![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The 4 Rs in order of priority.
|
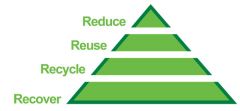
|
|
|
Smart Materials: Shape-memory alloys
|
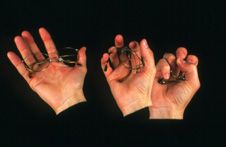
A Shape Memory Alloy is a Smart Material that if bent out of shape can refer back to its previous shape when heated above a certain temperature.
This is useful in products such as glasses when placed in hot water after damaging them. |
|
|
Smart Materials: Piezoelectric Materials
|

When a piezoelectric material is squeezed rapidly, it produces a small electrical voltage for a moment. If a voltage is put across the material it makes a tiny change in shape.
Piezoelectric materials are being used for contact sensors for alarm systems and in microphones and headphones. |
|
|
Smart Materials: Colour-Change Materials - Thermochromic
|

Thermochromic materials change colour as the temperature changes. These are used on contact thermometers made from plastic strips and test strips on the side of batteries (where the heat comes from a resistor under the thermochromic film). They are also used as food packaging materials that show you when the product they contain is cooked to the right temperature.
|
|
|
Smart Materials: Colour-Change Materials - Photochromic
|
Photochromic materials change colour according to different lighting conditions. They are used for security markers that can only be seen in ultraviolet light. I.E. Laser Tag venues where sun light does not reach the material, unlike Phosphorescent Pigments
|
|
|
Smart Materials: Phosphorescent pigments
|

Phosphorescent pigments glow in the dark, first absorbing light and then emitting it.
|
|
|
Smart Materials: Polymorph
|

Polymorph is a plastic that becomes mouldable at 62°C. It is used for product-modelling, curves (eg handles), and moulds for vacuum-forming.
|
|
|
Smart Materials: High-density modelling foam
|

High-density modelling foam is available in blocks. It can be shaped using hand and machine tools and takes fine detail well.
|
|
|
Smart Materials: Magnetic Smart Putty
|

The magnetic putty can be torn, moulded, bent and so much more. But when it gets near a strong magnet it can be pulled and can also swallow the magnet whole. This magnetic putty could be used as a fridge magnet for example.
|
|
|
Smart Materials: Shock Absorbing Smart Putty
|

This putty can be used to protect products such as smart phones when dropped. This putty gets tough when hit with a powerful force such as a hammer or when it falls to the floor.
|
|
|
The Basic Product Life Cycle
|
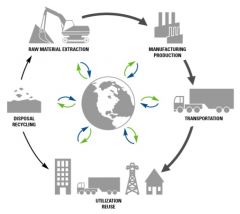
There is a basic life cycle that is followed by every single product in the world. It’s called the basic product life cycle and it shows the journey of the product from its raw materials to its eventual reuse & recycle back into raw materials.
Raw Materials Energy Consumed Packaging Manufacture Packaging Filler(s) Distribution (Made of Transport) Shops/Retailers/Supermarkets Consumer/User Recover Recycle Reuse |
|
|
Anthropometrics
|
Anthropometrics is the study of the sizes of people in relation to products. For example, chairs used in schools need to be suitable for the average size of pupils in the schools.
You match the product towards the intended audience. |
|
|
Ergonomics
|
Ergonomics is the relationship between people and the products which they use. Anthropometric data is used to help design products to meet ergonomic needs. Ergonomics also considers the force a person can apply, for example when using a tin opener, or the pedals of a car.
Anthropometrics uses the 90th percentile (Average) measurement. |
|
|
Sandals
|
The sandals believe that humanity should harvest energy through renewable energy sources such as wind turbines, solar panels and hydroelectric power.
|
|
|
Nukes
|
Nukes believe that technology is the way forward for humanity, therefore reducing our dependency on the planets natural resources.
These include nuclear energy and carbon-scrubbed natural gas |
|
|
Electronic Communications: E-mail
|
E-mail is now one of the simplest forms of electronic communications.
There are a range of Advantages from using e-mail, such as: ◦ Quick, Easy & Convenient – communicating around the world. ◦ Widespread Usage – anyone with a computer & internet. ◦ E-mail exchanges can be saved as proof of communication. ◦ Electronic Attachments – saved & edited easily. There are a range of Disadvantages from using e-mail, such as: ◦ Impersonal – misinterpreted. ◦ Message Influx – increase time read & respond. ◦ 'Spamming' commercial emails – inappropriate content. ◦ Privacy & Security Issues – emails intercepted. ◦ Size Attachments Limited. |
|
|
Electronic Communications: Electronic Data Interchange
|
Modern methods for companies and organisations to do 'paperless' business using a process that transfers business documents through a computer network.
There are a range of Advantages from using electronic data interchange, such as: ◦ Saves Money – no processing paper documents. ◦ Saves Time – information transferred digitally. ◦ Improves Customer Service – documents transferred quickly. ◦ Expands Customer Base – improved customer service from EDI processes. There are a range of Disadvantages from using electronic data interchange, such as: ◦ Documents Incomparability – range of formats. ◦ Standards Update Regularly – problems with different versions being used. ◦ Expensive Set-Up Costs ◦ Limits Trading – only companies with EDI |
|
|
Electronic Communications: Integrated Services Digital Networks & Broadband
|
The purpose of ISDN it to provide fully integrated digital services to users comprising digital telephony and data-transport services through existing telephone networks.
• The digitisation of telephone networks allow for voice, data, text, graphics, music and video to be sent at high speeds on existing telephone lines. • ISDN brings together internet services and telecommunications in a single package. • Integrated Services – ability to deliver a minimum of two 'dial-up' connections at the same time (data,voice,video or fax through a single phone line). • Digital – digital signal rather than analogue signal through the phone line result in very fast connection and clear transmission quality. • Network – access is available to the full telecommunications network rather than point-to-point in a normal phone line. • There are five types of broadband available: ◦ Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) ◦ Cable ◦ Wireless ◦ 3G Technology ◦ Satellite |
|
|
Electronic Communications: Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
|
• Description: most popular in the UK,sends data along an existing telephone line – using technology that packs more information to be sent into the signal.
The Advantages of Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) are: ◦ Easy to Install The Disadvantages of Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) are: ◦ Downloading information much faster than sending |
|
|
Electronic Communications: Cable
|
• Description: the cable is formed in a bundle of optical fibres that can carry much more information than a telephone cable and over long distances without decreasing of signal quality.
The Advantages of Cable are: ◦ Easy to Install ◦ Fastest Connection – potentially. The Disadvantages of Cable are: ◦ Limited Availability – only available in large cities and towns. |
|
|
Electronic Communications: CAD
|
• Description: CAD stands for Computer Aided Design and is used within the manufacturing industry to help designers create better designs at a faster speed at a lower cost.
The Advantages of CAD are: • Allows Designers to undo mistakes • Faster Speeds than Paper & Pen • Create more precise and overall better designs • Lower Cost The Disadvantages of CAD are: ◦ Saved to File – Files can corrupt or get lost. ◦ Expensive Hard Drives – All files need to be backed up to avoid loss of data meaning that multiple hard drives need to be bought. ◦ Requires Education – The employees need to be trained in using computer programs to create designs they can easily do with Pen and Paper. ◦ Software & Hardware – For a computer program to handle such intense software it needs powerful hardware which is expensive. |
|

Raymond Loewy
|

Born in Paris, 1893
Had a major part in many different design movements His biggest was the modernism industry. Loewy loved streamlined products. He worked very closely with his team and client engineers to produce incredible designs for companies such as Studebaker automobiles, buses for Greyhound and also contributed to simplistic designs by producing more streamlined products such as the toothbrush, electric shavers etc. His most famous design was for the Coca-Cola bottle which had solidified his name in the modernism design world forever. Other notable designs include designing the interior and graphics for the Air Force One in President John F. Kennedy’s presidency. |
|

Antoni Gaudí
|

Born in Spain, 1852
Gaudi was an architect who had many characteristics of Art Nouveau within his work. There are bright tile mosaics and curving lines. The most famous building that Antoni Gaudi is best known for, though, is La Sagrada Familia in Barcelona. He began this huge church in 1882 and he worked on it until he died in 1926. It still has not been finished. |
|

Design Movements: Pop Art
|

Pop Art was very popular in the 1960s and was an up and coming design. It was founded by 7 young artists at London’s Institute of Contemporary Art; this was around 1952-3.
Pop Art was a style that re-energized everyone after World War II. This is because of the bright colours that surrounded a distraught world recovering from a huge war in which millions were lost. Pop Art was used on famous faces, movies, TV shows and much more. |
|

|
Bauhaus
|
|

|
Pre-Raphaelites
|
|

|
Modernism
|
|

|
Art Deco
|
|

|
Modernism
|
|

|
Pre-Raphaelites
|
|

|
Arts and Crafts
|
|

|
Modernism
|
|

|
Modernism
|
|

|
Modernism
|
|

|
Bauhaus
|
|

|
Art Noveau
|
|

|
Art Noveau
|
|

|
Bauhaus
|
|

|
Art Deco
|
|

|
Art Deco
|
|

|
Art Deco
|
|

|
Arts and Crafts
|
|
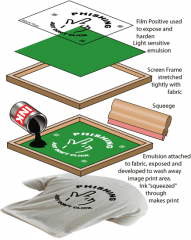
Screen Printing
|
Screen printing is a process that uses the 4 colours of CMYK, which stands for cyan, magenta, yellow and the key colour which is black.
These are added separately through the stencil, the stencil is the same shape as the image that is going to be printed and is held in place by a fine nylon mesh which can be made of paper, thin card or special photographic materials. This printing process is used on products such as T-Shirts, glass bottles and PVC signs as screen printing is only limited to simple shapes. |
|
|
Name the ID code for polymers
|
PET 1
HDPE 2 PVC 3 LDPE 4 PP 5 PS 6 |
|
|
What does PET stand for?
|
Polyethylene Terephthalate
|
|
|
What does HDPE stand for?
|
High Density Polyethylene
|
|
|
What does PVC stand for?
|
Polyvinyl Chloride
|
|
|
What does LDPE stand for?
|
Low Density Polyethylene
|
|
|
What does PP stand for?
|
Polypropylene
|
|
|
What does PS stand for?
|
Polystyrene
|

