![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Descending tracts - general |
Fxn's: - MN control (somatic & autonomic) - Sensory transmission modification Course of pathways: - synapsing directly on MN's (alpha) - synapsing on IN's (most) -> altering excitability - altering motor patterns (gamma loop) in spine |
|
|
Propriospinal tracts |
= fasciculus proprius - contains axons of IN's - interconnect SC segments -> involved in reflexes & patterning of normal movements |
|
|
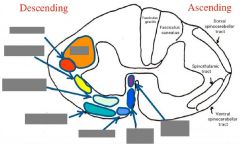
Medial vs. Lateral Motor Systems |
Medial: - in ventral/ventrolateral funiculus - regulate IN pools -> axial & proximal limb mm. Lateral: - lateral funiculus - regulate IN pools -> limb mm. (more precise) |
|
|
|
|
|
Medial motor systems |
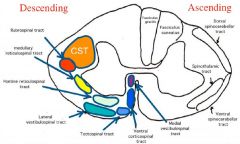
- axial m. tone & trunk/neck movement - SC: anterior funiculus, bilateral, up to thoracic - run in/near MLF via brain stem: -- tectospinal tract (adjacent) -- medial vestibulospinal tract -- pontine reticulospinal tract (-- anterior corticospinal tract) |
|
|
Tectospinal tract |
- from: Superior colliculus (multisensory input) -> dorsal tegmental decussation (midbrain lvl) -> adjacent to MLF, contralateral (brain stem) -> anterior funiculus -> upper thoracic lvls -> MN's to axial mm. (bilateral intermediate gray) => reflex head & neck movement to stimuli |
|
|
Medial Vestibulospinal tract |
- from: Medial vestibular nucleus (Pons) -> ipsilateral descending MLF -> anterior funiculus in SC -> upper thoracic lvls => vestibular stimuli-> reflex adjustment of head position (neck mm.) |
|
|
Pontine (/Medial) reticulospinal tract |
- from: Pontine lateral gaze center (PPRF, paramedian pontine reticular formation) -> ipsilateral MLF => head movement to follow eye movement |
|
|
Other medial motor tracts |
- run near the cap of the ventral horn - extend the length of the SC - involved in regulating m. tone & crude movements -- ventral corticospinal tract -- lateral vestibulospinal tract -- medullary (/lateral) reticulospinal tract |
|
|
Lateral vestibulospinal tract |
- from: vestibular nucleus -> anterior part of lateral funiculus -> runs the length of the SC, ipsilaterally => extensor MN's, vestibular righting reflex |
|
|
Medullary (/Lateral)reticulospinal tract |
-> in anterior part of lateral funiculus -> runs the length of SC, ipsilaterally =| gross movements, m. tone via gamma MN's => regulates sensory transmission => contains autonomic & respiratory ctrl fibers - regulated by corticobulbar tract (motor cortex -> brain stem) => indirect corticospinal projection pwy |
|
|
Lateral motor systems |
- in lateral funiculus -> lateral MN's & lateral intermediate gray -> mostly involved in limb motion -- Rubrospinal tract -- Lateral corticospinal tract |
|
|
Rubrospinal tract |
- from: red nucleus (<- cortex, cerebellum input) -> ventral tegmental decussation (midbrain) -> lateral funiculus (descends contralaterally) -> reaches all SC lvls -> intermediate gray (IN's) & dorsal horn => proximal limb flexor mm. (crawling) - small tract in humans - can be an indirect corticospinal tract |
|
|
Corticospinal-corticobulbar system |
Corticospinal - voluntary command for movement - regulates sensory transmission via dorsal horn Corticobulbar: cortex -> brain stem -> CN nuclei -> voluntary head & face movement -> sensory transmission nuclei -> brainstem nuclei -> movement (corticospinal) -> pons -> cerebellum relay |
|
|
Corticospinal tract |
- from: motor cortex - precentral gyrus (pyramidal neurons; largest: Betz cells) -> posterior limb of internal capsule -> cerebral peduncles -> basal pons -> medullary pyramids -> pyramidal decussation -> lateral funiculus in SC --> αMN's (distal) / IN's --> (uncrossed) anterior funiculus -> axial mm. --> dorsal horn -> alter sensory firing / reflexes |
|
|
Initiation of movement |
- primary motor A [active only w/ actual move] - premotor cortex (lateral premotor cortex - supplementary motor A (medial premotor C) - A activation location & size depends on movement type & complexity, respectively - MC n.'s encode movement direction (not a m.) - precedes movement (20-30 ms): pre-MC -> MC |
|
|
Abulia |
Lack of initiation of movement (due to lesion in supplementary motor area) |
|
|
Corticofugal fibers |
(= running from the cortex) ~ internal capsule: CC -> brain stem & SC - V-shape, posterior limb (A->P / M->L): -- Head (@ genu) ~ corticobulbar -- Arms -- Legs -> cerebral peduncle (center): medial-lateral |
|
|
Corticobulbar tracts |
= CC -> brain stem => targets (fxn's): - pontine nuclei (majority -> cerebellum relay) - CN nuclei (esp. CN VII) - eye movement control - indirect corticospinal tracts - sensory nuclei (regulate transmission) - visceral centers (autonomic: respiration, etc.) |
|
|
Corticobulbar tract: upper MN's for facial movement |
- from: MC closest to lateral fissure -> upper MN's -> via internal capsule -> --> lower face (CN VII): strictly crossed --> upper face (CN VII) & jaw (CN V) mm.: bilateral --> CN X & CN XII: mostly crossed Anterior cingulate cortex -> emotional facial expressions (not via internal capsule) |
|
|
Hypermimia |
Increased facial movement in response to emotional stimuli due to severe paralysis of voluntary face movement (lesion to internal capsule) |
|
|
Patterns of facial weakness & localizing neurologic injury |
Lower face weakness -> CNS, rostral to facial nucleus (supranuclear facial weakness) Entire face (lateral) weakness -> facial nucleus / nerve (Bell's palsy, herpes zoster, Lyme disease [infection], sarcoidosis [inflammation]) |
|
|
Indirect corticospinal tracts |
(pre-)MC -> brain stem areas
(-> descending motor tracts): -- red nucleus, reticular formation, superior colliculus - regulation of m. tone - affect motor patterns -> body stabilization during movement (anticipatory posture) |
|
|
Cortico-reticulo-spinal pathway (indirect) |
= premotor / supplementary MC -> corticobulbar tract -> medullary reticulospinal pwy --| spinal reflexes - dmg -> heightened reflexes |

