![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Mechanical Digestion |
Physical breakdown of food into smaller particles |
|
|
|
Chemical Digestion |
hydrolysis reactions that breaks macromolecules into monomers |
|
|
|
Absorption |
Taken in by specific chemical or molecular process; passage of liquids or other substances into villi |
|
|
|
Where does 90% of absorption happen? |
Small intestine |
|
|
|
Name the 3 tooth layers |
Crown: above gum Neck: where crown, root, gum meet Root: below gum |
|
|
|
ID 4 tooth types |
incisors: cutting to bite Canine: pointed to puncture Premolars: crush, shred, grind Molars: even broader to crush, shred, grind |
|
|
|
Sequence of the 4 layers of digestive tract |
Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis externa Serosa |
|
|
|
What layer lines the lumen of the digestive tract |
Mucosa |
|
|
|
What layer is thick and has blood and lymphatic vessels in the digestive tract |
Submucosa |
|
|
|
What layer has an inner circular and longitudinal layer of muscle in the digestive tract |
Muscularis externa |
|
|
|
What layer is most distal from the lumen in the digestive tract |
Serosa |
|
|
|
Stomach |
Muscular sac in upper left abdominal cavity immediately inferior to the diaphragm |
|
|
|
Stomachs 4 parts |
Cardial part Fundus Body Pyloric part |
|
|
|
The cardial part of the stomach |
Small area within about 3 cm of the cardial oriface |
|
|
|
Jaundice |
Yellow discoloration, excess of bilirubin |
|
|
|
Gall stones |
Form from bile cholesterol and bilirubin Can be caused by poor muscle tone, being female, overweight, birth control |
|
|
|
Fundas of the stomach |
Dome shaped portion superior to esophageal attachment |
|
|
|
Body (corpus) of the stomach |
Makes up the greatest part of the stomach |
|
|
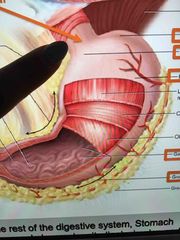
Front (Term) |
Gasteoesophageal spincter |
|
|
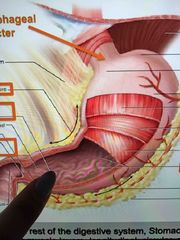
Front (Term) |
Pyloric antrum |
|
|
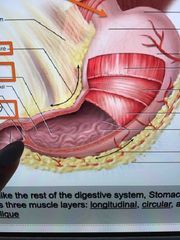
Front (Term) |
Pyloric sphincter |
|
|
|
Front (Term) |
Pyloric antrum |
|
|
|
Front (Term) |
Pyloric sphincter |
|
|
|
oral phase of swallowing |
Tongue forms food bolus and pushes into laryngopharynx |
|
|
|
Pharyngeal phase of swallowing |
Palate, tongue, vocal |
|
|
|
5 stages of digestion |
Ingestion Digestion Absorption Compaction Defecatiton |
|
|
|
Ingestion |
Selective intake of food 1st |
|
|
|
Digestion |
Mechanical and chemical 2nd |
|
|
|
Absorption |
Taken in by specific chemical or molecular process 3rd |
|
|
|
Compaction |
Absorb water and consolidate indigestible residue into feces 4th |
|
|
|
Defecation |
Elimination of feces 5th |
|
|
|
Segmentation (movement in digestive tract) |
Stationary ring-like constrictions appear several places along the intestine Relax and new constrictions form, most common, enteric pacemaker sets rhythm |
|
|
|
Peristaltic movement in digestive tract |
Contents of small intestine towards colon. Peristaltic wave begins in duodenum and travels 10-70 cm Mills chyme for 2 hours |
|
|
|
Esophageal phase of swallowing |
Peristalsis drives bolus downward, relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter admits it into the stomach |
|
|
|
Tongue |
Body (in oral cavity) Root (in oropharynx) Epiglottis |
|
|
|
Parotid salivary glands |
Extrinsic gland Produces bulk of saliva Near earlobe |
|
|
|
Salivary amylase |
Enzyme that begins starch digestion in the mouth |
|
|
|
Saliva |
Inhibits bacterial growth Dissolves molecules to stimulate taste buds Moistens food and binds it to bolus |
|
|
|
Extrinsic salivary gland |
Connected to oral cavity by ducts - parotid -sublingual - submandibular |
|
|
|
Parotid gland |
Anterior to earlobe, makes bulk of saliva |
Salivary |
|
|
Sublingual gland |
Floor of mouth Extrinsic gland |
Salivary |
|
|
Submandibular gland |
Along body of mandible Extrinsic gland |
Salivary |
|
|
Pharynx |
Muscular funnel connecting oral cavity to esophagus and nasal cavity to larynx |
|
|
|
Epiglottis |
Flap in throat that keeps food from entering windpipe and lungs |
|
|
|
Submandibular salivary glands |
Extrinsic gland produces bulk of saliva components, body of the mandible, duct empties at the side of the lingual finunulum (septum under the tongue) |
|
|
|
Esophagus |
25-30 cm long |
|
|
|
Salivary amylase traits |
Source: pancreases Breaks down starch into maltose (glucose and glucose) PH of 6.5-7 in mouth |
|
|
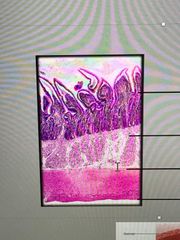
Segmentation (Intestinal motility)
|
Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis externa Serosa |
|
|
|
3 ways stomach protects itself from harsh acidic and enzymatic environment |
- mucous coat: high alkaline mucous - tight junctions: prevent gastric juices from seeping between - epithelial cell replacement: cells live 3-6 days |
|
|
|
Glands of stomach |
Cardiac Pyloric Gastric |
|
|
|
Mucous cells (gastric) |
Secrete mucous in cardiac and pyloric |
|
|
|
Regenerative (stem) cells (gastric) |
Base of pit and in neck of gland. Divide fast and replace cells |
|
|
|
Parietal cells (gastric) |
Secrete HCl and ghrelin |
|
|
|
Chief cells |
Secrete gastric lipase and pepsinogen Only in lower half of gastric glands |
|
|
|
Chloride shift (gastric) |
HCO3- exchanged for Cl- from blood plasma, forms HCl in parietal cells pH of blood leaving is high because stomach pumping bicarbonate |
|
|
|
Zymogens |
Digestive enzymes secreted as inactive proteins; converted to active enzymes through the cleavage General word for enzymes, broad like saying car |
|
|
|
Pepsinogen |
Zymogen secreted by chief cells |
|
|
|
Pepsinogen cycle |
Pepsinogen >HCL> Pepsin which activates pepsinogen to create more pepsin |
|
|
|
Pepsin |
Must be activated in stomach to not break down cells that just made it Digests dietary proteins into shorter peptides |
|
|
|
MALT |
Muscles-associated lymphatic tissue Abundance of lymphocytes and nodules in the mucosa |
|

