![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
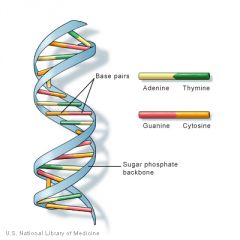
What is DNA? |
Double stranded molecules, each strnad is a polynucleotide made up of individual nucleotides. |
|
|
What is each nucleotide in DNA compromised of? |
A phosphate, deoxyribose sugar and nitrogenous base. |
|
|
What bases pair with which in DNA? |
Adenine pairs with Thymine, Guanine pairs with Cytosine |
|
|
Is the DNA in prokaryotes associated with proteins? |
no |
|
|
What DNA do prokaryotes have? |
Nucleoid- single loop of circular DNA Plasmids- small circular loops of DNA containing one or two genes. |
|
|
Describe the DNA of chloroplast and mitochondria (in eukaryotes): |
Is short and circular and not associated with proteins. |
|
|
Describe the DNA in the nuclei of Eukaryotes: |
Very long and linear molecule associated with histone proteins to form a chromosomes. |
|
|
What is the chromosome formed of? |
DNA molecules is wrapped around histone, the DNA histone complex is then coiled further. |
|
|
How is eukaryotic DNA arranged in chromosomes and wrapped around histones? |
It is wrapped around histones to fix it in position. THe coiling means that a very long molecules of DNA can be condensed into a single chromosome and a lot of genetic information can be stored in the nucleus of each cell. |
|
|
Describe the chromosomes during interphase: |
The chromosomes are dispersed throughout the nucleus and are not visible as separate structures. |
|
|
What type of chromosomes to diploid cells have and why? |
Homologous pairs of chromosomes as diploid organisms inherit a full set of chromosomes from each parent. |
|
|
What is the diploid number in humans? |
2n=46 |
|
|
Where do the chromosomes in a homologous pair come from? |
On member of the pair (maternal chromosome) is inherited from the mother. One member of each pair (paternal chromosome) is inherited from the father. |
|
|
True or false homologous chromosomes are gentically identical. |
FALSE!! Homologous pairs carry the same genes at the same locus but not necessarily the same alleles. |
|
|
What is a gene? |
A base sequence of DNA that codes for either: An amino acid sequence of a polypeptide or a functional RNA. (including rRNA and tRNA) |
|
|
What is a locus? |
Fixed position on a DNA molecule that a gene occupies. (A DNA molecule can have many genes). |
|
|
What percentage of DNA in humans codes for amino acid sequence? |
Only 2% (exons) |
|
|
What is inbetween genes? |
Non-coding multiple repeat sequences. |
|
|
What are the the parts of genes called that code for amino acid sequences called? |
exons |
|
|
What is the difference between (non-coding) multiple repeat sequences and introns? |
Introns are non-coding regions found within genes that separate exons. (non-coding) multiple repeat sequences are found between genes. |
|
|
What is the genome? |
The complete set of all the genes in a cell including the genes in the nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts. |
|
|
What is a proteome? |
The full range of all proteins that a cell is able to produce using its genome. |
|
|
What is an allele? |
Some genes have two or more alternative forms. Each allele has a different sequence of bases and consequently codes for a different polypeptide. |
|
|
What is gene pool? |
The different alleles of all the genes found within a population. |
|
|
What is a triplet? |
Every three bases in the sequence is a triplet and codes for a specific amino acid. |
|
|
How many different possible combinations of triplets are there and how many amino acids to they code for? |
64 (4^3) possible triplets for 20 amino acids |
|
|
Why is the code known as degenerate? |
Most amino acids are coded for by than one triplet. |
|
|
What is the first triplet always and what does it code for? |
ATG methionine. |
|
|
What is a stop triplet and how many are there? |
It is a triplet that doesn't code for an amino acid and is found at the end of each gene. It causes the disengagement of RNA polymerase during transcription. There are 3. |
|
|
Why is the code known as universal? |
It is the same for all organisms. |
|
|
Why is the code known as non-overlapping? |
Each base is read only once. |
|
|
What is RNA? |
A single polynucleotide strand . The nucleotides are compromised of phosphate, a ribose sugar and nitrogenous base: Uracil, Adenine, Guanine and Cytosine. |
|
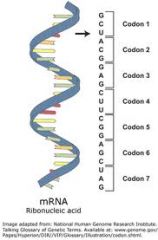
Describe the structure of mRNA: |
mRNA molecules are up to a few thousand nucleotides long. Each three bases is called a codon. The bases do not bond to each other. |
|
|
How many nucleotides does a tRNA molecule have? |
75 |
|
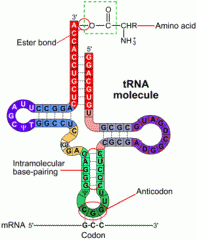
Describe and explain the structure of a tRNA molecule: |
Clover leaf shape. The strand folds back on itself and hydrogen bonds form between bases. At one end there is an amino acid binding site. At the other end there is an anticodon, where three of the bases are exposed. |
|
|
How many types of tRNA are there and how are they different? |
61(64-3 stop triplets) types of tRNA molecules. Each has a different sequence of bases in anticodon. Each type of tRNA molecule only carries one type of amino acid. |
|
|
What does the anticodon do? |
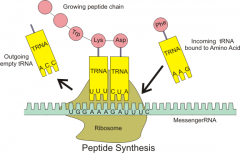
Binds to a complementary codon onmRNA during translation. |
|
|
True or false unlike in mRNA and tRNA in DNA there is a set ratio of A and T and of C and G? |
True- DNA is double stranded and the base pairs are complementary. RNA is single stranded. |
|
|
What are the three stages in protein synthesis? (in Eukaryotes) |
Transcription, splicing mRNA, translation |
|
|
Do prokaryotes have introns? |
Prokaryotic, mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA does not have introns. (so mRNA does not need splicing). |
|
|
Where does transcription take place? |
In the nucleus. |
|
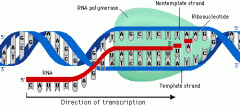
What is the first step of transcription? |
One geneunwinds due to hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs being broken. |
|
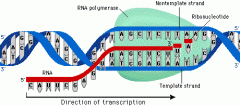
What happens after the gene has unwound? |
Complementary free RNA nucleotides bind to exposed bases on template strand. The sugar-phosphate backbone between free RNA nucleotides is joined using RNA polymerase. |
|
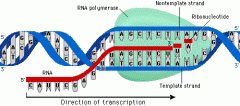
What enzyme forms the sugar-phosphate backbone in RNA? |
RNA polymerase. |
|
|
What is made when the sugar-phosphate backbone is made between free RNA nucleotides? |
pre-mRNA |
|
|
Why is it called pre-mRNA? |
It contains both intron and exon sections of the gene. |
|
|
When does transcription stop? |
When a stop triplet is reached that marks the end of the gene. The RNA polymerase disengages. |
|
|
True or false a gene is transcribed repeatedly to make many mRNA at once? |
true |
|
|
What can genes be transcribed to make? |
pre-mRNA, ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. |
|
|
Where does splicing occur? |
nucleus. |
|
|
What is splicing? |
pre-mRNA is spliced in eukaryotes, the non-coding sections (from introns) are cut out and the coding sections (from exons) are edited togeth |
|
|
Where does translation occur? |
in cytoplasm |
|
|
How does mRNA leave nucleus? |
Through a nuclear pore and then binds to ribosome. |
|
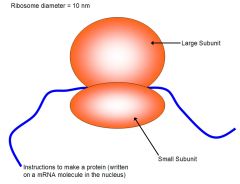
What do ribosomes contain? |
ribosomal RNA. |
|
|
What is the first step in translation of a gene? |
Ribosome binds to first two codons on the mRNA. A tRNA carrying methionine comes to the ribosomes and the anticodon on the tRNA binds to complementary codon on mRNA. |
|
|
What is the second stage of translation? |
A second tRNA carrying a specific amino acid, binds to the second codon. |
|
|
What is the third stage of translation? |
The two amino acids undergo a condensation reaction and peptide bonds form between them. |
|
|
What happens during the 4th stage of translation? |
The first tRNA leaves the ribosome. The ribosome moves along the mRNA to cover the next codon. The anticodon of a tRNA carryinbg an amino acid binds to codon of mRNA. |
|
|
Explain the experiment that was carried out to show that it is viral DNA that carries the genetic code for new proteins and not viral proteins which remain on the outside of the cell? |
Scientists made viruses that had DNA with radioactive phosphororus in it and proteins with radioactive isotopes of sulfur. The virues were allowed to infect bacteria then the bacteria were tested to see if they had taken up proteins or DNA. Radioactive sulfur was found on only on outside of cell whereas radioactive phosphorus was found on inside. New viruses were made and released as normal. |
|
|
WHy did scientists use radioactive isotopes of sulfur and phosphorus but not radioactive isotopes of carbon. |
Carbon is contained in most biological molecules. Only proteins contain sulfur and the phosphate group of nucleotides contain phosphates. |
|
|
How was the RNA code deciphered? |
Synthetic mRNA was made and this was then used to make proteins. The team used s cytoplasm extract which was treated with DNAase to remove any existing DNA which may have made its own mRNA. They then added all 20 amino acids attached to tRNA, one of the amino acids was labelled with radioactive isotope of carbon but others weren't. Measured the radioactivity of polypeptide produced. They used different sequences of mRNA each time and different radioactively labelled mRNA. |

