![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
em of melanosome
|
melanosome 4 stages- stage 2 - can tell it's a melanosome, stage 3 with pigmentation
elongated football shaped structure with lines in cytoplasm |
|
|
blue nevus
|
pigmented lesion spares epidermis, involves superficial dermis, heavily pigmented dendritic melanocytes (long, wavy)
increased fibroblasts and thicker collagen - NO EPIDERMAL INVOLVEMENT hmb45 is positive |
|
|
cellular blue nevus
|
children, lumbosacrum, dumbbell shaped, bullous base
cells that pigmented wavy dendritic melanocytes islands of spindled/epithelioid (pale abundant cyto, little to no pigment) macrophages in background NO EPIDERMAL INVOLVEMENT |
|
|
deep penetrating nevus, plexiform spindle cell nevus
|
bulky melanocytic lesion; occurs in upper back, shoulder
wedge-shaped fascicles/plexiform of spindle-epitheloid abundant, finely pigmented cytoplasm macrophages no or few mits |
|
|
abc cells of nevus
|
A - epitheloid (most superficial)
B - lymphocyte C - neural cells |
|
|
Spitz nevus (spindle and epitheloid cell nevus)
|
children most commonly
low mag - symmetric epidermal hyperplasia nests in junction (vertical orientation, bunch of bananas) cells disperse as single cells at base High mag up near junction - kimono bodies (eosinophilic lobules of BM material - right beneath epidermis), large nuclei, prominent nucleoli (smooth contours, fine chromatin), cytoplasm - amphophilic, delicate can have pagetoid spread, focally, groups, in center |
|
|
what benign pigmented lesions can have pagetoid spread
|
spitz nevus
acral nevus recurrent nevus congenital nevus |
|
|
melanoma SS types limited set of fx
|
pagetoid spread (even into corneum), diffuse
no maturation |
|
|
four types of melanomas
|
lentigo maligna - face, elderly, sun-damaged skin; if invasive spindled or desmoplastic, can run down hair follicle
SS - 70%, nests and single acral/mucosal/lentingous type - pigmented lesion with increase of continguous DE junction nodular melanoma - no epidermal component |
|
|
radial growth phase
|
in situ vs non tumorogenic
|
|
|
vertical growth phase
|
large in dermis is larger than any nest in epidermal or any dermal mits
|
|
|
how know on face
|
increased sebacous elements
|
|
|
b cell lymphoma how to distinguish between melanoma and lymphoma
|
b cell lymphoma - bottom heavy, bulky, spares epidermis, diffuse blue, no follicle formation
primary and secondary forms nodular melanoma vs. lymphoma - high mag and look for pigment, look more superficially for that pigment look for DE junction component |
|
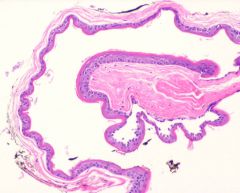
what
|
steatocystoma (multiplex)
epithelial lined cyst with no granular layer, corregated eosinophilic lining |
|
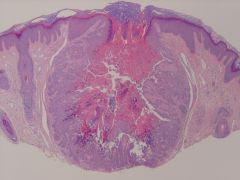
what
|
warty dyskeratoma (like darier's but isolated and centered on H&N, genital)
solitary lesion, face, cup-shaped invagination, filled with keratin, corrons, corgrains |
|
|
large cells with ample cytoplasm, prominent nucleoli, large nuclei, all layers, compress adjacent keratinocytes
|
paget's - do ihc
|
|
|
extramammary pagets
|
primary, originates from apocrine glands at those sites, vulva, anogenital (less associated with underlying neoplasm)
|
|
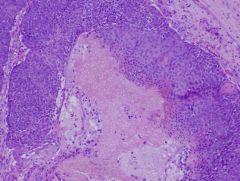
what
|
circumscribed, dermis, two cell types, basophilic (matrical), ghosts cells (shadow cells), FBGCrxn, calcium
pilomatricoma |
|
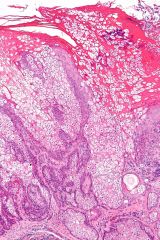
sebaceous adenoma
|
well-circumscribed, lobular, uniform sebaceous cells, nucleus can be scalloped, not assoc with follicle
two cells: peripheral basaloid cells, mature sebaceous cells (if adenoma 50% sebacous; if sebaceous epithelioma more of the peripheral cells; if carcinoma, on eyelid, aggressive) |
|
|
what is assoc with muir torre syndrome
|
sebaecous carcinoma, while carcinoma less aggressive than sporadic
|
|
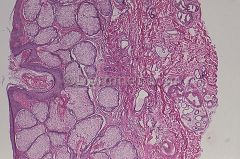
nevus sebaceous
|
abortive hair follicles, epidermal hyperplasia, sebaceous hyperplasia, ectopic apocrine gland formaiton
|
|
|
most common b9 and malign neoplasms to develop within nevus sebaceous
|
syringocytoadenoma papillerfum
bcc |
|
|
hidradenoma papilleferum
|
females, genital/vulvar
circumscribed, papillary, one-two cell layers, no connection to overlying epidermis, apocrine decapitation secretion |
|
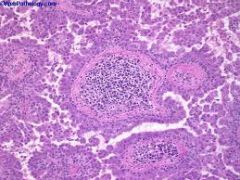
what
|
papillary, connects to epidermis, packed with plasma cells, apocrine decap secretion
scalp, face syringocystadenoma papillerfum |
|
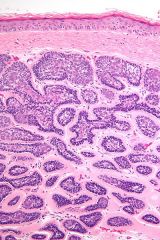
what
|
pieces of jigsaw puzzle, two cell types, darker peripheral cells, central pink cells, basement lamina-material
tubular lumina (eccrine origin) cylindroma |
|
|
??
|
like cylindroma: two cell types, darker peripheral cells, central pink cells, basement lamina-material
tubular lumina (eccrine origin) but anatomosing cords |
|
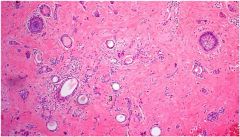
syringoma
|
tadpole lesions, epithelial cells with tails
dense collagen background protein debris (sweat jello) |
|
|
mac
|
follicular/eccrine differentiation (latter at base)
deep infiltrative |
|
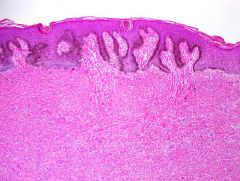
what
|
epidermal hyperplasia, elongation of rete ridges and basal hyperpigmentation (dirty fingers), grenz zone, spindle cell proliferation, entrapment of keloidal fibers
dermatofibroma |
|
|
ihc for dermatofibroma
|
13a + cd34-
|
|
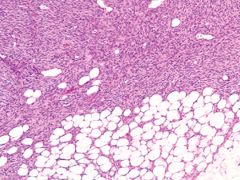
dfsp
|
infiltrative, spindle cells, honeycomb of fat, storiform
|
|
|
ihc of dfsp
|
13a-, cd34+
|
|
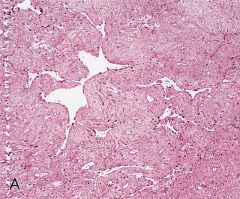
what
|
similar ihc to dfsp, in kids, vascular like spaces, multilobated cells
giant cell fibroblastoma (juvenile counterpart to dfsp) |
|
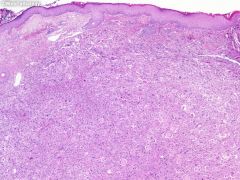
what
|
elderly, exophytic, ulcerated, atypical pleomorphic cells, high mits
AFX |
|
|
"mfh is a deeper form of"
|
AFX
|
|
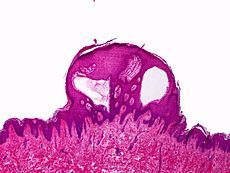
what
|
epidermal hyperplasia, dilated spaces right up to epidermis, protein debris (lymph fluid)
lymphangioma circumscriptum |
|
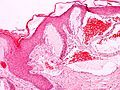
what, ass/w
|
dilated spaces with blood abut epidermis
angiokeratoma fabry's |
|
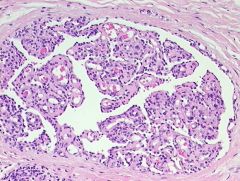
what, a/w
|
associated with Castlemans
glomeruloid hemangioma |
|
|
kaposi's sarcoma - evolution
|
increased in slit-like vascular spaces, increased dermal spindle cells, promitory sign
spindle cells proliferative, hyaline globules nodular formation with loss of vascular proliferation |
|
|
four flavors of kaposi's
|
-all HHV8 associated
- aids associated one, visceral more common |
|
|
angiosarcoma
|
vascular spaces, atypical cells
|
|
|
three clinical settings for angiosarcoma
|
1. elderly, white
2. chronic lymphadema (stuart-treves) 3. irradiated sites |
|
|
glomus tumor
|
uniform round cells
HAND glomus body is a modified smooth muscle cell solid form if thin walled vessels (glomangioma) if smooth muscle glomangiomyoma |
|
|
ihc for spindle cell lipoma
|
cd34 +
|
|
|
sites of granular cell tumor
|
tongue, skin
|
|
|
merkel cell
|
skin, elderly, extremities
neuroendocrine chromatin pattern with little cytoplasm, molding dot perinuclear staining of CK20 |
|
|
gorlin's syndrome
|
basal cell syndrome
AD patched, czome 9 numerous basal cell carcinomas associations: OKCs, palmar pits, rib abnormalities, medulloblastomas, calcificaiton of falx |
|
|
muir torre syndrome
|
AD
HNPCC MSI mlh1 msh2 sebaceous tumors, colon, gu, endometrial tumor |
|
|
burk hogg dube
|
AD
renal tumor/oncocytic, pulmonary cysts |
|
|
cowden
|
AD
czome 10 trichellommas, breast and thyroid |
|
|
gardners
|
AD
czome 5 apc EICs, osteomas, polyps, desmoid tumors |
|
|
Peutz jeghers
|
pigmented macules lips
hamartomatous polyps, colon carcinoma |
|
|
TS
|
AD
two proteins: angiofibromas (adenoma sebaceum), cns hamartomas, subependymal angiomyolipoma, etc |
|
|
NF1
|
pheo
|
|
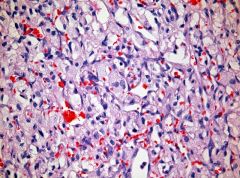
cerebral, a/w
|
pheo
cerebral hemangioblastomas skin: angiomatosis vhl |
|
|
men 2b
|
ret gene, pheochromocytoma
|

