![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
1. Asc. Aorta |
|
|
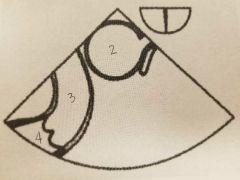
2. Aorta 3. Pulmonary Artery 4. RVOT |
|

|
5. RA 6. TV 7. RV 8. LA 9. MV 10. LV 11. Lateral wall |
|

|
12. LA 13. MV 14. LV |
|

|
15. LA 16. MV 17. LV 18. LAA 19. INFERIOR WALL 20. ANTERIOR WALL |
|

|
21. LA 22. MV 23. LV 24. LVOT 25. AO 26. RV 27. POSTERIOR WALL 28. ANTERO-LATERAL WALL |
|
|
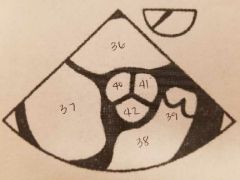
36. LA 37. RA 38. RV 39. RVOT 40. NONCORONARY CUSP 41. LEFT CORONARY CUSP 42. RIGHT CORONARY CUSP |
|

|
43. LA 44. MV 45. LV 46. LVOT 47. AV 48. AO 49. RV |
|

|
50. LA 51. IVC 52. SVC 53. RA |
|

|
54. R. PA 55. PA 56. AO 57. SVC |
|

|
58. AO 59. M. PA |
|

|
60. DESC. AO |
|
|
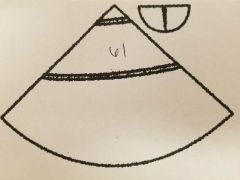
61. DESC. AO |
|

|
62. POSTERIOR LEAFLET MV 63. ANTERIOR LEAFLET MV 64. RV 65. ANTERIOR WALL 66.LATERAL WALL 67. POSTERIOR WALL 68. INFERIOR WALL 69. IVS |
|

|
70. POSTERIOR MEDIAL 71. ANTERIOR LATERAL 72. LV |
|

|
78. LV 79. MV 80. AO |
|

|
81. RV 82. TV 83. CHORDAE 84 RA |
|

|
85. RV 86. LV 87. MV 88. LA 89. AV 90. AO
|
|

|
73. PAPILLARY MUSCLE 74. LV 75. MV 76. LA 77. LAA |
|

|
29. LA 30. RA 31. TV 32. RV 33. RVOT 34. PV 35. AO |
|
|
What are the appropriate indications for a TEE? |
1. Evaluating valves 2. Thrombus 3. MitralClip procedure 4. A-fib ablation 5. LAA closure 6. PFO, ASD, VSD closure 7. Transcatheter 8. Surgical repair 9. Endocarditis 10. Mass 11. Dissections 12. Critically ill pts |
|
|
How are pts prepared for TEEs? |
1. Fast; 4 hrs for liquids, 6 hrs for solids 2. Outpatients need to bring driver 3. Medical history taken 4. Consent signed 5. Procedure explained 6. BP cuff 7. O2 used 8. False teeth/partials removed 9. Suction 10. EKG
|
|
|
What medications are used with TEEs? |
1. Midazolam (Versed) 2. Fentanyl (narcotic) 3. Cetacaine (gag reflex) 4. Viscous lidocaine (gag reflex) |
|
|
What position should the pt be put in for a TEE? |
1. Left lateral decubitus 2. Neck and knees flexed 3. Pillow under head to maintain midline |
|
|
What are the ABSOLUTE contraindications for a TEE? |
1. Esophageal: tumor, stricture, fistula, or perforation 2. Active upper GI bleed 3. Perforated bowel 4. Bowel obstruction 5. Unstable cervical spine 6. Uncooapetative pt |
|
|
What are the RELATIVE contraindications for a TEE? |
1. Barrett Esophagus ( abnormal cell change) 2. H/o dysphagia 3. Esophagitis 4. High grade esophageal varices 5. Active peptic ulcer 6. Neck immobility 7. Severe coagulapthy 8. Severe hiatal hernia 9. Prior neck/chest radiation 10. Esophageal diverticulum 11. Loose teeth |
|
|
Rotating the TEE probe from 0 to 180 degrees using the multiplane control knob is which kind of movement? |
Rotation |
|
|
Moving the entire transducer rotationally in the esophagus to show a mediolateral change in image plane is which kind of movement? |
Turning |
|
|
Bending and extending the probe to image superiorly or inferiorily at an angle is which kind of movement? |
Angulation. 1. Anteflexing: anterior 2. Retroflexing: posterior |
|
|
Lateral motion of the transducer to image different structures in the same plane is which kind of movement? |
1. Tilt, AKA flexing left or right |
|
|
The TEE window that is 20-25cm deep from incisor is: |
Upper esophageal |
|
|
The TEE window that is 30-40cm from incisor is called: |
Mid-esophageal |
|
|
The TEE window that is 40-45cm from incisor is called: |
Transgastric |
|
|
The TEE window that is 45-50cm from incisor is called: |
Deep transgastric |
|
|
What normal structures could be mistaken for pathology when performing a TEE? |
1. Crista terminalis (RA wall; mass) 2. Eustachian valve & chiari network ( atrial lesions) 3. Lipomatous hypertrophy of IAS (atrial mass) 4. Coumadin ridge (LAA and atrial insertion of the LUPV) 5. Moderator band ( mass) 6. Lambls excrescence ( AoV, MV; mass) 7. Valve strands & sutures ( valve lesions) |

