![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Upper and Lower Egypt unite |
3100 BCE |
|
|
Relief (low/high) |
carving into a 2D surface; deep carving is high relief |
|
|
Egyptian building materials |
-stone -adobe (baked mud bricks) |
|
|
Imhotep |
first recorded artist; designed Stepped Pyramid of Djoser; 2600 BCE |
|
|
3 Kingdoms of Egypt |
-Old -Middle -New |
|
|
Reserved Column |
column which doesn't bear weight |
|
|
Axial Temple |
temple plan designed around single line (axis) |
|
|
Straight-axis Approach |
axial temple based on a straight line directly into the temple |
|
|
Hypostyle Hall |
hall filled with closely-packed columns which support the roof |
|
|
Colossi |
large sculptures |
|
|
Atlantids |
man-shaped column |
|
|
Clerestory |
windows/cuts in walls to provide light |
|
|
Pylon Entryway |
simple, massive gateway with sloping walls |
|
|
Chamfered Column |
column which has straightened sides; octagonal when viewed from top |
|
|
Amarna Period |
short time in Egyptian history (during the New Kingdom) when Akhenaton broke religious and artistic conventions by worshiping only one god; didn't portray himself as a god |
|
|
Egyptian Conventions |
-use of registers -combined text/image -2D works seen from side, front or top -3D work very blocky - many horizontal/vertical lines -people of high rank in strict conventions (hieratic scale) |
|

|
Narmer Palette Old Kingdom - 3000BCE; stone, low relief -records history of uniting Upper/Lower Egypt -demonstrates Egyptian conventions -used to mix makeup |
|

|
Seated Scribe Old Kingdom - 2400BCE; painted limestone -shows naturalism in lower classes |
|
|
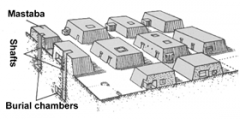
Mastabas Old Kingdom - pre-3000BCE -low structure built over buried tomb |
|
|
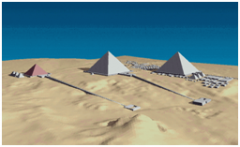
Great Pyramids Giza Old Kingdom - 2500BCE; cut stones, polished limestone -each a tomb for a specific pharaoh -poor tomb design, all robbed |
|

|
Great Sphinx Old Kingdom - 2500BCE -believed to be portrait of Khafre -head in unconventional pharaoh pose -purpose unknown; possibly a guardian |
|

|
Mortuary Temple of Queen Hatshepsut Middle Kingdom - 1450BCE -cut into cliff side, mimicking existing rock -axial design; straight axis approach -darkness indicates sacred places |
|

|
Mortuary Temple of Ramses II Abu Simbel New Kingdom - 1250BCE -colossi are conventional, but lack detail because of size -large works indicate turmoil -rock-cut tomb |
|

|
Statue of Akhenaton New Kingdom, Amarna Period - 1350BCE -large convention break: curves rather than blocks -reality shown in sagging skin -intended to break religion in favor of worship of Aten |

