulus:
ED tx? |
Gastric tube decompression --> broad abx & surg C/S
|
|
|
Volvulus:
What imaging? |
Upright GI series (rarely helpful) --> barium enema if equivocal
|
|
|
Volvulus:
In OR: if unclear viability of bowel --> next step? |
Close --> return in 24 hrs
|
|
|
What dz:
Neonate abd film: DOUBLE BUBBLE |
Volvulus (dxistic)
|
|
|
Suspect what dz in neonate:
Abd film: loops of bowel overlie liver shadow |
Volvulus
|
|
|
Malrotation: is barium enema useful?
|
NO - false positives & negs
Perform upper series w/fluoro |
|
|
Malrotation:
Best imaging |
Upper GI series w/fluoro
|
|
|
What dz:
GI series: Ligament of Trietz on R side; corkscrew or obstructed duodenum |
Volvulus
|
|
|
Volvulus: what % infants have vomit? Is it always bilious?
|
90%
May not be bilious |
|
|
What dz:
GI films: pneumatosis intestinalis; dilated & thick loops; |
Necrotizing enterocolitis
|
|
|
#1 surg or medical emergency in neonates
|
NECROTIZING ENTEROCOLITIS
|
|
|
NEC: only occur in preemies?
|
No (although 85% cases are in premies)
|
|
|
NEC: occur how many weeks after birth in
-premature -term |
TERM EARLIER THAN PREMAT
Term : w/in 1 w Premie: up to 3w |
|
|
NEC: incidence affected by breastmilk?
|
Lower in breastfed
|
|
|
NEC: mortality? what % develops comps? 2 common comps?
|
20-40% mortality
50% comps; 1. short gut 2. intestinal stricturs |
|
|
Intussception:
Plain films useful? |
YES - dilated loops, pneumoperitoneum (2/2 perf); target sign
|
|
|
What dz:
Abd plain film: TARGET sign (what is it?) |
= 2 concentric rings superimposed on R kidney
= INTUSSCEPTION w/peritoneal fat stranding |
|
|
What dz:
U/S: BULLS-EYE |
Intussception
|
|
|
Intussception:
U/S useful? |
Yes - can be 100% accurate
|
|
|
Intuscception w/suspeted perf:
What would barium enema show? |
TRICK - do NOT perform barium if suspect perf; use H2O-contrast
|
|
|
Intussception:
-more common after what type of illness? -what vaccine? |
Increased risk if: recent URI, ROTA VACCINE, CF/Chron's/celiac dz
|
|
|
Intussception:
What % have triad (pain, sausage, currant jelly) |
15%
|
|
|
Intussception:
What is risk of perf 2/2 barium or air enema? |
<1%
|
|
|
Suspect appendicitis: give morphine?
|
YES - does not mask sxs
|
|
|
Suspect appendicitis in CHILD:
-1st imaging in non-obese? -obese? |
Non-obese: U/S --> CT if unequiv
Obse: CT |
|
|
Suspect what dz:
Neonates w/distension, vomit, abd wall cellulitis, palp mass |
Appendicitis!
|
|
|
Appenditicits: risk of perforation in:
-<4yo -adols & adults |
<4yo: 70%
adol & adult: 10-20% |
|
|
Fever in infant: definition (CELSIUS)
|
rectal > 38
|
|
|
Nuchal rigidity in what % 0-6mo with meningitis?
|
Only 25%
|
|
|
#1 etio SBI in 0-3mo w/rectal temp 38
|
UTI
(>occult bacteremia, meningitis) |
|
|
Neonatal infxn: top 2 BACTERIAL pathogens
|
GBS
Ecoli (account for 80% bact infxns) |
|
|
Neonate w/fever: does HEIGHT of fever correl w/risk of serious bact illness?
|
YES - higher fever --> higher risk
|
|
|
Neonate w/fever: does response to Tylenol predict risk of SBI?
|
YES
Non-SBI: 90% fevers resolve SBI: only 50% resolve |
|
|
UTI in neonate: what % have bactermia? meningitis?
|
3% bacteremia; 0.5% meningitis
|
|
|
Neonate w/suspected meningitis: does normal CSF WBC r/o BACTERIAL mening?
|
NO
|
|
|
Suspect what dz: <4w neonate with fever plus:
CSF pleocytosis (>8 WBC) & negative G stain |
HSV meningitis
|
|
|
How tx neonatal HSV meningitis? (drug & dose)
|
ACV 20 mg/kg IV
|
|
|
AOM in febrile infant: increased risk of serious bact illness?
|
NO
i.e. AOM does NOT explain why they have SBI --> do w/u as if the infant did not have an AOM |
|
|
Infant w/fever & diarrhea: test stool for WBC & RBC?
|
YES
|
|
|
Ovarian torsion:
Does Color Doppler have low or high PPV? |
High
|
|
|
What % kids with abd pain have ovarian torsion?
|
3%
|
|
|
Ovarian torsion: salvage ovary in what % pts if operate within:
-8h -24f |
8h: salvage 40%
24h: 0% |
|
|
Definition of premature birth
|
<37w
|
|
|
Which is better predictor of pulm infxn:
O2 sat or rr |
O2 sat
|
|
|
What % infants (0-6mo) with bact meningitis have nuchal signs?
|
only 25%
|
|
|
Strep pneumo:
Increase or decrease risk from neonate to 3mo |
at 3mo: higher risk than neonate
|
|
|
#1 SBI in 0-3mo
|
UTI
|
|
|
SBI in 0-3mo: what 2 bact account for 80%?
|
E coli
GBS |
|
|
0-3mo: does Strep pneumo have low or high mortality?
|
HIGH (15%)
|
|
|
0-3mo: does higher fever correlate with higher risk of SBI?
|
yes
|
|
|
0-3mo: if tactile fever at home but no fever in ED --> req further w/u?
|
NO
However if rectal fever at home but afebrile ED --> still need w/u |
|
|
0-3mo fever: what % respond to acetaminophen if:
-non-SBI -SBI |
non-SBI: >90%
SBI: only 50% |
|
|
1mo with fever:
How collect urine? |
CATH (not bag)
|
|
|
0-3mo with UTI:
-what % also have bactermia? -what % also have meningitis? |
Bact: 3%
Mening: 0.3% POINT: just because they have UTI --> doesn't mean they don't have another SBI (i.e. don't stop the w/u) |
|
|
0-3mo w/fever: if normal WBC in CSF --> r/o meningitis?
|
No
|
|
|
Suspect what dz:
0-3mo with fever & CSF pleocytosis (≥8 WBC/hpf) with negative gram stain |
HSV meningitis
|
|
|
0-3mo with fever: is HSV meningitis assoc with:
-PROM -fetal electrodes |
Yes-- both increase risk HSV
|
|
|
0-3mo with fever:
How dx HSV menignitis? |
1. CSF PCR
2. Culture oro/urine/lesion/CSF 3. PCR lesion |
|
|
0-3mo with fever: how tx HSV meningitis? (drug & dose)
|
Acyclovir 20 mg/kg/dose IV
|
|
|
0-3mo with CXR evidence of PNA: req admission?
|
YES
|
|
|
Infant with viral illness (e.g. bronchiolitis):
-high risk of concurrent SBI? -if SBI is present --> what is #1 source? |
If viral illness --> very low risk of SBI
Usually UTI |
|
|
>1mo old with known viral illness & fever:
-what labs do you need to order? |
can limit labs to UA & Ucx
|
|
|
If 0-3mo with fever:
-if detect AOM --> need to continue w/u? |
YES! AOM does not account for fever
|
|
|
0-3mo with diarrhea: culture for what pathogen?
|
Salmonella
(Can lead to meninigitis) |
|
|
<1mo with fever: if negative w/u --> req admission?
|
YES --> until afebrile
(contrast 1-2mo: can d/c home with abx & with PCP f/u in 1d) |
|
|
<1mo with fever: admin what abx?
|
Amp & gent
|
|
|
<1mo: safe to give ceftriax?
|
NO --> unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
|
|
|
1-2mo & fever: admin what abx:
-UTI -CSF pleo |
UTI: amp & gent
mening: CTX (safe >1mo) & amp |
|
|
Febrile infant --> require LP?:
-0-1mo -1-2mo -2-3mo |
0-2mo: YES; always admit <1mo (even if CSF neg), consider d/c home 1-2mo if CSF neg
2-3mo: if no perform LP --> f/u PCP in 1d |
|
|
Definition of fever in:
0-3mo 3mo-3yo |
0-3mo: >38
3mo-3yo: >39 |
|
|
3mo-3yo with oral lesions: suspect what dz:
-Anterior ulcers -Pharyngeal vesicles |
Anterior ulcers → herpes gingivostomatitis
Pharyngeal vesicles → coxsackie virus |
|
|
Admin H flu vaccine (Hib) at what ages?
|
2mo
4mo 6mo 1yr |
|
|
Hib vaccine effective in what % pts?
|
98%
|
|
|
Prevnar:
-what pathogen? -admin vaccine what ages? |
pneumo
2,4,6,12 mo (same as Hib) |
|
|
Prevnar: leads to what changes in:
-serotypes infecting kids? -abx-resistance? |
Increasing rates of non-covered serotypes
PCN & cephalo resistance |
|
|
Which pneumo vaccine: covers serotype 19A?
|
PCV-13
(increasing rate & resistance) |
|
|
3mo-3yo: suspect what dz if gram-POS rods in blood cx?
|
CONTAMINANT
|
|
|
Infant with fever: elevated CRP indicates bact or viral infection?
|
EITHER
|
|
|
Pedi UTI: what % E coli UTI resistance to amox?
|
50%
|
|
|
3mo-3yo with UTI: admin what abx?
|
2-3rd gen cephalo: cefixime or cefurox
|
|
|
Children >____ (age) with pyelonephritis can be treated out-pt
|
2mos!!
|
|
|
<3yo with UTI & vomiting: able to tx as outpt?
|
NO -- if vomit --> need to admit
|
|
|
3mo-3yo: how tx PNA?
|
Amox + CTX
|
|
|
What % US children have 1 episode of asthma?
|
10%
|
|
|
most sensitive indicator of lower airway obstruction in children
|
tachypnea
|
|
|
How classify (as % of PEF):
-mild asthma exac -mod -severe |
mild: >80%
mod: 50-80 severe: 30-50 life-threatening: <30% |
|
|
Severe asthma exacerb: admin via what route:
-epi -steroid |
Epi: SQ or IM
Steroid: IV |
|
|
Asthma exacerb: goal O2 sat?
|
>90%
|
|
|
Asthma exacerb:
What is most effective drug to releive obstruct? time of onset? |
albuterol --> onset <5min
|
|
|
Albuterol: mxn of action
|
Selective B2-AGONIST
|
|
|
Albuterol: S/E --- how affect:
-K+ -glucose |
HypoK
Hyperglyc |
|
|
Atrovent: generic name
|
Ipratropium
|
|
|
Atrovent in pediatric pts:
-improve outcomes? -increase S/E? |
Improved outcomes without increased in SE
|
|
|
Atrovent: mxn of action
|
weak bronchodilator by blocking acetylcholine-mediated bronchoconstriction
|
|
|
Atrovent:
-how long until onset? -better in mod or severe asthma exacerb? -use for how long during hosp? |
use in severe
takes 60-90min to effect --> give early only useful in 1st hr of tx |
|
|
Which more effective:
nebulizer or MDI with spacer? |
SAME
|
|
|
asthma exacerb:
when initiate CONTINUOUS albuterol neb? |
IF no improvement after 3 doses of alb in 1hr
|
|
|
Steroids in asthma exacerb: more effective IM/po or IV?
|
SAME!!!
GIVE STEROIDS ORALLY (Same bioavail as inhaled) |
|
|
Asthma exacerb:
what is prednisone dose? |
2mg/kg
|
|
|
Asthma exacerb: what is dose of epi?
|
0.01 cc/kg/dose of 1:1000 Epi SQ or IM (max 0.3cc)
` |
|
|
Asthma exacerb: what is mxn of Mg sulfate?
|
counteract calcium ions to prevent bronchial smooth muscle contraction
|
|
|
Asthma exacerb: Mg sulfate:
-route of admin? -improve outcomes? |
IV
improves outcomes |
|
|
Asthma exacerb:
Give terbutaline? |
Last resort
|
|
|
Asthma exacerb:
If give terbutaline --> concerned about S/E? |
Yes --- cardiac monitor (EKG, troponin, CK)
(hypo/HTN, lyte abns) |
|
|
Asthma exacerb: proven to be useful?
-Heliox -BiPAP |
YES
|
|
|
Asthma exacerb: what agents used in RSI?
|
Atropine (decrease secretions) --> ketamine (has bronchodil effects) --> roc
|
|
|
Asthma exacerb: if intubate:
-allow hypercap? -maximize PEEP? |
Permissive hypercap
try to minimize PEEP |
|
|
Definition of fever in:
0-3mo 3mo-3yr |
>38
>39 |
|
|
The drug likely to be associated with the greatest toxicity in the treatment of severe asthma is:
|
terbutaline
|
|
|
A 2 yr old has severe asthma. She is anxious, crying, and not responding to albuterol by nebulizer. An appropriate next step would be to administer:
|
EPI (sq or im)
(NOT continuous alb if not responding) |
|
|
Our 8 yr old patient has received 3 albuterol/atrovent nebs and prednisone. Exam demonstrates much better air movement, but she is still tachypneic with mild retractions. A treatment that may prevent PICU admission would be:
|
Mg sulfate IV
|
|
|
Trauma: #1 death in what age groups?
|
0-40yo
|
|
|
Trauma: which greater - permenant disability or mortality?
|
Disability 3x > mortality
|
|
|
Trauma: death occurs in how many PEAKS (Describe each)? What is GOLDEN HOUR? ATLS focuses on which peak?
|
peak 1: instant (secs-mins)
peak 2 (GOLDEN HOUR; focus of ATLS): TBI, PTX, hemorrhage peak 3: days-wks |
|
|
Trauma: 3 most imp assessors that influence survival
|
1. ID injuries
2. Establish aw 3. Expedite disposition |
|
|
Trauma: when logroll pt (between which steps)?
|
ABCDE --> LOG ROLL --> CXR/FAST
|
|
|
Trauma: should you impose a tx/intervention if you are not 100% sure about dx?
|
YES - apply tx
|
|
|
Trauma: req detailed hx to being eval?
|
No
|
|
|
If pt is talking --> assume they have an airway?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Trauma: AIRWAY: what steps if not speaking & no chest rise?
|
Sweep mouth --> 2 breaths with bag (look for chest rise) --> endotrach tube (combi --> THEN try cricothyrotomy)
|
|
|
Trauma: BREATHING: what steps?
|
Inspect: cyanosis, JVD (tension pneumothorax or cardiac tamponade), asymmetric movement of the chest (flail chest), accessory muscle use (tension pneumothorax) or open chest wounds (open pneumothroax).
Ausculate: listen for stridor (upper airway injury), lung breath sounds (pneumo or hemothorax) Percuss: feel for hyper-resonance (pneumothorax) or dullness (hemothorax), subcutaneous emphysema (airway injury), paradoxical movements (flail chest) crepitence & point tendnerness(rib fractures) or bruising (pulmonary contusion). ***If ETT --> attach a ventilator now! |
|
|
Trauma: if sucking chest wound --> what intervention?
|
Occlusive dressing
|
|
|
If suspect tension PTX --> next step
|
NEEDLE DECOMPRESSION (14-16g angiocath)
(NOT chest tube, CXR) |
|
|
Massive hemothorax: definition
|
> 1500 mL blood loss initially
> 400 cc per hour for 2 hours |
|
|
Trauma: CIRCULATION:
1st step to stop bleeding |
direct pressure
(tourniquet is last resort) |
|
|
Trauma: CIRCULATION:
What steps to assess? |
1. Radial pulse (SBP 80) --> femoral/carotid (SBP 60)
2. |
|
|
Requires what SBP?:
1. Radial pulse 2. Femoral pulse 3. Carotid pulse |
Radial: >80
Femoral & carotid: >60 |
|
|
Trauma: CIRCULATION:
Is normal HR reassuring? |
Not always -- many pts not mount tachycardic response (spinal shock, CEBS/Bbs)
|
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
750mL |
I
|
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
750-1,500 mL |
II
|
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
1,500 - 2,000 mL |
III
|
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
>2,000 |
IV
|
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
15% blood loss |
I
|
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
15-30% loss |
II
|
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
30-40% loss |
III
|
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
>40% |
IV
|
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
100-120 pulse |
II
(15-30% loss) |
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
p120-140 |
III
(30-40%) |
|
|
What CLASS (I-IV) of blood loss?:
p >140 |
IV
(>40%) |
|
|
Trauma: if TREATED pelvic fx --> what % survive?
|
only 50%
|
|
|
2 most common pelvic binders
|
T pod
Sam sling |
|
|
Traumatic arrest (pulseless & apneic): how long continue CPR?
|
15minutes
(universally fatal -- but good for family) |
|
|
Trauma: CIRCULATION:
Initiate NS at what dose? |
20 cc/kg
|
|
|
Trauma: how assess DISABILITY (neuro)?
|
1. AVPU : alert, verbal response, pain, unresponsive
2. GCS 3. WIGGLE TOES (not a full neuro exam in 1' survey) |
|
|
Uncal herniation: how appear pupils?
|
BLOWN PUPILS
(lose parasymp to CN III) |
|
|
Trauma: indicates what underlying patho?:
Blown pupils |
Uncal herniation
|
|
|
Standard trauma XRays (2)
|
AP chest
AP pelvis (NOT abdomen) |
|
|
FAST: how accurate (%)
|
85-95%
|
|
|
If FAST+ and unstable pt --> next step?
|
Immed to OR (NOT CT)
|
|
|
Trauma: remove impaled objects?
|
NO
|
|
|
Name for:
ecchymosis behind ear indicative of basilar skull fracture |
Battle sign
|
|
|
Name for:
periorbital ecchymosis without edema indicative of basilar skull fracture |
Raccoon sign
|
|
|
Trauma: motor/strength grading: what indicate:
-1 out of 5 strength -2 -3 -4 -5 |
0: Total paralysis
1: Palpable/visible contraction 2: FROM w/gravity eliminated 3: FROM against gravity 4: FROM, less than normal strength 5: Normal strength |
|
|
Where is aw obstruction:
-insp stridor -exp stridor |
Inspiratory stridor (supraglottic)
Expiratory stridor (subglottic) |
|
|
Trauma: suspect what injury:
subcutaneous emphysema --> chest tube fails to inflate lung (also -- how tx?) |
Tracheobronchial tree disruption
[ if 2nd CT tube fails --> OR |
|
|
Trauma: what injury:
Mild hypoxia --> worse hypoxia s/p fluid resuscitation |
Pulmonary contusion
|
|
|
Pulmonary contusion:
-how dx? -tx? |
*can see on CXR
Tx w/normovolemia (don't overload with fluid) --> often req ETT |
|
|
Trauma: what injury:
ECHO: hypokinetic heart |
blunt cardiac injury
|
|
|
Trauma: what injury:
wide mediastinum |
Ao dissection
|
|
|
Trauma: what injury:
Unequal leg lengths |
Pelvic fx
|
|
|
Trauma: pelvis can hide how much blood? (L)
|
5L
|
|
|
Crush injury: common what 2 anatomic locations?
|
Forearm
Tibia |
|
|
How much time for results?:
-fully x-matched blood -type-specific & Rh-tested blood -type O negative (fem) or pos (male) |
Fully crossmatched blood: 1 hour processing time
Type-specific blood: ABO and Rh only tested, 10 minute processing time. Type O Negative (males may receive O Positive blood): is immediately available |
|
|
C-spine X-ray: lateral view detects what % fxs?
|
80%
|
|
|
C-spine: what XR view detects most fxs?
|
Lateral
|
|
|
Trauma: what imaging if suspect ureter injury?
|
Retrograde-urethrogram if concern for urethral injury.
|
|
|
DPL: how sensitive? great at what type of injury?
|
98% sensitive for bleeding and is used to detect bowel injury (more sens than CT!)
|
|
|
DPL: positive if:
-___ mL blood - ____ RBC/hpf -____ WBC/hpf |
10mL blood
100,000 RBC/hpf 500 WBC |
|
|
Suturing:
If ligate minor vessels --> NON/ABSORBABLE sutures |
absorbable
|
|
|
Wound irrigation:
-low/high pressure? -low/high volume? |
low pressure, high volume
|
|
|
Wound cleaning:
use povidone iodine? hydrogen peroxide? |
Avoid both
|
|
|
Suturing: if give ppx abx --> how long duration?
|
3-5d
|
|
|
Bites: what pathogen #1? what abx?:
-human bite -animal bite |
Human: eikenella --> AUGMENTIN
Animal: pasteurella --> AUGMENTIN |
|
|
Bite: what ABX for full-thickness bite?
|
Penicillin
|
|
|
Wound: what pathogen? give which abx?
-fresh H2O contam -puncture thru shoe |
H2O: AEROmonas --> cipro
Shoe: PSEUDOmonas --> cipro |
|
|
What abx:
open fx or tendon |
IV ancef+/-gent+/- pcn
|
|
|
Tenatus: update if:
>__yrs clean wound >__ yrs dirty wound |
Clean: >10y
Dirty: >5y |
|
|
When give tetanus IMMUNOGLOBULIN?
|
If never recieved 3 dose series
|
|
|
Non/absorbable?:
Vicryl |
ABSORB
(VVVVVery abosrb) |
|
|
Non/absorbable?:
Nylon |
NON-ABSORB
|
|
|
Non/absorbable?:
Lower infection rate |
NON-absorbable!
|
|
|
Non/absorbable?:
Use for deep sutures |
Absorb
|
|
|
Non/absorbable?:
Use on mucus membranes |
Fast absorb (e.g. gut)
|
|
|
Non/absorbable?:
Use on face |
Fast absorb (e.g. gut)
|
|
|
What SIZE suture:
face |
6-0 face; 5-0 hand; 4-0 trunk/extremity; 3-0 high tension, thick skin
|
|
|
What SIZE suture:
hand |
6-0 face; 5-0 hand; 4-0 trunk/extremity; 3-0 high tension, thick skin
|
|
|
What SIZE suture:
trunk/extrem |
6-0 face; 5-0 hand; 4-0 trunk/extremity; 3-0 high tension, thick skin
|
|
|
What SIZE suture:
high-tension/thick skin |
6-0 face; 5-0 hand; 4-0 trunk/extremity; 3-0 high tension, thick skin
|
|
|
When remove sutures (days):
face |
3-5d
|
|
|
When remove sutures (days):
scalp |
5-7d
|
|
|
When remove sutures (days):
Extrem/torso |
7-10d
|
|
|
When remove sutures (days):
Mobile (joint) or high-tension skin |
10-14d
|
|
|
What type of KNOT?:
significant tension of skin |
Horizontal mattress or deep
|
|
|
What type of KNOT?:
skin edges invert |
Vertical mattress
|
|
|
Deep knot: disadvantage?
|
Increased infxn
|
|
|
Horizontal mattress: advantages?
|
Good under high tension
Everts skin (vertical mattress also everts) |
|
|
What type of knot?:
far-far-near-near |
Vertical mattress
|
|
|
ACLS:
if no breathing --> 1st step |
2 slow breath
|
|
|
Normal value:
CVP |
3-8
|
|
|
Normal value:
Pulm artery |
15-30 / 3-12
|
|
|
Normal value:
A-a gradient |
5-15
|
|
|
Normal value:
Ejection fraction |
60-75%
|
|
|
Asystole: can be caused by which electrolyte abn(s)?
|
Hypo OR hyperkalemia
|
|
|
ACLS - asystole:
-what dose of epi? how often? -give atropine? |
Epi 1mg IV push q3-5min
Atropine 1 mg IV push q3-5min to MAX 0.04 mg/kg total (*different dose & max total than brady) |
|
|
ACLS: what is MAX TOTAL DOSE of atropine you can give in:
-asystole -bradycardia |
asystole: 0.04 mg/kg
(admin as 1 mg pushs q3-5m) Brady: 0.5 mg IV push --> total 3 mg |
|
|
ACLS: brady w/serious s/sx:
-what dose epi? -give dopamine? -give atropine? -transQ pace? |
Epi 2-10 MICROgrams/min
Dopamine 2-10 MICROgram/min Atropine 0.5 mg IV push (max 3mg) TransQ pace |
|
|
ACLS: use cardioversion if HR >____
|
>150
(generally not used if <150) |
|
|
ACLS - shock: admin what drug if:
-SBP <70 & s/sx -SBP 70-100 & s/sx -SBP 70-100 w/out s/sx -SBP >100: |
<70 w/sx: NORepi 0.5-30 ug/min
70-100 w/sx: dopamine 5-15 ug/kg/min IV 70-100 w/out sx: dobutamine 2-20 ug/kg/min >100: nitroglycerin 10-20 ug/min IV --> nitroprusside |
|
|
ACLS: pulmonary edema --> admin what 3 drugs?
|
1. Nitroglycerin subling
2. Furosemide 0.5-1.0 mg/kg IV 3. morphine IV 2-4mg |
|
|
ACLS: VF/PVT --> admin shocks at which doses?
|
3 shocks: 200 --> 200-300 --> 360
|
|
|
ACLS: AMI --> give 02 at what rate
|
4L/min
|
|
|
AMI: give what 4 interventions immed?
|
MONA
1. morphine 2. O2 at 4L/min 3. Nitrogly SL or spray 4. ASA 325mg po |
|
|
Contraindications to fibrinolytics:
Surgery w/in how many mos? |
2mos
|
|
|
Contraindications to fibrinolytics:
BP? |
>180/110
|
|
|
Contraindications to fibrinolytics:
Pregnancy? |
YES -- contraI to fibrinolytics
|
|
|
AMI: goal time ED --> fibrinolytic
|
<30min
|
|
|
ACLS - pulseless electrical activity:
-epi dose & freq -atropine? |
Epi 1 mg IV push q3-5min
ATropine 1 mg IV q3-5 (max total 0.04mg/kg) |
|
|
ACLS tachycardia:
1st step if p >150 & unstable pt |
Immed cardioversion (3 jolts)
|
|
|
ACLS tachycardia:
Use VAGAL maneuvers if NARROW or WIDE qrs? |
NARROW
|
|
|
ACLS tachycardia:
What drug if narrow QRS & regular rhythm? |
Adenosine 6mg IV push over 1-3sec
(adeno - Decels heart; atropine accels) |
|
|
Wide QRS tachycardia: give what drug if:
-vent tachy OR uncertain rhythm -SVT w/aberrance |
VT: amiodarone 150 mg IV over 10 min
SVT: adenosine 6 mg rapid IV push over 1-3 sec |
|
|
Torsades de pointes: give what drug?
|
MAGNESIUM 1-2 g over 5-60 min --> then infusion
|
|
|
ACLS VF/VT algorithm:
-epi dose & freq -defib: dose (J) & time -amiodarone? -lidocaine? |
EPi 1 mg IV push q3min
Defib 360 J w/in 30-60s Amiodarone 300 mg IV push Lidocaine 1 mg/kg push q3min PATTERN: CPR--> DRUG --> SHOCK |
|
|
Stroke: you can admin fibrinolytics w/in how much time?
|
<3h
|
|
|
Asthma exacerb: steroids req taper if:
-5d? -10-14d? |
5d: no
10-14: yes |
|
|
Dilate SMALL or LARGE aws?:
-b-agonists -anticholin |
Beta: small
anti-cholin: large |
|
|
How tx in ED:
-intussception -volvulus |
Intussception: air enema
Volv: NGT & Abx --> OR |

