![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Electric Field |
It is a property associated with matter due to which it produces and experience electric field. |
|
|
Dielectric Strength |
It is the max. electric field an insulator can withstand without becoming a conductor. |
|
|
Properties of charge |
i) Conservation of Charge ii) Additive Property iii) Quantisation of Charge |
|
|
Coulomb's law of electrostatics |
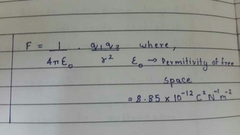
|
|
|
Principle of superposition of charges |
Not effected by presence of any other charge. Force of a given charge is the sum of forces applied by all individual charges. |
|
|
Electric Field |
It is a region around a charged particle where electric effect can be detected. |
|
|
Electric Field Intensity |

The amount of force experienced by a unit charge placed at that point in a electric field. S.I unit : N/C |
|
|
Electric Dipole Moment (P) |
P = (q)(2l) S.I unit : C-m Direction : -ve to +ve |
|
|
E.F due to dipole at a point on axial line |

|
|
|
E.F due to dipole at a point on equatorial line |

|
|
|
Torque |

|
|
|
Workrdone to rotate electric dipole |

|
|
|
Potential Energy of a dipole kept in E.F |

|
|
|
Electric Flux |

No. of electric field lines passing through unit area. |
|
|
Gauss Law ( Φ E.ds) |

Electric Flux linked to a closed surface is 1/ε times the charge enclosed in the surface. |
|
|
E.F due to point charge |

|
|
|
E.F due to long wire |
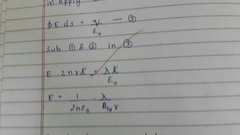
|
|
|
E.F due to thin infinite plane sheet |

|
|
|
E.F due to conducting shell |

|

