![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Economic Indicator |
Any economic statistic such as GDP, inflation rates, or unemployment rates that indicate how well the economy is doing or will do in the future. |
|
|
Procyclic |
Economic indicator is one that moves in the same directions as the economy. (example:GDP) |
|
|
Countercyclic |
Economic indicator is one that moves in the opposite direction as the economy. (unemployment rate gets larger = worst economy) |
|
|
Acyclic |
Economic indicator is one that has no relation to the health of the economy and is generally of little use. (# homeruns pirates hit in a year) |
|
|
Frequency of Data |
GDP is released quarterly (3 months) Unemployment rate is released monthly. |
|
|
Timing |
indicates the timing of their changes relative to how the economy as a whole changes.
|
|
|
Leading |
indicators which change before the economy changes. (Stock market) |
|
|
Lagged |
indicators in which one does not change direction until a few quarters after the economy does. (Unemployment rate) |
|
|
Coincident |
Indicator in which one simply moves at the same time the economy does. (GDP) |
|
|
GDP |
is used to measure economic activity and thus is both pro cyclical and a coincident economic indicator. Includes the effect of profits from foreign investments and of foreign workers wages. focuses on the activity within the geographic boundaries of the fifty states and DC. Excludes profits of U.S owned companies earned from foreign operations and wages of U.S workers employed abroad. |
|
|
Implicit Price Deflator |
measure of inflation |
|
|
Inflation |
is procyclical as it tends to rise during booms and falls during periods of economic weakness. A sustained increase in overall prices. |
|
|
GNP |
The nation's total economic output valued in dollars. It is derived by organizing the various sectors of the economy. Treats multinational corporations profits according to the nationality of the company's ownership, and foreign workers wages according to the nationality of the worker. |
|
|
Characteristics of GDP |
Annual aggregate output, market value of all final goods and services, inventory items are included in the value of nation's output, excludes social entitlements, inheritance, stocks and bonds |
|
|
Economic Growth |
economy that is constantly creating more production and more wisely using scare resources. Most significant factor is new technology. |
|
|
Business cycle |
a pattern of periodic changes in the general level of ecomonic activity. |
|
|
Picture of Business cycle |
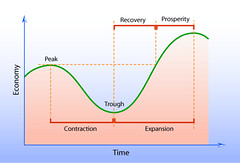
|
|
|
Recession |
a period in which GDP declines for 2 quarters or more |
|
|
Depression |
An especially long or severe decline in general economic activity |
|
|
Recovery |
A period of increasing GDP and lower unemployment |
|
|
Trough |
The lowest point in an economic contraction, when real GDP stops falling |
|
|
Peak |
The height of an economic expansion, when real GDP stops rising. |
|
|
Demand-Pull Theory |
States that inflation occurs when demand for goods and services exceeds existing supplies. |
|
|
Cost-Push Theory |
Inflation occurs when producers raise prices in order to meet increased costs. |
|
|
Consumer Price Index (CPI) |
Is computed each month by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Price index determined by measuring the price of a standard group of goods meant to represent the "market basket" of a typical urban consumer. |
|
|
Poverty |
the condition in which people do not have enough income to provide for their basic need such as food, clothing and shelter. |
|
|
Poverty Line |
This level was determined by Molly Orshansky by figuring out how much a family needed to maintain a minimally adequate diet and then multiplying it by three. The government adopted this standard to calculate the number under which people are seen as poor or living poverty. |
|
|
Causes of Poverty |
Unemployment, low productivity, or restrictions job entry ( education/skills necessary or geographic location) |
|
|
Income distribution |
how the nations total income is distributed among its population. unequal. |
|
|
Redistribution |
Welfare, Social security, other social programs. |
|
|
Unemployment |
Not having a job or career. hurts the country, society and the family. |
|
|
Structural Unemployment |
resulting from skills that do not match what the employers require or being geographically separated from job opportunities. (new technology, new resources, change in consumer demand, globalization, and lack of education) |
|
|
Cyclical Unemployment |
resulting form too low a level of aggregate demand. Economic downturns result in high unemployment layoffs.Lack of new jobs creations etc.. (Recessions,downturns, or demand for goods and services drops) |
|
|
Frictional Unemployment |
Unemployment of people who are temporally between jobs due to change in career, company or location (looking for a new job) |
|
|
Seasonal Unemployment |
Unemployment of people who are out of work because of factors that vary with the time of the year. |
|
|
John Maynard Keynes |
The general theory of employment, Interest and money.(1936) States that national incom and employment are determined by demand forces. Advcoated government intervention to stimulate an econmy that stabilized below full employment levels. |
|
|
Keynesian Fiscal Policy |
Use government spending to stimulate the economy before a recessio occurs. |

