![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Outline DNA nucleotide structure in terms of sugar (deoxyribose), base (4) and phosphate
|
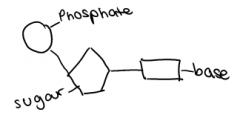
DNA is made up of sub units (nucleotides)
A nucleotide is made of the sugar deoxyribose, a base (either adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine)(nitrogen based) and a phosphate group |
|
|
State the names of the four bases
|
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
|
|
|
Outline how DNA nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds into a single strand
|
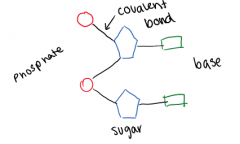
Two DNA nucleotides can be linked together by a covalent bond between the sugars of one and the phosphate of another
More can be repeated in this way to create a strand of nucleotides, aka polynucleotide |
|
|
Explain how a DNA double helix is formed using complementary base pairing and hydrogen bonds
|
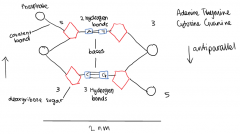
1. DNA molecules consist of 2 polynucleotide strands that are held together by hydrogen bonds through the base pairing
2. Even though hydrogen are weaker than covalent bonds, there are many between the strands which holds them together securely 3. Adenine pairs with Thymine, 2 hydrogen bonds 4. Cytosine pairs with Guanine, 3 hydrogen bonds 5. For the bases to be able to pair, the polynucleotides must run in an antiparallel direction 6. Intermolecular forces and base polarity influence the DNA shape 7. These strands then twist and turn, forming a double helix |
|
|
Draw and label a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA
|
|

