![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an element? |
A substance that consists of only one type of atom. It cannot be broken down into a simpler substance by chemical means. |
|
|
What is a compound? |
A substance that consists of two or more different elements chemically bonded together. |
|
|
What is a mixture? |
Two or more substances that can be easily separated |
|
|
Define soluble |
describes a substance that dissolves, eg. salt will dissolve in water. |
|
|
Define insoluble |
describes a substance that does not dissolve, eg. sand will not dissolve in water. |
|
|
Define solute |
a substance that dissolves in the solvent, generally referring to a solid but can be a gas, eg. salt is the solute because it dissolves in water. |
|
|
Define solvent |
a liquid that dissolves the solute, eg. water is the solvent because it dissolves the salt. |
|
|
Define solution |
a mixture of dissolved solute and solvent, eg. salt dissolved in water gives a salt solution. |
|
|
Define residue |
the material left after distillation, evaporation, or filtration. |
|
|
Define filtrate |
a liquid that has passed through the filtration process.
|
|
|
Define distillate |
the vapour in a distillation that is collected and condensed into a liquid.
|
|
|
Define miscible |
If two liquids dissolve in each other they form a single continuous layer. |
|
|
Define immiscible |
Liquids that are not soluble in each other form two distinct layers.
|
|
|
Explain filtration |
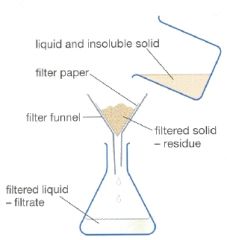
This separates the liquid and the insoluble solid. The liquid passes through tiny pores in the filter paper. The insoluble grains are to big to pass through. The insoluble solid stays on the paper. |
|
|
Explain evaporation |
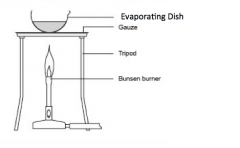
This separates the solute from the solvent. The solvent is evaporated and escapes into the air. The solute is left in the evaporating basin. |
|
|
Explain chromatography |
This separates the components of a mixture in a solution using differences in their solubility in a solvent. |
|
|
Physical properties of metallic elements (9 points) |
Shiny, usually high melting and boiling points, high density, malleable, ductile, conducts heat, conducts electricity, hard, sonorous |
|
|
Physical properties of non-metallic elements (8 points) |
Usually dull, usually low melting and boiling points, low density, brittle, soft (except gold), poor conductors of heat, do not conduct electricity (except graphite), non-sonorous |
|
|
Physical properties of compounds |
Different to those of the elements that make up the compound, the composition is always the same |
|
|
Physical properties of mixture |
The same as those of the elements that make up the mixture, the composition can vary, |
|
|
What happens when a compound is formed? |
A chemical reaction takes place and there is an energy change |
|
|
What is mass spectrometry used for? |
To determine the RAM and RMM. |
|
|
How does mass spectrometry work? |
By accurately comparing the masses of the atoms and molecules, atoms are too 'small' to be weighed on normal lab balances. |
|
|
What is high performance liquid chromatography? |
A technique used to separate mixtures of volitile liquids into their individual components. Once separated it is possible to identify what these components are. Often necessary to combine this technique with another eg. mass spectrometry to get a complete identification of the substance. |
|
|
What are the benefits of mass spectrometry and high performance liquid chromatography? |
Fast results, only small samples needed. |
|
|
What are the drawbacks of mass spectrometry and high performance liquid chromatography?
|
Needs trained analytical chemist, expensive. |
|
|
What are the risks of mass spectrometry and high performance liquid chromatography?
|
Potentially dangerous chemicals, chemicals could be tampered with. |

