![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the diencephalon consist of and where is it derived from |
Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus. (These structures surround the third ventricle.)
-diencephalon is derived from the posencephalon (rostral most part- forebrain) |
|
|
Thalamus 2 basic input |
-input that is being relayed to cortex -modulatory input, arises from the cerebral cortex, as well as from the reticular thalamic nucleus and various brain stem areas. |
|
|
What 3 regions is the the thalamus divided into |
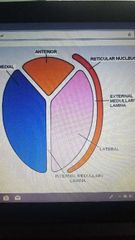
-anterior -medial -lateral Divided by the interior medullary lamina. Exterior medullary lamina seperate the rericular nucleus from the thalamus. |
|
|
Functions of thalamus |
Relay station for all sensory signals on their way to cerebral cortex. -lateral geniculate nucleus receives input from the optic tract and sends signal to area 17 of cerebrum (primary visual cortex). -medial geniculate nucleus receives input from inferior colliculus and organ of corti. Sends input to primary auditory area. - |

