![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is PLASMA?
|
The 4th STATE OF MATTER. When atoms are torn apart, their particles become charged (IONS) - nucleus (+) and electrons (-).
|
|
|
The sun gets its energy from FUSION. What is FUSION?
|
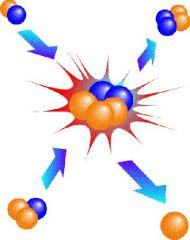
COMBINING of LIGHTER ELEMENTS to form a HEAVIER element. ENERGY is released in the process.
|
|
|
Why does fusion happen in the sun?
|
Charged particles normally repel each other. But IN THE SUN'S HEAT AND CROWDING, they fuse together.
|
|
|
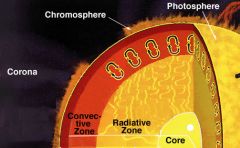
Name the layers of the sun and its atmosphere.
|
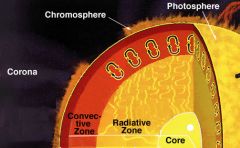
Core
Radiative Zone Convection Zone Photosphere Chromosphere Chromosphere Corona |
|
|
What elements make up the CORE?
|
HELIUM & HYDROGEN in a PLASMA state.
|
|
|
What layer has rising and falling currents of plasma that CARRY ENERGY TO THE SURFACE.
|
CONVECTION ZONE
|
|
|
What is the visible surface of the sun called?
|
PHOTOSPHERE
|
|
|
Which layer forms dense clouds that can erupt into space suddenly?
|
CHROMOSPHERE
|
|
|
Name the HOTTEST and COLDEST layers of the sun
|
Hottest - CORE (15.6 million degrees C)
Coldest - CORONA (1 million degrees C) |
|
|
What are SUNSPOTS and are they really dark?
|
They are spots with STRONGER MAGNETIC FIELDS than the surrounding areas (1000 times greater). They look dark only because the surrounding area is so much hotter and brighter.
|
|
|
Describe how the sun rotates.
|
UNEVENLY because it is a gas. Once in 25 days at the equator. Once in 34 days at the poles.
|
|
|
How long is a cycle of sun spots (from peak activity period to peak activity period)?
|
About 11 years.
|
|
|
What is SOLAR WIND?
|
A constant STREAM of ELECTRICALLY CHARGED PARTICLES. They fly from the Corona into space (through CORONAL HOLES)
|
|
|
Why doesn't most of the solar wind reach us?
|
Earth's MAGNETIC FIELD deflects it.
|
|
|
What are SOLAR FLARES
|
OUTBURSTS OF LIGHT - they rise up suddenly where there are sunspots.
|
|
|
What causes AURORAS (also called Northern and Southern Lights).
|

Some particles of SOLAR WIND INTERACT with the Earth's MAGNETIC FIELD. They look like displays of colored lights in the atmosphere near the poles.
|
|
|
What is the GEOCENTRIC MODEL of the universe? Who developed it in history?
|
EARTH in CENTER
PTOLEMY developed it in Greece about 200 A.D. |
|
|
What is a HELIOCENTRIC MODEL of the universe and who first developed it?
|
SUN in CENTER
COPERNICUS - Poland in the Middle Ages |
|
|
Why was TYCHO BRAHE able to get the most precise observations about the planets before the telescope was invented?
|
He studied the planets ALL THE WAY THROUGH THEIR ORBITS, instead of just at certain points.
|
|
|
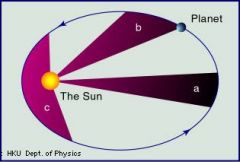
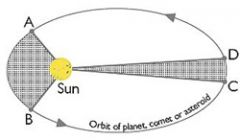
Explain Kepler's SECOND LAW OF PLANETARY MOTION or how PLANETS COVER EQUAL AREA.
|
The EQUAL AREA LAW explains that planets cover the same amount of area in the same amount of time throughout the orbit. Planets move FASTER when they are CLOSER TO THE SUN.
|
|
|
Explain KEPLER'S THIRD LAW OF PLANETARY MOTION, or how you figure out a planet's distance from the sun.
|
The HARMONIC LAW gives the formula: p2 = D3 (period of a planet equals the cube of its mean distance from the sun).
|
|
|
What is RETROGRADE MOTION and why does it happen?
|
A planet APPEARS TO MOVING BACKWARD (east to west) because a FASTER PLANET IS PASSING IT.
|
|
|
What was Newton's LAW OF GRAVITY.
|
Every mass exerts a force of attraction on every other mass. The strength of the force is proportional to SIZE and DISTANCE APART of the two objects. (The larger mass has more force; the closer two masses are, the greater their gravitational pull).
|
|
|
What did it explain about our solar system.
|
WHY THE PLANETS STAY IN ORBIT around the sun. He said that a mass will move forever in a straight line unless another force changes it. For planets, it is the SUN's GRAVITY that pulls them out of the straight line.
|
|
|
SKIP
|
SKIP
|
|
|
skip
|
skip
|
|
|
skip
|
skip
|

