![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
102 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Abiotic
|

Non-living things
Temperature, Sun, Water, Soil, Rocks... |
|
|
Adaptations
|

A change that helps an organism survive
The peppered moth changed from white to black to survive the industrial revolution |
|
|
Behavioural adaptation
|
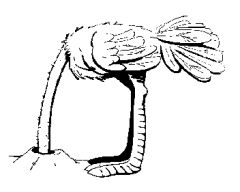
What an animal does to survive
The ostrich sticks its head in the sand when scared |
|
|
Biodiversity
|

Different types of plants and animals living in an area
|
|
|
Biome
|

The largest division of the biosphere (Permanent ice/Desert)
|
|
|
Biosphere
|

The air, land, and water where everything lives
|
|
|
Biotic
|

Living things (plants and animals)
|
|
|
Climate
|
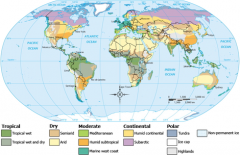
Precipitation and temperature in an area for a long time
|
|
|
Climatograph
|
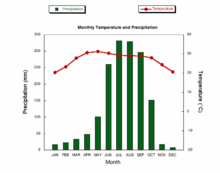
Records temperature and precipitation in a chart
|
|
|
Elevation
|

The height of land above sea level
|
|
|
Latitude
|
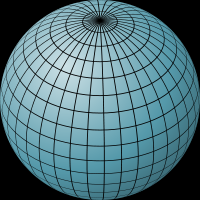
The distance from the equator (North pole is 90°N)
|
|
|
Physiological adaptation
|

A chemical adaptation that helps an animal survive
The ostrich maintains constant temperature year round |
|
|
Structural adaptation
|

A physical adaptation that helps an animal survive
Arctic fox has short ears and legs to save heat |
|
|
Terrestrial
|

Land (extra terrestrial – from another land)
|
|
|
Commensalism
|
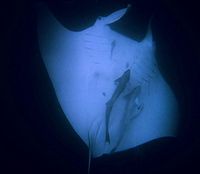
One animal benefits the other isn’t helped or harmed
(2 Remora attached to the Ray....the remora gets food, but the ray gets nothing) |
|
|
Community
|

All living plants and animals in an area
|
|
|
Competition
|

A fight (normally for food, shelter or a mate)
|
|
|
Ecological hierarchy
|
Organism -> population -> community -> ecosystem
Smallest ------ to ------> Biggest |
|
|
Ecosystem
|

Biotic and abiotic and abiotic living in an area
|
|
|
Eutrophication
|

Excess nutrients cause an increase in the number of plants
Too much algae growing in the pond because of the large amounts of nutrients |
|
|
Habitat
|

Where an organism lives (a lake, a rotten log, an area of the boreal forest)
A picture of a lake |
|
|
Mutualism
|

Both animals benefit
The anemone gets food the clownfish gets protection |
|
|
Niche
|
The role that an organism plays in an ecosystem
|
|
|
Parasitism
|

One animal benefits the other is harmed
Warbler lost all her eggs and is taking care of the cuckoo baby who threw the eggs out of the nest |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|

Plants convert carbondioxide to oxygen and energy
Trees, Grass and other plants |
|
|
Population
|
The number of 1 species in an area (The population of Canada is 36 million)
|
|
|
Predation
|

Predator hunts the prey
Tiger eating a Gazelle |
|
|
Species
|
One type of plant or animal (humans or dogs)
|
|
|
Symbiosis
|
The interaction between two different species
Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism |
|
|
Biodegradation
|
The breaking down of dead organic matter
|
|
|
Biomass
|
The total mass of all of one species in an area
(all the trees in the world) |
|
|
Carnivores
|

Meat eater
|
|
|
Consumer
|

An animal that eats other plants or animals
|
|
|
Decomposers
|

Organism that breaks down dead things into nutrients
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
Break down dead things
|
|
|
Ecological pyramid
|
Includes the pyramids of: numbers, energy, and biomass
|
|
|
Energy flow
|
The flow of energy from one organism to another
|
|
|
Food chain
|

Shows one feeding relationship
|
|
|
Food pyramid
|
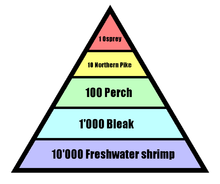
A pyramid showing the loss of energy from one trophic level to another
|
|
|
Food web
|
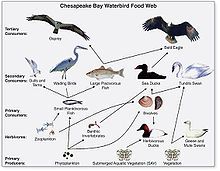
Shows many feeding relationships and how they are interconnected
|
|
|
Herbivores
|

Plant eater
Zebra eating grass |
|
|
Nutrients
|
Elements like Nitrogen and Phosphorus needed for growth
|
|
|
Omnivores
|

Eat both plants and animals
Bear eats fish and berries |
|
|
Primary consumers
|

Eat producers
Zebra eating grass |
|
|
Primary producers
|

All plants (grass, algae, and cyanobacteria)
Trees |
|
|
Producers
|

All plants (grass, algae, and cyanobacteria)
Trees |
|
|
Pyramid of biomass
|
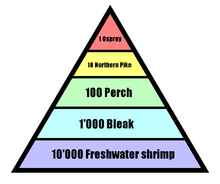
The relative mass of organisms at each trophic level in a food chain
|
|
|
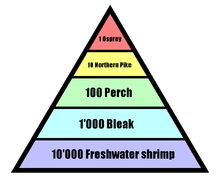
Pyramid of energy
|
Shows the amount of energy available at each trophic level
|
|
|
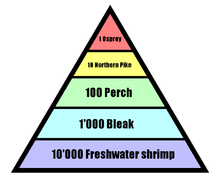
Pyramid of numbers
|
Shows the number of organisms at each trophic level
|
|
|
Secondary consumers
|

Eat primary consumers (3rd trophich level)
|
|
|
Tertiary consumers
|

Eat primary and secondary consumers (4th trophich level)
The bear eats the fish which eats the algae |
|
|
Trophic levels
|
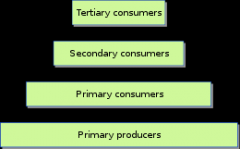
The level that an organism is in a food chain
|
|
|
Carbon cycle
|
How carbon moves through biotic and abiotic things
|
|
|
Carbonate
|

CO3 2- store for carbon either as Calcium Carbonate (Limestone) or in Shells
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Breathing
|
|
|
Denitrification
|
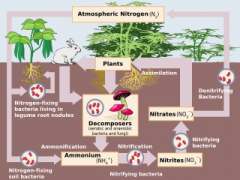
Nitrogen returns to the atmosphere
|
|
|
Denitrifying bacteria
|
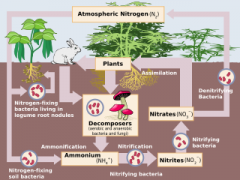
Bacteria that convert nitrate (NO3–)into nitrogen gas (N2)
|
|
|
Detrivores
|

Eat dead things
|
|
|
Geologic uplift
|

Buried rock layers that are pushed up
|
|
|
Leaching
|
Water removes nutrients from rocks and soil
|
|
|
Nitrification
|
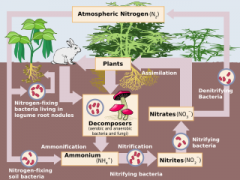
Ammonium (NH4+) is converted into nitrate (NO3–)
|
|
|
Nitrifying bacteria
|
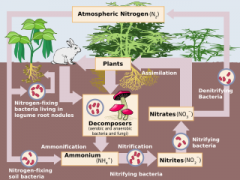
Bacteria in the soil that convert ammonium (NH4+) to nitrite (NO2–) to nitrate (NO3–)
|
|
|
Nitrogen cycle
|
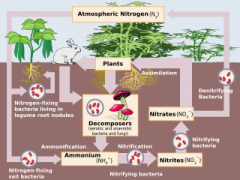
How nitrogen moves through biotic and abiotic components of an environment
|
|
|
Nitrogen fixation
|
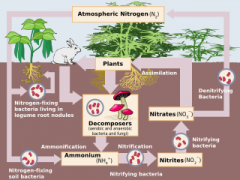
Nitrogen in the air is converted to nitrate or ammonium in the ground
|
|
|
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
|
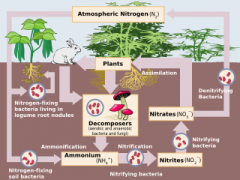
Convert nitrogen gas (N2) into ammonium (NH4+)
|
|
|
Nutrient cycles
|
How nutrients move through biotic and abiotic components of an environment
|
|
|
Phosphorus cycle
|
How phosphorus moves through biotic and abiotic components of an environment
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|

Plants convert carbondioxide to oxygen and energy
|
|
|
Sedimentation
|

Soil particles build up in layers on the bottom of a lake
|
|
|
Stores
|

A place where something is kept for a long time
A picture of a coal deposit or coal store |
|
|
Weathering
|

Rock is broken down into smaller pieces
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|

The build-up of toxins from the environment
The shark is getting toxin from the polluted water |
|
|
Biomagnification
|

The amount of toxin gets bigger up the food chain
The bird will have more toxin than the shrimp |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Using bacteria to make pesticides non-toxic
|
|
|
DDT
|
A toxin that can bioaccumulate
|
|
|
Heavy metals
|

Lead Mercury and Cadmium
|
|
|
Keystone species
|

A plant/animal that has a big impact on the food chain (usually producer)
The sea otter is a keystone species |
|
|
ppm
|
Parts per million
|
|
|
PCBs
|
A toxin that can be bioaccumulated and biomagnified
|
|
|
Pesticides
|
A Chemical used to kill insects on farms
|
|
|
Adaptive radiation
|

One species adapts to fill many niches at once making many species (finches of the Galapagos islands)
|
|
|
Climax community
|

The end community (tall trees)
|
|
|
Ecological succession
|

Change in the types of plants and animals that live in an area over time
The picture shows the climax community...the last stage of succession |
|
|
Natural selection
|
The process where the strongest will survive and reproduce.
|
|
|
Pioneer species
|

The first plant to arrive
Lichens (in photo) and Moss in primary succession Grass in secondary succession |
|
|
Primary succession
|

Growth of plants on bare rock (no soil – glacier/lava flow)
Picture shows lava flow destroying a house |
|
|
Secondary succession
|

Growth of plants on soil (forest fire/agriculture or farming)
Picture is of a forest fire |
|
|
Aeration
|
Put holes into ground so oxygen and water can enter ground
|
|
|
Contamination
|
A toxin enters an environment (pollution)
|
|
|
Deforestation
|

Cut down trees in an area
|
|
|
Habitat fragmentation
|
The division of habitats into smaller pieces
|
|
|
Habitat loss
|

The destruction of habitats (human activities/flooding/forest fire)
|
|
|
Land use
|

How we use land (urban development, agriculture, mining)
The picture is of a large open mine |
|
|
Overexploitation
|
Using a resource until it is gone
|
|
|
Resource exploitation
|
Using resource
|
|
|
Soil degradation
|
Breakdown of soil
|
|
|
Sustainability
|
The balance between using and renewing a resource so it isn’t overexploited
|
|
|
Traditional ecological knowledge
|

The knowledge of what plants and animals can heal us.
|
|
|
Foreign species
|
Plants or animals from another country
|
|
|
Introduced species
|
Bring plants/animals from one country to another for food work or entertainment
|
|
|
Invasive species
|

Introduced organisms that outcompete native species
The picture is of Kudzu that outcompeted the trees |
|
|
Native species
|

Plants and animals that originally lived in an area
Panda is from China |

