![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
3 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three types of Congenital Heart Defects?
|
1. Left to Right Shunt
2. Right to Left Shunt 3. Obstruction |
|
|
In L to R stunting, what happens? Are pts cyanotic right away? What's the mnemonic to remember that?
|
You get volume overload of pulmonary circulation. It might take years to find become cyanotic. Mnemonic is "L to R won't make you bright (blue)."
|
|
|
1. What is VSD? 2. What type of shunting is that? 3. Does it occur most often in the membranous or muscular portion of the heart? 4. According to Wiki, how can it be diagnosed with the stethoscope? Note that this is the most common congenital cardiac anomaly.
|
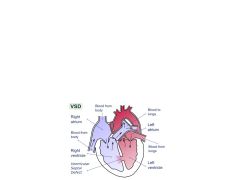
1. A defect in the ventricular septum.
2. This is L to R shunting 3. Most often occurs in the membranous part of the heart. 4. It can be diagnosed fairly easily by auscultation. |

