![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the head fold and its effect on the location of the oropharyngeal membrane, primitive heart, septum transversum, and yolk sac.
|
mesoderm from cranial end of trimlaminar embrionic disk is called cardiogenic area and is involved in future heart and septum transversum
Before- heart cranial on anterior rim to oropharyngeal membrane, septum transversum cranial to developing heart After- 1. oropharangeal membrane separates foregut from amniotic cavity, overlied by stomodeum (future mouth site) 2. septum transversum- rotates into ventral surface and encloses yolk sac as foregut and will lie caudal to heart |
|
|
Review the tail fold and its effect on the cloacal membrane, connecting stalk, yolk sac, and allantois
|
axis formed by allantois-
on axis of cloacal membrane, part of yolk is incorporated into primitive gut tube, and moves more ventral to form umbilical cord |
|
|
Describe the lateral folds 4 main results...
|
1. reversal of heart position
2. formation of ventral and lateral body walls 3. enclosure of dorsal part of yolk sac cavity to form primitive gut 4. umbilical cord formation |
|
|
Describe the two basic kinds of blood vessel formation in the embryo and when does it occur?
|
week 3
form in 2 ways: 1. vasculogenesis- blood vessels from blood islands 2. angiogenesis- vessel formation from branches of vessels from vasculogenesis |
|
|
Briefly describe the 3 steps of vasculogenesis...
|
1. Mesodermal cells induced by FGF form hemangioblasts that induce blood islandas
2. VEG-F cause regional changes in blood islands-- 3.peripheral regionalization form angioblasts, center form hematopoietic stem cells |
|
|
What conditions occur from abnormalities in the following...
a. vitelline duct b. gut has hole that pops to umbilical cord c. migration of musculature or mesoderm |
a. omphalocele
b. gastroscisis c. prune belly or eagle burret |
|
|
What three features do patients with prune belly or eagle burret show?
What type of lateral mesoderm surrounds gut tube? |
1. abdominal muscle weakness
2. UTIs 3. bilateral cryptorchidism gut tube- splanchic |
|
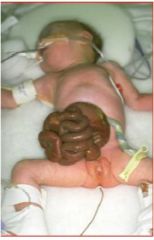
What is this and what causes it?
|
Gastroschisis
1. problems in formation of the anterior abdominal wall. 2. no sac covers herniated bowel |
|
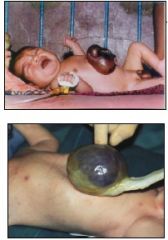
What is this condition and what are causes?
|
omphalocele
1. gut contents herniate into cord and does not return as embryo grows 2. vitelline duct problems |
|
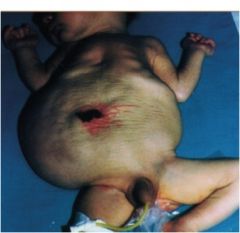
What is this syndrome and what causes it?
|
mostly in males PRUNE BELLY SYNDROMe due to abnormal migration of mesoderm or musculature
|
|
|
Describe the lateral folds and their effect on the lateral plate mesoderm and on the relationship between the extraembryonic and intraembryonic coelom.
|
1. each lateral (somatic lateral plate mesoderm) folds towards midline and ventral fold seals off intraembryonic coelom to form body cavity
2. yolk sac squeezed and the narrow path between it and gut is narrowed forming vitelline duct 3. amniotic area of attachment to embryo reduced to small umbilicus |

