![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When was the Predynastic Period? |
3000-2920 BCE |
|
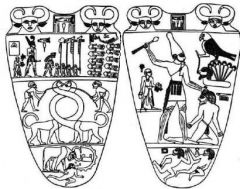
|
Palette of Narmer - Predynastic Period - hierarchal scale - body represented in composite cubic form
|
|
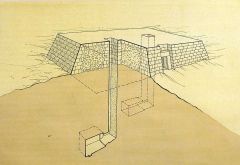
|
Mastaba - tomb type for important Egyptians during the predynastic period and early dynasties |
|
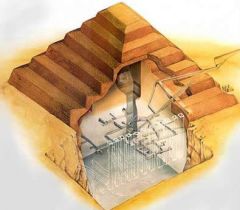
|
Stepped Pyramid - created by stacking mastabas - popular around beginning of Old Kingdom (2600s BCE) - "Stepped Pyramid of King Djoser" |
|

|
Flat-Sided Pyramids - popular during Old Kingdom - found at Giza - conspicuous size attracted grave robbers |
|

|
Rock-cut Tomb - popular during Middle Kingdom (c. 1900 BCE) |
|
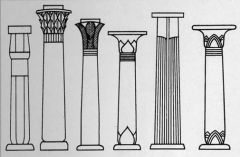
|
Early Egyptian Columns - made to look like bundled papyrus plants - designs became more complex over time |
|
|
How are pharaohs depicted in Egyptian sculpture? |
- youthful, strong, idealized - little negative space (preventing breakage) - expressionless gaze - clenched fists (strength) |
|

|
Khafre (2500 BCE) |
|

|
Hatshepsut (1470 BCE) |
|

|
Akhenaten (1350 BCE)
- Amarna style - break in traditional style, more relaxed |
|

|
Seated Scribe (2450 BCE) - canons of depiction are relaxed because the scribe is lower ranking in society than the godlike rulers |
|
|
What are some characteristics of New Kingdom temples? |
- grander in scale and complexity - some were built into sides of mountains - straight axis, not bent axis |
|

|
Temple of Hatshepsut (1470 BCE) |
|

|
Temple of Ramses II (1290 BCE) |
|
|
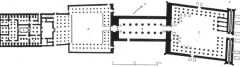
Temple of Amun-Mut (1279 BCE) |
|

|
Temple of Amen-Re (1290 BCE)
- Innovations: - hypostle hall and clerestory (sunlight) - development of sunken reliefs |

