![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
198 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
SAFETY FUNDAMENTALS |
AIRCRAFT HANDLING FUNDAMENTALS |
|
|
Discuss the concept of ORM and it's process |
(IAMIS) |
|
|
Respiratory Protection Program |
Respiratory- identifies employee respirator requirement due to the nature of their work or job |
|
|
Identify the EA-18G danger areas. |
canopy, seat, DFIRS, external stores locations, engine, radar, antenna, exhaust, movable sufaces, flammable liquids and compressed gases |
|
|
Identify the minimum safe distances from aircraft intakes/exhaust at: |
Intake Exhaust |
|
|
Purpose and Location of the aircraft STEP, NO STEP Areas |
To avoid damaging composite material. |
|
|
Safety precautions when applying and removing external power |
Ensure Circuitbreakers and switches are properly positioned |
|
|
Identify the danger areas during Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) operations. |
The Exhaust velocity of the APU reaches 142 MPH |
|
|
Precautions/Restrictions that Apply to Ordnance Loaded Aircraft |
Major maintenance on aircraft is prohibited. |
|
|
WEAPONS LOADED placard/control stick cover indicates maintenance/servicing with electrical power is limited to: |
Refueling |
|
|
Precautions when handling Graphite or Carbon/Epoxy Composite Materials. |
Wear respirator and close weave cotton gloves |
|
|
State the number of tie-down points on the EA-18G and identify their location. |
12 tie-down rings: |
|
|
State the proper procedures for aircraft grounding |
Connect grounding cable to approved ground receptacle |
|
|
State the purpose of aircraft plugs and covers. |
Protect aircraft openings and protruding surfaces from FOD and physical and environmental damage |
|
|
Move Director |
Primarily responsible for move, delivers the move brief. |
|
|
Brake Rider |
Conducts a pre-movement inspection of aircraft Ensures aircraft pins are installed and aircraft is free from servicing equipment / external cords |
|
|
Chock Walker |
Stays alert to director's signals |
|
|
Safety Observer (Wing-Walker/Tail-Walker) |
Conduct's a pre-tow inspection of the aircraft |
|
|
Tractor Driver |
Pre-OP's tractor |
|
|
Discuss towing preparations |
a. Minimum structural access doors must be installed |
|
|
State the purpose of the landing gear aircraft ground safety pins |
Locks the nose and main landing gear in the down position, preventing gear retraction. |
|
|
Describe the hazard associated with canopy static buildup |
a high voltage static electrical charge of up to 100,000 volts may build up and be stored in the canopy during flight or when aircraft is exposed to prolonged high winds |
|
|
Discuss the canopy static discharge process |
Make sure a/c is properly grounded |
|
|
AIRFRAMES FUNDAMENTALS |
x |
|
|
State the purpose of Hydraulic Fluid Contamination Analysis |
Analyzes fluid contaminant level to ensure purity |
|
|
State the purpose of a tactical paint scheme |
Lessen the probability of visual or photographic detection |
|
|
State the purpose of the following publications and their application: |
509- Provides information on material & procedures to prevent & repair of corrosion |
|
|
3 modes of wheel brake operation |
Normal |
|
|
Discuss the purpose of composite airframe materials |
limit weight, increase strength, and decrease effects of corrosion |
|
|
Describe the 3 types of repair |
Temporary Repair- simple and practical, allows aircraft to be flown until permanent repair can be made. |
|
|
Radome |
Covers radar and provides an electrically transparent window for transmission and reception of radar signals. |
|
|
Forward Fuselage |
Includes the windshield, canopy, cockpit, leading edge extension, and nose landing gear. |
|
|
Center Fuselage |
Includes main landing gear, intake ducts, external stores stations, fuselage fuel tanks and airframe mounted accessory drive. |
|
|
Aft Fuselage |
Includes the engines, speed brake, vertical stabilizers, horizontal stabilators, and arresting hook |
|
|
Wings |
Provides lift for the aircraft, stores fuel, houses LEF's, TEF's and Ailerons, outboard section folds for carrier operation, allows for attachment of non jettison pylons for weapons and stores. |
|
|
Leading Edge Extension (LEX) |
Provides added lift at high angles of attack. Mounted on either side of the Forward Fuselage they are an extension of the wing leading edge. |
|
|
Ailerons |
Deflect Asymmetrically to produce roll, Symmetrically to change lift. |
|
|
Leading Edge Flaps |
Deflect Symmetrically to change lift. |
|
|
Trailing Edge Flaps |
Deflect Asymmetrically to aid the ailerons in producing roll. |
|
|
Stabilators |
Deflect Symmetrically to produce pitch. |
|
|
Rudders |
Toe-in- increases lift and improves stability at AOA les than 8 degrees |
|
|
LEX Spoiler |
Provides speed brake when commanded by pilot at speeds less than MACH 1.5, provides a high nose down pitch movement when transitioning from a high AOA. |
|
|
Hydraulic System 1 (HS1) |
HS1- Provides hydraulic fluid pressure to the primary flight controls either as a primary or backup source. |
|
|
Auxiliary Power Unit Accumulator |
Gas Charge cylinder provides required fluid pressure to the APU start motor and emergency hydraulic systems |
|
|
Switching Valves |
allow backup hydraulic pressure to replace the primary hydraulic pressure, should it fail. If primary hydraulic is restored, the switching valve shifts to normal operating position |
|
|
Nose Landing Gear |
Nose landing gear strut assembly provides landing, takeoff and taxi energy absorption, and tire/runway compliance. |
|
|
Main Landing Gear |
Absorbs the energy during landing and taxi operations. Also provides a stable platform for aircraft carrier and shore-based operations. |
|
|
Wheel Brakes |
Provides modulated individual wheel-controlled braking combined with an anti-skid system to prevent wheel skid. |
|
|
Launch Bar |
Provides a means of steering the aircraft during carrier deck tracking and engages the catapult, applying catapult tow forces to the aircraft. |
|
|
Arresting Hook |
Engages the arrestment cable on the carrier to stop the aircraft, also provides a means of stopping the aircraft where normal runway landings are unavailable |
|
|
Discuss basic operation of the Electronic Flight Control System |
The Electronic flight control system is made up of two flight control computers that combine inputs with air data and inertial inputs and provide electrical signals to servo actuators which move control surfaces. A built-in test provides failure warning and fault isolation. |
|
|
Discuss Emergency Extension of the Landing Gear |
Emergency extension is primarily free fall aided by stored energy in the MLG shock absorber and hydraulic system no. 2B pressure. |
|
|
POWER PLANTS |
xx |
|
|
State the 3 modes of operation for the APU |
Environmental Control Systems |
|
|
State the purpose and location of the IFR probe |
Right forward fuselage |
|
|
Purpose of Aircraft Fuel Storage System |
Manage and store fuel for delivery to aircraft engines |
|
|
State the purpose of the foam-lined wing tanks. |
To self-seal holes or damage, decreasing fire and explosion hazards |
|
|
What are the secondary power systems? |
APU |
|
|
Auxilary Power Unit (APU) |
A centrifugal flow gas turbine engine that supplies air for ECS operation and MES and GMM through AMADs. |
|
|
Airframe Mounted Accessory Drive (AMAD) |
Consists of two identical interchangeable gearboxes that are mechanically connected to the engine by a power transmission shaft (PTS). And is pneumatically connected to the APU through the air turbine starter (ATS). The AMAD transmits power to the engine for starts. |
|
|
Secondary Power Compressed Air |
Provides pneumatic power for operating the air turbine starter or the environmental control system, provided by the APU or engine bleed air. |
|
|
State the model type and engine used in the EA-18G |
F414-GE-400 is a low by-pass axial flow turbo fan engine of modular construction with afterburner |
|
|
Ignition |
An automatic, intermittent duty, AC powered, capacitor discharge system. |
|
|
Lubrication |
Provides lubrication and cooling to required bearings and gears. |
|
|
Main fuel |
Primarily supplies fuel for all main fuel combustion operations from IDLE to MIL power. |
|
|
Afterburner fuel |
Governs the correct afterburner fuel flow controlling afterburner operation from start through MAX |
|
|
Variable Exhaust Nozzle (VEN) |
throat area for exhaust gasses from the turbine and afterburner. |
|
|
Variable Geometry |
Consists of: |
|
|
Anti-icing |
Manually activated system that provides anti-ice air flow to prevent ice buildup on air inlet hardware. |
|
|
Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) |
Receives aircraft and engine sensor information and determines the appropriate engine scheduling to operate the engine. |
|
|
Throttle |
Provides pilot control of engines. |
|
|
Fuel Systems |
x |
|
|
Fuel storage |
Fuel is stored in: |
|
|
Refuel/Defuel System |
A manifold with a single point ground and an outlet in each tank. |
|
|
Internal Fuel Transfer |
Keeps tanks 2 and 3 full and controls the sequence of tank-to-tank transfer. |
|
|
Center of Gravity (CG) Control |
The SDC monitors the amount of fuel in tanks 1 and 4; so, if fuel in tank 4 becomes excessive the computer will close its valves to prevent an aft center of gravity problem |
|
|
Hot Fuel Recirculation |
Cools the fuel by circulating fuel up into the wings to be cooled by means of convection, which is used to dissipate heat from the AMAD and hydraulic system |
|
|
Fuel Pressurization and Vent |
Maintains positive pressure on the fuel in all tanks and vents fuel vapors overboard |
|
|
Fuel Quantity Gauging |
Fuel quantity is measured using capacitance gauging transmitters that send signals to the SDC |
|
|
State the components driven by the AMAD. |
fuel boost/motive flow pump |
|
|
How does the AMAD interface with the APU and engine? |
The AMAD is pneumatically connected to APU through the air turbine starter (ATS). The AMAD transmits power from the ATS to the engine for starting and motoring. Power to drive the AMAD accessories is provided by the engine during normal operation and by the APU in the ground maintenance mode of operation. |
|
|
What safety precautions must be observed during engine ground turn-up? |
During engine ground turn-up, danger can stem from exhaust velocity and temperature, air intakes, and noise. |
|
|
What special safety precautions apply to: |
Do NOT do within: |
|
|
AVIONICS/ELECTRICAL |
xx |
|
|
Barometric Altimeter |
Barometric- uses pitot-static pressure to indicate altitude above sea level |
|
|
1) Azimuth |
1) Angular position in a horizontal plane usually measured clockwise from true north. |
|
|
1) Heading |
1) Actual orientation of aircrafts longitudinal axis |
|
|
State the advantage of using Fiber Optic Cables in the EA-18G |
The provide improved system performance |
|
|
State the purpose of the following communication systems |
provides air-to-air and air-to-ground communications in fixed frequency or anti-jam mode |
|
|
State the purpose of the following communication systems |
Provides amplification and routing of audio signals between cockpit, ground crew, and rear cockpit. |
|
|
Name the Navigation Systems |
TACAN |
|
|
Tactical Air Navigation (TACAN) |
determine the relative bearing and distance to a TACAN ground station or TACAN equipped aircraft. |
|
|
Inertial Navigation System (INS) |
Fully automatic dead reckoning navigation system. |
|
|
Global Positioning System (GPS) |
A navigation system that receives reference information from a satellite source and provides the pilot and other aircraft systems with updated present position, velocity and time information. |
|
|
Attitude Reference Indicator (ARI) |
A self-contained attitude reference system that provides backup pitch and roll attitude for use by other systems. Provides 3 minutes of attitude information with loss of power. |
|
|
Instrument Landing System (ILS) |
An all weather approach guidance system. The ILS decodes transmitted azimuth and elevation signals during an aircraft approach and provides steering information to be displayed on the head-up display (HUD) |
|
|
Tactical Mission Systems |
Data Link |
|
|
Data Link |
A two-way uhf communication link between the aircraft and other ship, air, or ground systems. |
|
|
Radio Detection and Ranging (RADAR) |
Provides Air-to-air (A/A) and Air-to-ground (A/G) modes for target detection, designation, tracking and navigation |
|
|
Mission Computer (MC) |
MC System is made of 2 identical digital data computers that control the display sent to the multipurpose display group. |
|
|
Tactical Electronic Warfare Systems |
xx |
|
|
Communication Countermeasures Set (CCS) |
Produces waveforms for jamming low frequency communication - and provides growth provisions for a high power CCS transmitter |
|
|
ALQ-99 |
Provides Very Low to High Band radar and communication jamming of hostile radar and communications, in order to enable a safer penetration of enemy airspace. |
|
|
ALQ-165/214 |
onboard jamming system; uses multiple techniques to defeat tracking and acquisition radar |
|
|
ALQ-218 |
Detects, classifies, locates, and reports radar emitters and associated signals received by antennas mounted around the aircraft on the forward and aft fuselage and on the wingtips. |
|
|
What are the major components of the AN/ALQ-99 Tactical Jamming System |
Turbo-generator housing (hardback) |
|
|
Identify the location of the major components of the AN/ALQ-99 Tactical Jamming |
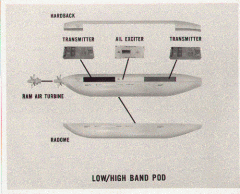
|
|
|
What are the multipurpose display group (MDG) components? |
HUD |
|
|
Heads-Up Display (HUD) |
Provides flight, navigational steering, and weapon delivery information to the pilot's forward field of view. |
|
|
Digital Display Indicators (DDI) |
LDDI-used primarily for stores management, caution, advisory, and BIT displays. |
|
|
Up Front Control Display (UPCD) |
Touch screen, provides for entry and display of aircraft data, used for selection and control of communication, navigation, and identification functions. |
|
|
Multipurpose Color Display (MPCD)- |
MPCD has mechanical pushbuttons for operator inputs and is used as a multifunction display; if two different map formats are selected on the front and rear MPCD: |
|
|
Describe the function of the Digital Map Set (DMS) |
The DMS is made up of a Digital Map Computer (DMC) and a high speed interface cable. It's part of the Tactical Aircraft Moving Map Capability (TAMMAC) system which provides enhanced navigational/tactical situational awareness to aircrew, using a moving map and image database. |
|
|
Describe the function of the Solid State Recorder |
Records cockpit and sensor video, also stores off-board images and allows access to images loaded on the Removable Memory Module (RMM) |
|
|
State the location, purpose, and color of the following exterior lights |
xx |
|
|
Position |
Show position of A/C at night |
|
|
Strobe |
Two red (anti-collision) lights, one on each outboard vertical stab. |
|
|
Landing/taxi |
White light on the nose gear strut. Used to illuminate the taxiway/runway |
|
|
Approach |
On NLG strut, activated when all landing gear are down and locked and weight off wheels. Displays the AOA to the LSO during carrier approach. |
|
|
Formation Lights |
8 green LED lights. Two on each wing tip, one outside of each vertical stab, and one on each side of the forward fuselage just forward of the lex. They indicate changes of attitude and relative position of aircraft flying in formation. |
|
|
State the purpose of the Deployable Flight Incident Recorder Set (DFIRS) |
The purpose of DFIRS is to store flight data and to deploy it before a crash. In door 300; a thin layer explosive, impact initiator, and detonation cord provide deployment operations. A beacon will transmit signals to be detected by search and rescue sattelite for 72 hours. |
|
|
Flight Reference Equipment |
Pitot Static System |
|
|
Pitot Static System |
Measures temperature, pitot and static pressures surrounding the aircraft. |
|
|
Indicated Airspeed Indicator |
Displays airspeed as a function of the pitot and static pressure. Airspeed is indicted in 10-knot increments from 50 to 200 and 50-knot increments from 200 to 850 |
|
|
Standby Pressure Altimeter |
Displays altitude with 3 displays: |
|
|
Vertical Speed Indicator |
Senses changes in air pressure and displays them in the form of climb or dive rate from 0 to 6000 feet per minute |
|
|
Air Data System Components |
Air Data Pressure Transmitters |
|
|
Air Data Pressure Transmitters |
Converts pneumatic static and total pressure inputs from pitot probes into digital signals. Air data is sent to the roll-pitch-yaw computers where it is evaluated to produce true air data. Air and true air data are used by roll-pitch-yaw computer software for flight control law computations, pilot displays, and other avionics systems. |
|
|
Angle of Attack (AOA) indexer |
Operates with landing gear down and weight off wheels, shows pilot approach AOA with lighted symbols |
|
|
Angle of Attack Transmitters (AOAT) |
measures the difference between the longitudinal axis of the aircraft and the airstream |
|
|
Describe the function of the following electrical power components: |
X |
|
|
Power Supply |
Consists of two generators, two transformer-rectifiers (TR), one battery with battery charger, and a power distribution (bus) system. |
|
|
Maintenance Battery |
Supplies 28vdc to the essential and maintenance buses. It will supply power to the essential buses if both power supplies and generators are inoperative. It also supplies power for engine start when external power is not applied. |
|
|
Generator |
Each generator is a variable speed constant frequency power system supplying 115/200vdc, 400 Hz, three phase electrical power. |
|
|
Describe the function of the Automatic Flight Control System (AFCS) |
Provides autopilot and automatic throttle control (ATC) |
|
|
State the purpose of the nose wheel well Digital Display Indicator (NDDI) |
Receives and stores maintenance codes and displays them upon operator request. |
|
|
Digital Memory Device (DMD) |
Programmable solid state memory device. Records mission and maintenance data on two downloadable memory cards. |
|
|
State the purpose of Flight Incident Recorder and Monitoring System (FIRAMS) |
Monitors engine and airframe operational status for unit failures and caution/advisory conditions. |
|
|
Discuss the Joint Helmet Mounted Cueing System (JHMCS) |
JHMCS improves situational awareness, increases aircraft survivability and increases the ability to acquire a visual target. |
|
|
State the objective of the Explosive Handling Qualification and Certification Program |
To certify and train all personnel in safely performing tasks involving explosive devices |
|
|
State the purpose of suspension/accessory equipment |
To suspend and release stores, bombs, and a variety of missiles |
|
|
State the purpose of an impulse cartridge (Cartridge Actuated Devices (CADS)) |
To eject single stores and a variety of weapons from the aircraft |
|
|
Define the following acronyms: |
Air-Launched Intercept-Aerial Guided Missile. (Air Intercept Missile) |
|
|
Describe the application of the following types of bombs: |
Retarded- Used during low-level bombing, fins open to slow down weapon, allowing jet time to clear the area |
|
|
Explain the significance of the following color-coding on weapons: |
Yellow- High Explosive |
|
|
Define the following types of weapon-guided systems: |
Active- target illumination is supplied by component inside the missile |
|
|
Describe the purpose of chaff and flares as countermeasure devices. |
Chaff- Finely shredded metal strips that disperse into the atmosphere and jam radar |
|
|
Describe the hazards associated with forward firing ordnance. |
auto-ignition |
|
|
Describe the type of bomb rack used on the EA-18G. |
BRU-32 |
|
|
Describe the location and purpose of the ICM switch. |
On left forward fuselage. |
|
|
State the purpose of the following components of the Stores Management System or (SMS) |
1) Provides electrical interface between weapon stations and aircraft. Consists of the Armament Computer and up to nine Signal Data Converter Controls. |
|
|
State the purpose of the Countermeasures Dispensing system: |
47- The system provides protection for the aircraft against enemy radars and missiles by ejecting chaff, flares, or other jammer payloads. |
|
|
State the basic armament configuration of the EA-18G aircraft. |
Fuselage LAU-116 missile launchers |
|
|
Stations: |
1) LAU-127 - 2 or 10 |
|
|
State the basic characteristics of the following air-to-air missiles: |
Solid fuel rocket propelled air-to-air missile with a conventional warhead that uses SEMI-ACTIVE radar homing |
|
|
AIM-9 series (Sidewinder) guided missile |
9M- A supersonic, air-to-air weapon, with a PASSIVE infrared target detection, proportional-navigation guidance, and torque balance control system. |
|
|
AIM-120 Advanced Medium Range Air-to-Air Missile (AMRAAM) |
Is a supersonic, air-to-air weapon, with active radar target detection and on-board inertial navigation guidance. |
|
|
State the basic characteristics of the following air to ground missiles: |
A solid fuel rocket propelled AGM missile with a conventional warhead, uses imaging infared guidance. |
|
|
AGM-84 series missiles |
AGM-84 series: Liquid fuel jet engine propelled AGM missiles with conventional warhead, primarily used as anti-ship weapons. |
|
|
AGM-88 High-speed Anti-Radiation Missile (HARM) |
A solid fuel rocket propelled AGM with conventional warhead, uses proportional guidance to home in on threat radar emissions. |
|
|
AVIATION LIFE SUPPORT/EGRESS |
X |
|
|
Identify the minimum requirements for aircrew Personnel Protective Equipment |
1) Flight suit |
|
|
State the purpose of the Environmental Control System (ECS) |
Provides Avionics Cooling and Aircrew Comfort |
|
|
Environmental Control System (ECS) 12 subsystems: |
1) Bleed air control |
|
|
State the purpose of the following personal flight equipment: |
Provides breathing gas upon demand at a pressure schedule dependent on the altitude. Also provides facial protection from projectiles and fire as well as being qualified for depths of 16ft under water. |
|
|
The CRU-103/P Oxygen regulator |
A chest mounted, positive pressure, g-modulated regulator that provides on demand oxygen flow to the aircrew |
|
|
The LPU-36/P Life Preserver |
A Low Profile Floatation Collar equipped with the FLU-8B/P automatic/manual inflation assembly authorized for use only with aircraft equipped with ejection seats. |
|
|
Anti-G Suit |
Consist of a bladder system encased in fire-resistant cloth, As G-forces increase the bladders inflate automatically to apply pressure on the body to restrict downward bloodflow and lessen the effects of blackout. |
|
|
State the objective of the Egress Systems Checkout Certification Program. |
To familiarize and monitor personnel working in or around the cockpit with the ejection systems. |
|
|
State the purpose of the ejection seats. |
Provides a place for the aircrew to sit and for emergency egress during flight |
|
|
Define the following conditions: |
Hypoxia- Decrease in the amount of oxygen per unit volume of air which results in an insufficient amount of oxygen in the bloodstream causing the eyes, body and muscles to fail. (Blackout) ((Insufficient oxygen-causes blackout)) |
|
|
Identify the two types of Aviator's Breathing Oxygen (ABO |
Type I: Gaseous oxygen - MIL-0-272710D |
|
|
State the purpose of the Dry Bay Fire Suppression System (DBFSS) |
The Dry Bay Fire Suppression System suppresses fire events associated with ballistic damage to the aircraft before a significant fire occurs. Performs without pilot action and consists of 14 optical fire detectors, 6 dry bay extinguishers and a fire suppression control alarm. |
|
|
State the purpose of the Parachute Harness Sensing Release Unit (PHSRU) |
A sea water activated release system that provides a backup automatic mode of separating the parachute from the aircrew. |
|
|
Describe the A/A24A-56 Helmet Unit, Intergrated, Joint Helmet Mounted Cueing System (JHMCS) |
A display system used to cue, verify, and employ weapons and sensors in high off bore sight angles. |
|
|
State the purpose of the Helmet Mounted Display Unit (HDU) |
HDU displays symbology onto the visor and is superimposed on the operators view. |
|
|
Discuss the location and type of ejection seat used in the EA-18G. |
The ejection seat is a SJU-17B (V) 2/A (front) 9/B (back) |
|
|
Discuss the location and procedures for the operation of the canopy system. |
Normal Operation- Electrically with internal or external switch. Manually as backup when electrical power fails. |
|
|
Discuss the location and operation of the Aircraft Fire Detection and Fire Extinguishing Systems. |
The fire detection system monitors the AMAD, APU, and engine bays for fire or overheat conditions. Provides audible and visual warnings of these conditions. |
|
|
Environmental Control Systems: |
Consists of various clamped, insulated metal ducts that connect system control valves and sensors. |
|
|
Air Cycle Air Conditioning System |
Cools and conditions engine bleed air for use in ECS and other systems. |
|
|
Anti-Gravity System |
Made of tubing and a valve that automatically regulates air pressure to the pilot's anti-g suit to increase pilot tolerance to high acceleration levels. |
|
|
On-board Oxygen Generation System (OBOGS) |
Series of lines valves and a concentrator that regulate pressure, control flow and distribute oxygen to the crew station. |
|
|
Ejection Seat System |
Operated by ballistic gas pressure. Each seat initiator contains 2 cartridges. Gases from the right cartridge start canopy jettison, activate the seat electronic sequencer and restraints, and fires the seat catapult after a delay inserted by the escape system. Gases from the left cartridge redundantly activate the seat electronic sequencer and also provides a backup source to fire the seat catapult. |
|
|
Canopy System |
Provides the capability to explosively jettison the canopy from the aircraft in case of emergency. |
|
|
Emergency Oxygen System |
Located in the seat pan and is manually operated by a green handle located on the left side of the seat platform. |
|
|
Describe the safety precautions that apply to: |
Ejection Seats- Pins are installed and handle safe |
|
|
OPERATIONAL FUNDAMENTALS |
X |
|
|
Define the following acronyms: |
AIRNAV- Airborne Navigation |
|
|
Define the following acronyms: |
FCLP- Field Carrier Landing Practice |
|
|
Aviator Flight Rules: |
(Visual Meteorological Conditions) |
|
|
Aviator Flight Rules: |
(Visual Flight Rules) |
|
|
Discuss the purpose of the Carrier Air Traffic Control Center (CATCC) |
Primary control of airborne aircraft operating from the carrier, responsible for the status and upkeep of all carrier air operations. |
|
|
Describe the following Landing Systems: |
The FLOLS or “meatball” is an optical system on board the carrier that aids pilots in landing aboard the ship. |
|
|
Command's Mission Statement |
To indoctrinate, train, and qualify USN, USMC, and USAF aircrew in the EA-18G aircraft to fight and win in electronic combat. We enhance fleet combat readiness with direct support. |
|
|
Warfare Mission Areas: |
AAW- The detection, tracking, destruction or neutralization of enemy air platforms and weapons, whether launched by the enemy from air, surface, subsurface, or land platforms. |
|
|
Warfare Mission Areas: |
C2W- The integrated use of psychological operations (PSYOP), military deception, operations security (OPSEC), electronic warfare (EW), and physical destruction; mutually supported by intelligence, to deny information to, influence, degrade, or destroy adversary. |
|
|
Warfare Mission Areas: |
MIW- use of mines in sea control and mine countermeasure over, under, or on surface. |

