![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
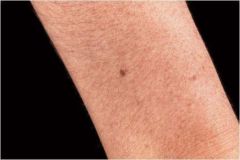
circumscribed lesion of < 5mm in diameter characterized by flatness and usually distinguished from surrounding skin by its coloration
|
Macule
|
|
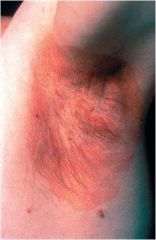
circumscribed lesion of > 5mm in diameter characterized by flatness and usually distinguished from surrounding skin by its coloration
|
Patch
|
|
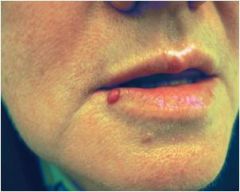
elevated dome-shaped or flat-topped lesion < 5mm in diameter
|
Papule
|
|
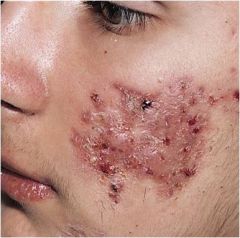
elevated lesion with spherical contour > 5mm in diameter
|
nodule
|
|
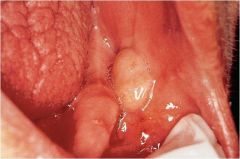
: elevated flat-topped lesion,usually > 5mm in in diameter
|
Plaque
|
|
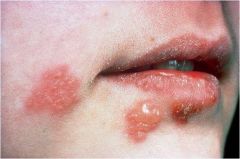
fluid filled raised lesion < 5mm in diameter
|
Vesicle
|
|
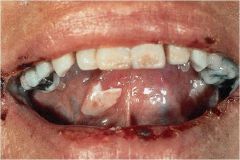
fluid filled raised lesion > 5mm in diameter
|
Bulla / Blister
|
|
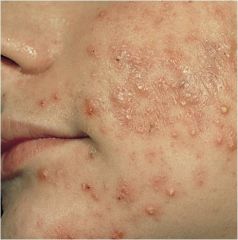
discrete, pus-filled, raised lesion
|
Pustule
|
|
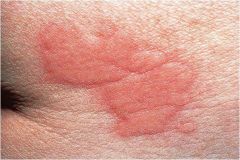
itchy, transient, elevated lesion with variable blanching and erythema formed as the result of dermal edema
|
Wheal
|
|
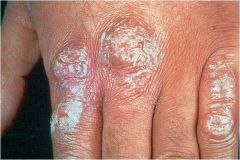
dry, horny, platelike excresence, usually the result of imperfect cornification
|
Scale
|
|
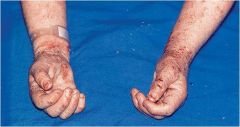
thickened and rough skin characterized by prominent skin markings; can be the result of repeated rubbing
|
Lichenification
|
|
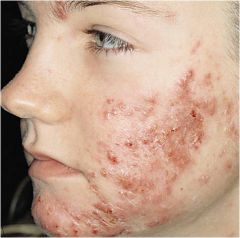
traumatic lesion characterized by breakage of the epidermis causing a raw linear area; often self-induced
|
Excoriation
|
|
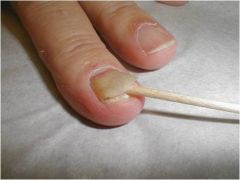
separation of the nail plate from the nail bed
|
Oncholysis
|
|
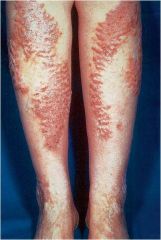
thickening of the stratum corneum, often associated with a qualitative abnormality of the keratin
|
Hyperkeratosis
|
|
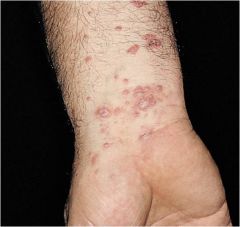
diffuse epidermal hyperplasia
|
Acanthosis
|
|
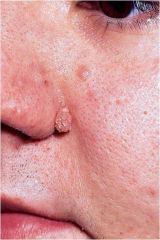
surface elevation caused by hyperplasia and enlargement of contiguous dermal papillae
|
Papillomatosis
|
|
abnormal keratinization occurring prematurely within individual cells or groups of cells below the stratum granulosum
|
Dyskeratosis
|
|
loss of intercellular connections resulting in loss of cohesion between keratinocytes.
|
Acantholysis
|
|
intercellular edema of the epidermis
|
Spongiosis
|
|
infiltration of the epidermis by inflammatory or circulationg blood cells
|
Exocytosis
|
|
infiltration of the epidermis by inflammatory or circulationg blood cells
|
Erosion
|
|
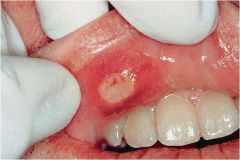
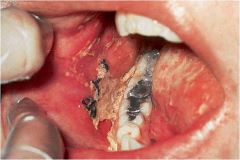
discontinuity of the skin exhibiting complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat
|
Ulceration
|
|
a linear pattern of melanocyte proliferation within the epidermal basal cell layer
|
Lentiginous
|
|
|
-Symmetric
-Well-defined, rounded border -Uniformly pigmented -Small (usually <6 mm across) -No increase in size are general characteristics of? |
Nevocellular Nevus
|
|
|
What are the 3 classifications of Nevocellular Nevus?
|
1) junctional (macule)
2) dermal (nodule/papule) 3) compound (nodule/papule) |
|
|
a benign neoplasm of melanocytes that may be acquired or congenital
|
Nevocellular Nevus
|
|
|
What is a malignant neoplasm of melanocytes that in skin, begins as a macule and may become a patch or papule?
|
Melanoma
|
|
|
What are precursor lesion(s) to a Melanoma that may be seen?
|
Dysplastic Nevi and congenital melanocytic nevi
|
|
|
What some risk factors for acquiring a melanoma?
|
- family history
- skin type - excessive sun exposure -precursor lesions (dysplastic nevi) |
|
|
What type of nevi have the highest risk of developing into melanomas?
|
-large or giant types (6%)
-3-5 yo |
|
|
6th most common cancer in US?
|
Melanoma
|
|
|
most common fatal malignancy amongst young adults?
|
Melanoma
|
|
|
Prognosis of a melanoma is based upon?
|
1) Thickness of tumor
2) presence/absence of ulceration 3) clinical stage |
|
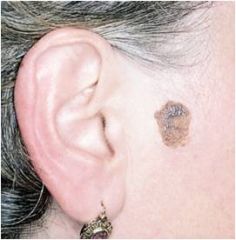
-warty surface
-waxy, tan/brown plaque -solitary/multiple -spontaneous -mistaken as melanoma |
seborrheic keratoses
|
|
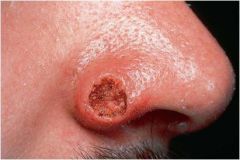
-flesh-colored lesion
-dome shaped nodule -central erosion -occurs on facial skin or hands -well-developed collarette |
Keratoacanthoma
|
|
|
is a rapidly developing benign epidermal neoplasm that clinically and histologically may mimic well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma
|
keratoacanthoma
|
|
|
how is a keratoacanthoma differientiated from squamous cell carcinoma?
|
rapid growth
spontaneous remission |
|
|
may occur explosively in large numbers as a part of paraneoplastic syndrome: Leser-Trelat sign
|
Seborrheic keratoses
|
|
|
what is the 2nd most common type of skin cancer ?
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
what is the most common type of skin cancer?
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
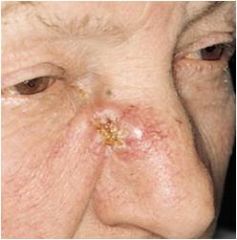
a malignant neoplasm of kertinocytes
|
Squamous cell Carcinoma
|
|
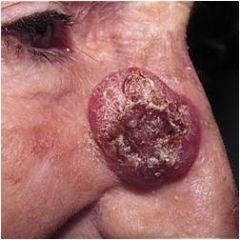
a malignant neoplasm of basal keratinocytes?
|
Basal cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the demographics of Sqamous cell carcinoma?
|
Males
>55 |
|
|
What are the demographics of Basal Cell carcinoma?
|
Males
>40 |
|
|
Pearly papule or nodule containing prominent, dilated subepidermal blood vessels +/- ulceration
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
what is the metastatic rate of squamous cell carcinoma?
|
3-4%
|
|
|
Which cell carcinoma may present due to HPV or chronic infection or industrial carcinogens?
|
SCC
|
|
|
urticaria
erythema multiforme are examples of? |
acute inflammatory dermatoses
|
|
|
psoriasis
seborrheic dermatitis lichen planus are examples of? |
chronic inflammatory dermatoses
|
|
|
What is the length of acute inflammatory dermotoses flare ups?
|
days ---> weeks
|
|
|
What is the length of chronic inflammatory dermatoses flare ups?
|
months ----> years
|
|
|
Acute inflammatory dermatoses are characterized by?
|
edema
+/- epidermal/vascular/subcutaneous injury |
|
|
-inlfammation
-altered epidermal growth (atrophy/hyperplasia) |
erythema multiforme
|
|
|
what age group does urticaria most often affect?
|
20-40yo
|
|
|
What are the categories of urticaria causing agents?
|
allergic: pollen, foods, drugs, insect venom
non-allergic: physical; pressure, hot/cold |
|
|
urticaria is a result of ________ process?
|
IgE degranulation
|
|
|
what is the age group erythema multiforme most commonly affects?
|
NO age predilection
|
|
|
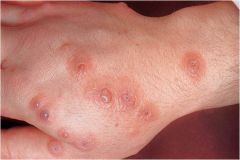
is an uncommon, self-limited disorder that appears to be a hypersensitivity reaction to certain infections and drugs
-involving skin of hands and feet -presents in a concentric ring form |
erythema multiforme
|
|
|
sulfonamides, penicillin, barbiturates, salicylates, are examples of drugs that might instigate what sort of lesions?
|
erythema multiforme
|
|
|
These 4 main categories of culprits causing erthema multiforme?
|
1) infections: herpes, mycoplasmal
2) drugs: penicillin, barbituates 3) malignant disease :carc-, lymphoma 4) Collagen vascular disease |
|
|
-a common
-chronic -T-cell mediated inflammatory deramatosis -2/3 w/ HLA Cw0602 allele |
psoriasis
|
|
|
what is the demographics of psoriasis?
|
- peak 22yo
- no gender predilection |
|
|
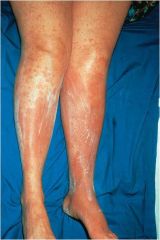
-salmon-colored plaque, w/ silver white scale
- nail changes present (30%) - affects elbows, knees, scalp, penis |
psoriasis
|
|
|
What chronic dermatoses is associated with :
-arthritis -myopathy -enteropathy -spondylitic joint disease |
Psoriasis
|
|
|
What are the 4P's regarding the presentations of Lichen Planus?
|
pruritic
purple polygonal papules |
|
|
Oral lesions occur in ______% of Lichen Planus cases
|
70
|
|
|
What is the demography for Lichen Planus?
|
Females
40-60 yo |
|
|
Wickham striae are white dots are lines associated with what lesions?
|
Lichen Planus: chronic dermatoses
|
|
|
Patients with Lichen Planus have an increase risk for developing what?
|
SCC
|
|
|
Lichen Planus =
lesions:Multiple/Single? asymmetrical/symmetrical? neck, trunk / extremities? |
multiple
symmetrical extremities |
|
|
an inflammatory process that consists of tiny papules or macules
-erythematous -greasy base -scaly and crusty |
Seborrheic Dermatitis
|
|
|
what is the seborrheic region that S. dermatitis will affect?
|
scalp
forehead eyebrows folds (nasal/ paranasal) retroauricular zone |
|
|
when is one likely to present with gradually with seborrheic dermatitis?
|
fall and winter
|
|
|
What are 2 examples of blistering disease?
|
Bullous Pemphigoid
Pemphigus Vulgaris |
|
|
a distinct vesicobullous disease affecting elderly individuals characterized by formation of tense bullae
|
Bullous Pemphigoid
|
|
|
Pathogenesis:caused by antibodies directed against proteins at the dermal-epidermal junction (BP1 and BP2)
? |
Bullous Pemphigoid
|
|
|
What % of Bullous Pemphigoid presents in the oral cavity?
|
10-15%
|
|
|
Immunofluorescence is a diagnostic tool for what 2 condtions?
|
Bullous Pemphigoid
Pemphigous Vulgaris |
|
|
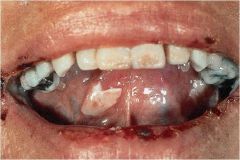
Which of the blistering diseases more commonly presents in the mouth?
|
Pemphigous Vulgaris
|
|
|
blistering disorder of adults (40-60 yo) characterized by superficial vesicles and bullae that are easily ruptured
|
Pemphigous Vulgaris
|
|
|
antibodies form against desmoglein-3
|
Pemphigous Vulgaris
|
|
|
What is the crucial therapy of Pemphigous Vulgaris preventing fatality?
|
immunosuppresive therapy
|

