![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
consists of a durable, lightweight plastic material; backed by a thin sheet of aluminum or lead that absorbs backscatter x-ray photons |
PSP cassette |
|
|
PSP |
photostimulable phosphor |
|
|
contains an antistatic material (usually felt) that protects against static electricity buildup, dust collection, and mechanical damage to the PSP plate |
PSP cassette |
|
|
a very thin, rough, clear plastic that protects the phosphor layer |
protective layer |
|
|
a layer of PSP that "traps" electrons during exposure; usually made of phosphors from the barium flourohalide family |
phosphor layer (or active layer) |
|
|
a layer that sends light in a forward direction when released in the cassette reader; may be black to reduce the spread of stimulating light and the escape of emitted light |
reflective layer |
|
|
a layer of material that absorbs and reduces static electricity |
conductive layer |
|
|
located between the active layer and support, that absorbs the stimulating light but reflects emitted light |
color layer |
|
|
a soft polymer that protects the back of the cassette |
backing layer |
|
|
allows the technologist to match the image information with the patient-ID barcode on the examination request |
barcode label |
|
|
how is the patient positioned with PSP systems? |
the same way as in conventional radiography, using appropriate positioning techniques, and the body part aligned with the IR |
|
|
in PSP, what does the remnant beam interact with? |
electrons in the barium fluorohalide crystals contained within the IR |
|
|
what interaction stimulates, or gives energy to, electrons in the crystals, trapping them in an area known as the color or phosphor center?
|
the interaction of the remnant beam and electrons in the barium fluorohalide crystals contained within the imaging plate
|
|
|
2 types of PSP readers |
point scan and line scan |
|
|
how is a PSP cassette read? |
without a chemical processor or darkroom, the cassette is fed into a reader that removes the imaging plate and scans it with a laser to release the stored electrons |
|
|
a device that creates and amplifies a narrow, intense beam of coherent light |
laser, or Light Amplification of Stimulated Emission of Radiation |
|
|
what are the characteristics of the laser beam that scans the plate with red light in a raster pattern and gives energy to the trapped electrons? |
about 100 micrometers wide with a wavelength or 633 nm (or 670 to 690 nm for solid state) |
|
|
how many eV is necessary to energize the trapped electrons by the red laser light emitted to read the imaging plate? |
2 eV |
|
|
the visible blue light is emitted at an energy of ____ as they relax into lower energy levels |
3 eV |
|
|
what is meant when talking about digitizing a signal, such as the light signal from a photodetector? |
assigning a numerical value to each light photon |
|
|
what is the time frame a digital clock is capable of representing? |
only a finite number of times (e.g., every tenth of a second) |
|
|
the amount of detail present in any image |
spatial resolution |
|
|
how often should imaging plates be erased to prevent a buildup of background signal? |
at least once a week |
|
|
how are imaging plates erased by the readers? |
by flooding it with light to remove any electrons still trapped after the initial plate reading |
|
|
how is image recognition accomplished in the part selection menu? |
through complex mathematical computer algorithms |
|
|
what is the consequence if improper part and/or position is entered in the part selection menu? |
the image may be processed incorrectly and fail to display properly |
|
|
what is the result when insufficient light produces a grainy image? |
quantum mottle or quantum noise |
|
|
a wavy artifact that occurs because the grid lines and the scanning laser are parallel |
moire pattern |
|
|
what blurs grid lines and eliminates interference? |
the oscillating motion of a moving grid, or Bucky |
|
|
the reduction of the area of beam that reaches the patient through the use of two pairs of lead shutters encased in a housing attached to the x-ray tube; results in increased contrast resolution as a result of the reduction of scatter |
collimation |
|
|
post-exposure image manipulation; a black background that can be added around the original collimation edges, virtually eliminating the distracting white or clear areas |
shuttering |
|
|
a graphic representation of the numerical tone of values of an x-ray exposure |
histogram |
|
|
term used by AGFA for image recognition |
collimation |
|
|
term used by Carestream for image recognition |
segmentation |
|
|
term used by Fuji for image recognition |
exposure data recognition |
|
|
any undesirable densities on the processed image other than those caused by scatter radiation or fog |
artifacts |
|
|
where images are sent to be analyzed and sent to the PACS for long-term storage |
QC station |
|
|
how is spatial resolution of the digital image determined? |
by the thickness of the phosphor layer and the size of the pixels; the thinner the phosphor layer, the greater the sharpness of the image, and the smaller the pixel size, the higher the spatial resolution |
|
|
collects light and sends it to a signal digitizer |
photodetector |
|
|
ADC |
analog-to-digital convertor |
|
|
assigns a numerical value to each pixel in a matrix according to the intensity of the detected light |
ADC |
|
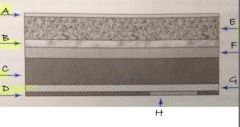
A
|
protective layer
|
|
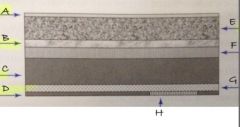
B
|
light reflective layer
|
|
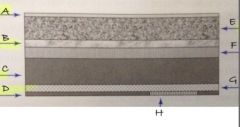
C
|
support layer
|
|
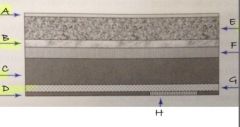
D
|
backing layer
|
|
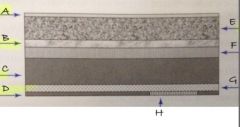
E
|
phosphor layer
|
|
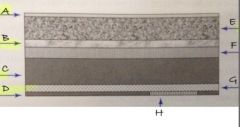
F
|
conductive layer
|
|
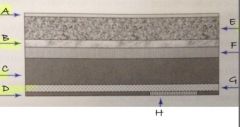
G
|
light shielding layer
|
|
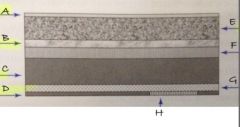
H
|
barcode label
|

