![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the shape of a planet’s orbit?
|
Elipse
|
|
|
What theory states that the universe began in a violent explosion? What evidence(s) do we have to support this theory?
|
Big Bang Theory. Radiation, expansion (red shift/blue shift)
|
|
|
Why does Earth experience precession?
|
Change in direction of the axis of the Earth
|
|
|
Identify 1-3 on the diagram of Earth’s motions to the right
|
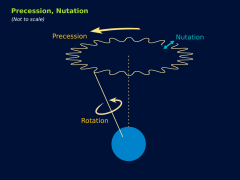
Precession, Nutation, Rotation
|
|
|
How are the following terms related to one another: galaxy, universe, star, and planet?
|
Galaxy = massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and dark matter
|
|
|
As a planet moves closer to the sun in its orbit, how is its motion affected?
|
Kepler's 2nd Law; “The Law of Equal Areas”
Planets sweep out equal areas in time The speed of a planet is faster at its perihelion |
|
|
Define the following terms:
|
Rotation- How many days does it take for the Earth to spin on its axis
Revolution- How many days does it take for the Earth to orbit the sun? Precession- Change in direction of the Axis Every 26,000 years. Nutation- A small irregularity in the tilt of the Earth due to gravitational pull of moon ½ a degree every 18 yrs. (Avg. 23.5) “Wobble Baby”he point at which the objects are balanced. NOT exact center the point at which the objects are balanced. NOT exact center Barycenter- The point at which objects are balanced. Not the exact center. |
|
|
Even though it appears that planets orbit the center of the sun, explain what is really happening (consider barycenter).
|
The center of mass of two or more bodies, usually bodies orbiting around each other, such as the Earth and the Moon. Based upon the mass of the two objects.
|
|
|
How can astronomers determine if a star is moving toward or away from Earth? Explain thoroughly.
|
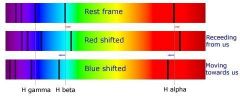
|
|
|
Why are the seasons in the Southern Hemisphere opposite to those in the Northern Hemisphere?
|
Due to the 23.5 degree tilt of the axis one hemisphere is tilted toward the sun while the other is tilted away.
|
|
|
Why does the Earth experience seasons?
Due |
Due to the 23.5 degree tilt of the axis and the revolution of the Earth around the Sun.
|
|
|
At what point is the tidal range at its greatest?
Draw a picture to show the positions of the earth, sun, and moon. |
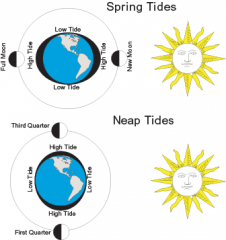
|
|
|
What is a tidal bulge and how is it formed?
|
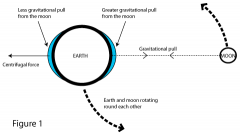
|
|
|
What chemical reaction produces the sun’s energy?
|
Fusion of Hydrogen atoms into Helium
|
|
|
Energy is transferred from the Sun to Earth mainly by
|
Radiation
|
|
|
At the higher latitudes, there is a lower concentration of solar energy than at the equator. What does this mean?
|
The rays of the sun are not hitting directly at this location. The areas with more direct rays of sun will have a warmer climate.
|
|
|
How does Earth’s atmosphere filter some of the electromagnetic radiation?
|
Radio Waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultra violet, x-ray, gamma
|
|
|
How is solar energy essential to plants?
|
The plants use solar energy to produce the nutrients the need to survive.
|
|
|
How does the sun’s energy affect food webs on Earth?
|
The plants absorb the suns energy and transfers it into food and nutrients. Smaller animals eat the plants and uses it for energy, in turn larger animals eat the smaller animals. This is the process that occurs in the food chain/web. As the energy passes form species to species, it decreases in amount.
|
|
|
What is the difference in the heating of land and the heating of water?
|
The land heats and cools more quickly than water.
|
|
|
How does the earth’s magnetic field interact with space? How does it protect us from radiation?
|
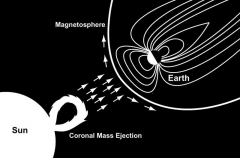
The Earth’s magnetic field redistributes the radiation from a CME (coronal mass ejection) out around the Earth. This radiation can also be seen as the aurora at the North and South Pole.
|

