![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
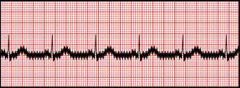
Electrical interference Regular sharp high frequency spikes giving an impression of thick baseline It is due to electric motors in bed & electric wirings |
|
|
Sharp irregular spikes of the baseline |
Seen in unrelaxed patient |
|
|
Normal paper speed |
25mm/sec |
|
|
Einthoven triangle |
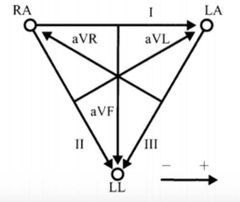
|
|
|
Lead commonly used to identify rhythm |
Lead ll |
|
|
Heart rate by ECG |
1500/no of boxes in between RR |
|
|
One large box of ECG |
200 msec |
|
|
Lown ganong levine syndrome |
Short PR Normal QRS complex Pre excitation syndrome |
|
|
Stimulation of right stellate ganglion |
Stimulates SA node & increases heart rate |
|
|
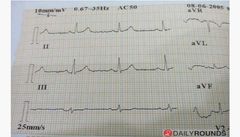
Pulseless electrical activity
Rx Start CPR & give 1 mg iv epinephrine
5H's & 5T's |
|
|
De winter's T waves |
Equivalent to anterior STEMI but without ST elevation, instead has hyperacute T waves Suggestive if near occlusion of LAD in V2 |
|
|
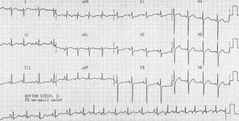
PSVT |
Rhythm is regular 150 to 200 bpm Narrow QRS complexes DOC is adenosine |
|
|
Multifocal atrial tachycardia Features HR > 100 Irregular rhythm Discrete P waves with > 3 different morphologies Variable PR interval Narrow QRS complex Commonly seen in COPD patients also in hypoxia & pulm hypertension |
|
|
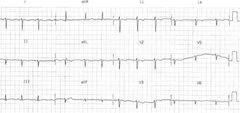
Dextrocardia Global negativity Inverted P wave Negative QRS complex Inverted T wave Progressive decreasing voltage in precordial leads |
|
|
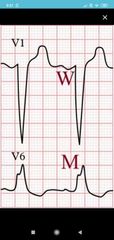
RBBB ECG RSR pattern (M shaped QRS) Wide slurred S waves in lateral leads T wave inversion Broad QRS |
|
|
LBBB ECG |
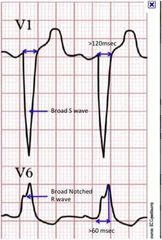
QRS > 120 msec |
|
|
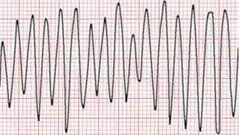
Monomorphic VT |
Broad QRS Rate >100 bpm |
|
|
Ventricular flutter Continuous sine waveform vs (chaotic irregular deflections in V fib) No identifiable P, QRS, T waves Rate > 200 bpm |
|
|
J wave |
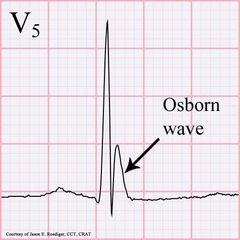
Also called Osborn/ camel hump wave Seen in hypothermia |
|
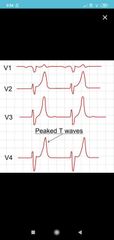
|
Seen in Hyperkalemia |
|
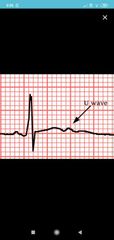
|
U waves seen in hypokalemia |
|
|
ST-T & T-U alterans |
LV dysfunction & torsades de pointes Respectively |
|
|
Rx of wenckebach |
Atropine 0.5 mg If no improvement Transcutaneous pacing If not improved IV dopamine or epinephrine If everything fails Transvenous pacing |
|
|
DOC for bradyarrhythmias in children & infants |
Epinephrine |
|
|
Rx of PSVT without hemodynamic detoriation |
Vagal maneuver
Adenosine 6 mg iv first Then 12 mg iv (3 & 6 mg if through central line) |
|
|
Rx for PSVT with hemodynamic detoriation |
Cardioversion with 50 to 100 joules |
|
|
Sensitive investigation for MI |
In new regional wall motion abnormalities & decreased systolic wall thickening, peri operative settings - TEE > ECG |
|
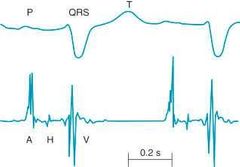
|
HBE (His Bundle Electrogram) A - AV node activation H - His bundle activation V - Ventricular activation Along with ECG and HBE 3 intervals are seen PA - SA node to AV node AH - AV node to His bundle HV - His bundle & Bundle branches |
|
|
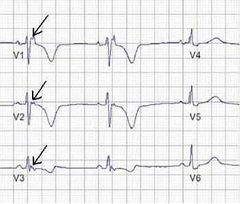
Epsilon wave buried in the end of QRS is characteristic of arrythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy T wave inversion seen in V1 to V3 |
|
|
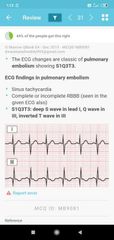
Pulmonary embolism |
|
|
|
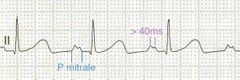
P mitrale seen in atrial enlargement
Notched P wave Biphasic wave with a positive negative terminal component (represent delayed depolarization of enlarged LA) |
|
|
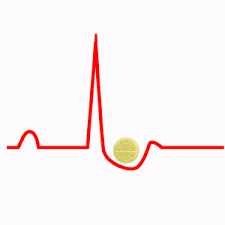
Digoxin effect Downslopping ST depression with 'Salvador dali sagging' or 'hockey stick' appearance Shortened, inverted, or biphasic T waves Short QT interval |
|
|
Ventricular bigeminy Every other beat is PVC (Premature Ventricular Complex |
|
|
Narrow complex tachy without visible P waves & sudden onset palpitations |
AV node reentrant tachycardia Rx is carotid sinus massage Drugs are Adenosine > beta blockers |
|
|
Rx for sustained monomorphic VT |
Hemodynamically stable
IV amiodarone
IV lidocaine/procainamide can also be given
Synchronized cardioversion in unstable patient Carotid massage is C/I |
|
|
Takotsubo |
Myocardial stunning The dysfunction extends more than specific coronary supply as implied in ECG (MI change) Ventriculography shows global ventricular dilatation with basal contraction |
|
|
Pseudo P pulmonale |
P wave peaking Seen in hypokalemia |
|
|
ECG changes in hypothyroidism |
Bradycardia with low voltage complexes |
|
|
Diffuse ST segment elevation in acute pericarditis |
|
|
ashman phenomenon |
Long RR interval followed by small RR interval Confused with PV Complex RBBB morphology |
|
|
CHADS2 VASc score |
Need for anti coagulation in AF Congestive heart failure - 1 Hypertension - 1 Age > 75 years - 2 Diabetes - 1 Stroke history - 2 Vascular disease - 1 Age > 65 years - 1 Sex, category, female - 1
|
|
|
Rx for recurrence in PSVT |
Catheter ablation |
|
|
Lev's disease |
Idiopathic fibrosis of conduction system |
|
|
DOC in multifocal atrial tachycardia |
Verapamil This is usually seen in COPD patients |
|
|
MC mechanism of Arrythmias |
Re entry |
|
|
MC benign cardiac rhythm |
Atrial premature contraction |
|
|
Arrythmias in MVP |
PSVT V T A Fib Premature ventricular contractions |
|
|
Non synchronous DC shock |
Monomorphic VT In Hypotension Impaired consciousness Pulmonary edema
|
|
|
Ecg changes with SAH |
Deep symmetrical T wave inversion Left axis deviation U waves R wave abnormalities Non specific ST-T changes |
|
|
Osborn waves |
J waves Seen in SAH Hypercalcemia Hypothermia Brain injury Cardiopulmonary arrest Idiopathic ventricular fibrillation |
|
|
R on T phenomenon Superimposition of an ectopic beat on T wave of a preceding beat that triggers polymorphic VT |
|
|
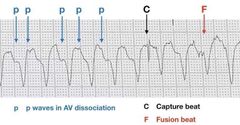
Seen in V tachy |

