![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Economic objectives
|
Economic goals
|
Definition
|
|
|
Economic growth
|
Percentage change in national income measured over time
|
|
|
|
Full employment
|
Where all those seeking work are in employment
|
|
|
|
Economic objectives
|
Economic growth
Full employment Stable prices Balance of payments |
List of objectives
|
|
|
Governments want economic growth to be...
|
Governments want economic growth to be high because high growth adds to national income, leading to a higher standard of living
|
|
|
|
Governments want full employment...
|
Governments want full employment because then people will not be on jobseekers allowance. Also people have money to spend so will help inflation which allows economic growth.
|
|
|
|
Governments want stable prices...
|
Governments want stable prices because it allows the economy to slowly grow and to control inflation.
|
|
|
|
Governments want balance of payments
|
Governments want balance of payments where the value of exports is equal to the imports. This is because the value of imports is more important than exports, money coming into the country.
|
|
|
|
Factors of production
|
Land
Labour Capital Enterprise |
Get of my...
Baby! Dublin, London ect Star ship... |
|
|
Equality
|
Where incomes are distributed more equally.
|
|
|
|
Absolute poverty
|
Those with incomes lower than the level needed for necessities at
|
|
|
|
Relative poverty
|
Those on low income relative to the country's average
|
|
|
|
Benefits of growth
|
Higher living standards
Reduction of poverty(no absolute poverty, some relative poverty) Investment in infrastructure (schools, hospitals and transport) Lower crime |
|
|
|
Disadvantages of growth
|
Environmental costs
Inequality of growth (rich people richer while poor people don't benefit as much) |
|
|
|
Economic growth - conflicts with other economic objectives
|
Low inflation (high growth - high inflation)
Balance of payemnts |
|
|
|
Welfare state
|
Financial or practical help for those who need the most support
|
Homeless people ect
|
|
|
Benefits of the welfare state
|
Poverty is reduced
Inequality is reduced Overall health is improved |
|
|
|
Disadvantages of the welfare state
|
Remove of incentives to find work
Higher taxation |
|
|
|
Alternatives to the welfare state
|
Volunteers
Everyone gets the same benefits Only benefits for certain conditions |
|
|
|
Free market economy
|
A system share all economic decisions are taken by private individuals and businesses
|
|
|
|
Mixed economy
|
A system that is partly a free market economy but also had government involvement in economic decisions.
Things such as health and education is still run by government so people can afford it. |
|
|
|
Benefits of a free market economy
|
Prices should be low due to competition between companies
Quality of goods should be high dues to competition between companies |
|
|
|
Drawbacks of a free market economy
|
Some businesses may monopolies a market and will NOT have to provide low prices and high quality
Consumers may not be able to afford vital products |
|
|
|
Market failure
|
Failure of the market to allocate resources efficiently
|
|
|
|
Merit goods
|
Goods that are under consumed by society largely because the benefits of the good are not fully appreciated by society
|
|
|
|
Private benefits
|
The benefit to private businesses or individuals
|
|
|
|
Demerits goods
|
Goods that are over consumed by society. Negative externalities are generates by consumption of these goods
|
|
|
|
What would happen if a market failed?
|
Some goods may be under-produced or not even produced at all
|
|
|
|
How can markets fail?
|
Lack of competition-no incentive for a business to improve quality of output or to keep prices low
Not all our values are market values- people may not purchase services such as education and health care. Also some people may use goods without seeing negative consequences such as tobacco and drugs. |
|
|
|
Public goods
|
Goods that display the following two characteristics: consumption of them doesn't prevent others consuming them; once they are provided, people cannot be prevented from consuming them.
|
|
|
|
Externalities
|
The additional costs or benefits beyond private ones imposed on society that arise our of production or consumption decision.
|
|
|
|
Private cost
|
The cost to private businesses or individuals
|
|
|
|
Social cost
|
The cost to society of an action consisting of private costs and external costs
|
|
|
|
Social cost equation
|
Private cost + external cost = social cost
|
|
|
|
Social benefit
|
The benefit to society consisting of private benefits and external benefits
|
|
|
|
Social benefit equation
|
Private benefit + external benefit =social benefit
|
|
|
|
Example of a negative externalities
|
Pollution from a factory. The factory does not pay for the dirty air or polluted rivers, instead that is the price that society has to pay.
|
|
|
|
Example of a positive externalities
|
Employment from large businesses set up in a town will generate extra income and new available jobs
|
|
|
|
Why does the government's do about negative externalities?
|
Raise taxes to pay for the damage. Or in the example of cars, raising the prices of petrol will discourage people to drive.
|
|
|
|
Why does the government's do about positive externalities?
|
The government offers assistance to encourage it. In the example of education, they encourage people to attend university's, by giving grants.
|
|
|
|
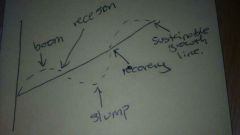
Economic cycle
|
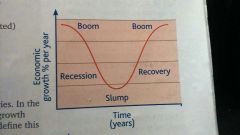
Boom, recession, slump, recovery (repeat cycle)
|
|
|
|
Boom (economic cycle)
|
When economic growth is above average. Low unemployment, increased demand for goods. As a result inflation will rise.
|
|
|
|
Recession (economic cycle)
|
Economic growth will fall below average. Unemployment rising, less consumer spending.
|
|
|
|
Slump (economic cycle)
|
In a slump, economic growth will be low or negative. Prices will be low tring to encourage spending, unemployment high, and jobs insecure.
|
|
|
|
Recovery (economic cycle)
|
Economic growth will stay to rise towards the average level. Consumer spending will rise and unemployment will start to fall. Inflation will stop falling.
|
|
|
|
Taxation
|
Money collected by the government to finance it's expenditure
|
|
|
|
Indirect taxes
|
Taxes of expenditure eg VAT
|
|
|
|
Direct taxes
|
Taxes on incomes eg income tax
|
|
|
|
Corporation tax
|
Tax on the profits of limited companies
|
|
|
|
Government expenditure
|
Money spent by the government on public service and welfare
|
|
|
|
Direct taxes examples
|
Income tax, there are two rates of taxation: basic rate of 20% and higher rate 40% of income.
Also national insurance is a tax on income. |
|
|
|
Other taxes examples
|
Stamp duty I'd placed on the purchase price of a house at varying rates
council tax is charged on each house in the country and varies according to the value of the property. Inheritance tax is paid on any inheritance earned when the estate passes on to someone else when the individual dies |
|
|
|
Government expenditure examples in order of the cost
|
Social protection - jobseekers allowance, benefits, child benefits. Biggest spending.
Health - NHS. Second largest Education - next largest |
|
|
|
Fiscal policy
|
Decisions made by the government for government expenditure and taxation
|
|
|
|
Effects of fiscal policy
|
Inflation - government spending can contribute to inflation. Also a reduction in taxes encourages spending pushing inflation higher.
Economic growth - higher government spending will cause economic growth. Many countries government spend when they are in a recession or slump. Unemployment - government spending reduces unemployment, as there is a demand for output Balance of payemnts - high growth leads to high imports, it small exports |
|
|
|
Monetary policy
|
Policy to control the supply or cost of money, via changing interest rates
|
|
|
|
Interest rates
|
The cost of borrowing and reward for saving money
|
|
|
|
High interest rates encourages...
|
High interest rates encourages savings due to high interest money on people's savings, this leads to less spending in the economy
|
|
|
|
Low interest rates encourages...
|
Low interest rates encourages higher speeds ding and faster economic growth. Increasing employment because of demand for output.
|
|
|
|
Supply side policy
|
Government policy to encourage the economy tonincreae3 it's potential growth rate
|
|
|
|
Supply side policy examples
|
Education and training - increase quality, education maintenance allowing 18 to stay in school, increase uni students, work based training.
Competition between businesses - cheaper and high quality Labour market policies |
|
|
|
Eutrophication history
|
27 countries
Began in 1950's Free trade, single European market |
|
|
|
Free trade
|
Free trade with European members. No tariffs on goods and services.
|
|
|
|
Protectionism
|
Businesses are protected from competition from non European members. But no competition s8 no drive to make high quality and cheap prices.
|
|
|
|
Single European market
|
Free movement of workers
Free movement of capital (money moving with no barriers) Common product standards (all conforming health and saftey) |
|
|
|
When did UK join the eu
|
Joined in 1973
|
|
|
|
Benefits of eu membership
|
Greater choice for consumers
Larger market for business Higher incomes Political influence |
|
|
|
Drawbacks of eu membership
|
Competition for UK firms
Lack of freedom Common agricultural policy |
|
|
|
Reasons for joining the euro
|
Reduced transactions costs
Uncompetitive exports East of price comparisons Greater economies of scale |
|
|
|
Reasons against joining the euro
|
Cost of preparation
Loss of control over interest rates Use of eu hang rates |
|
|
|
Enlargement
|
Bringing new member countries I to the eu
|
|
|
|
Effects of expansion
|
Cheaper labour costs
Greater competition More choice for Co sumers |
|

